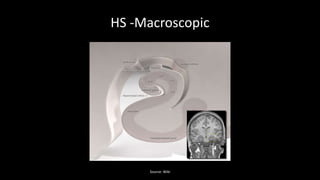
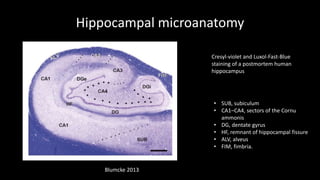
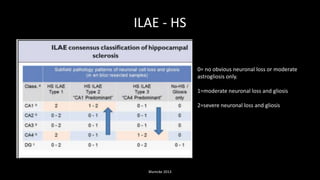
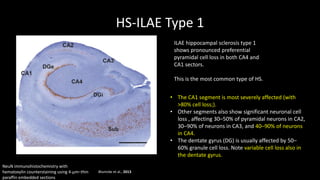
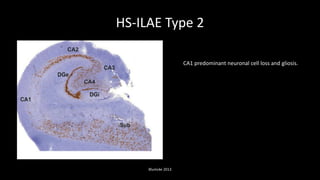
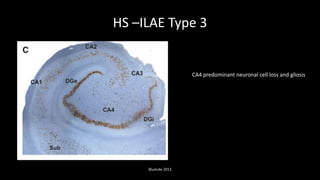
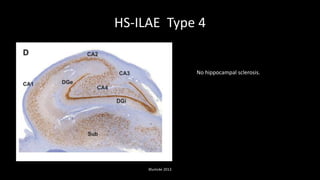
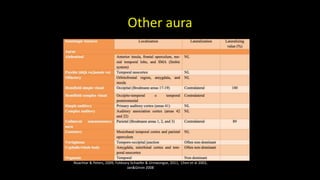
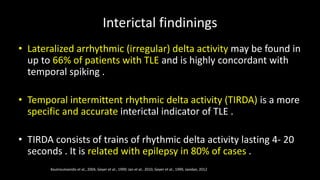
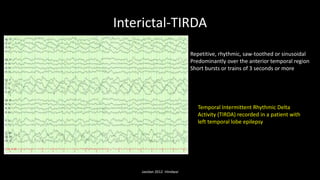
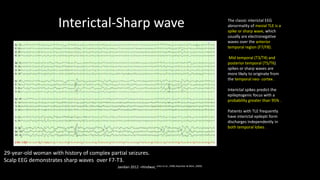
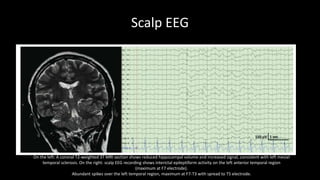
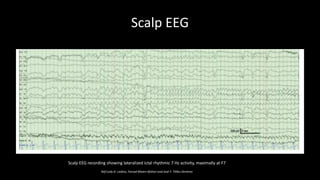
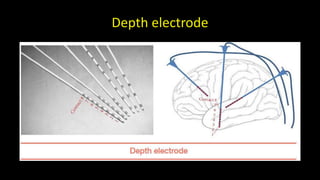
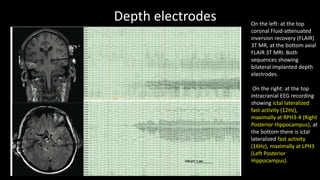
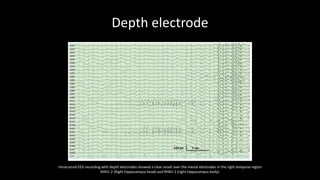
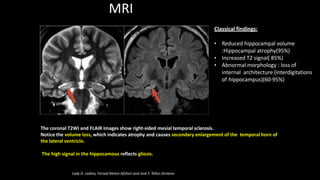
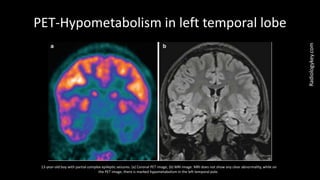
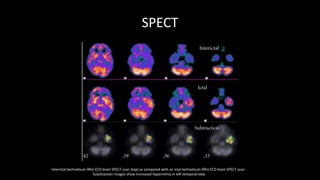
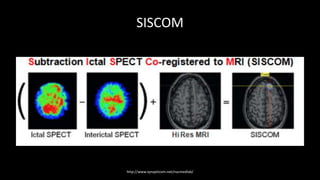
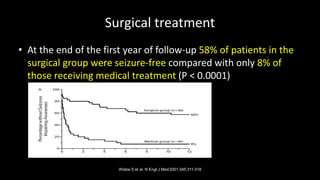
Temporal lobe epilepsy is one of the most common forms of epilepsy. It can be caused by hippocampal sclerosis or lesions in the temporal lobe. Hippocampal sclerosis involves neuronal loss and gliosis in the hippocampus and is the most common pathological finding in temporal lobe epilepsy patients. Interictal EEG findings like temporal intermittent rhythmic delta activity and temporal sharp waves help lateralize the seizure focus. Video EEG monitoring helps capture seizures and interictal discharges. Treatment involves antiepileptic drugs and potentially resective surgery for drug-resistant cases.