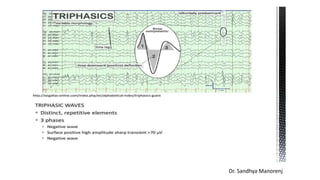
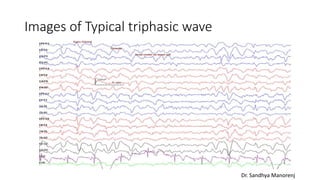
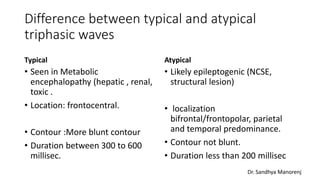
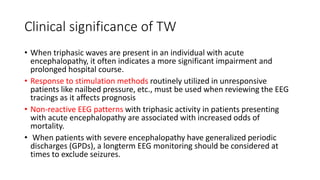
Triphasic waves are abnormal EEG waveforms seen in association with metabolic encephalopathies and structural brain lesions. They were first described in 1950 in a patient with hepatic encephalopathy. Triphasic waves result from dysfunction of the oscillatory system between the cortex and thalamus. They have a characteristic three-phase morphology visible on EEG. Triphasic waves can be typical or atypical depending on their characteristics and underlying etiology. Typical triphasic waves are seen in metabolic encephalopathies while atypical may indicate an epileptogenic condition. The presence of triphasic waves provides guidance for treatment of the underlying condition.