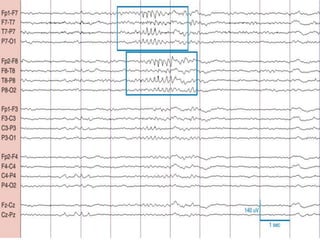
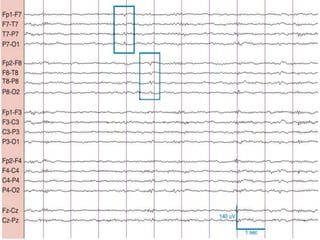
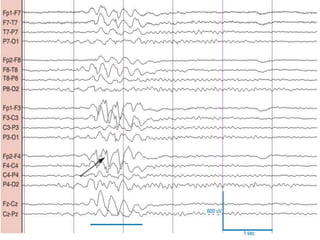
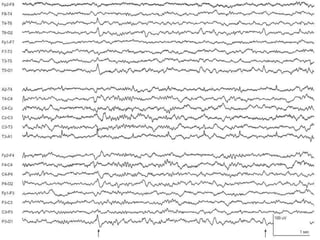
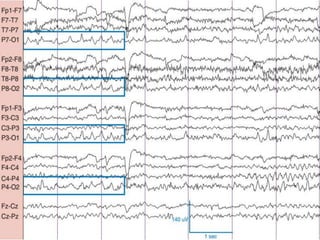
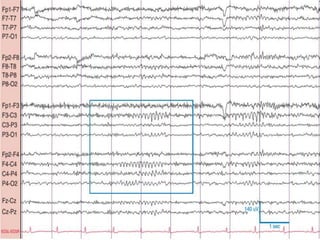
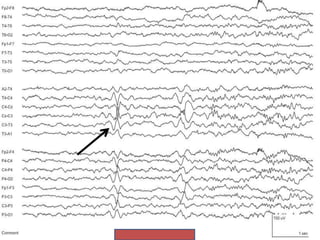
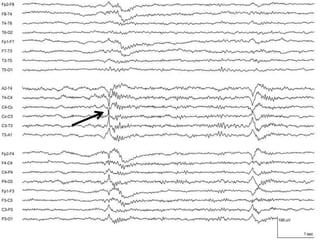
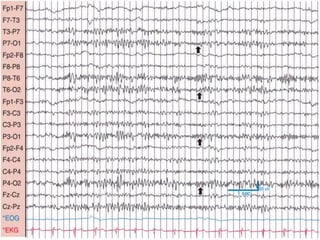
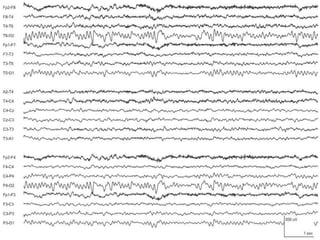
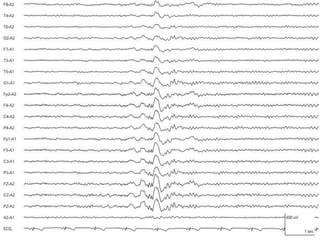
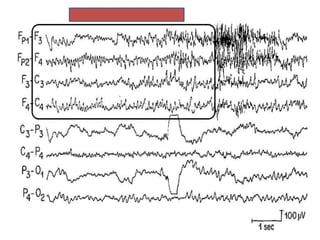
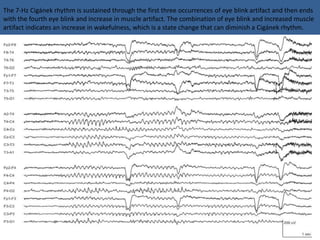
1) The document describes several benign EEG variants that can occur but are not associated with epilepsy. These include wicket waves, benign sporadic sleep spikes, 6 per second spike-waves, 14 & 6 Hz positive spikes, and more.
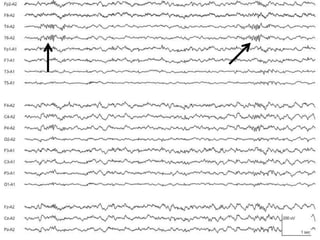
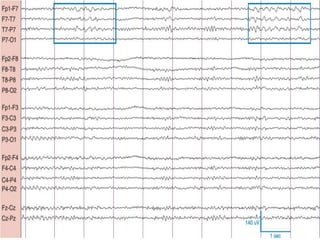
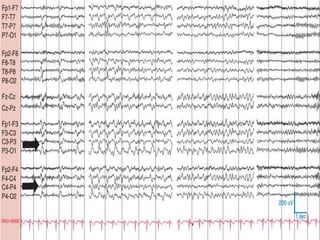
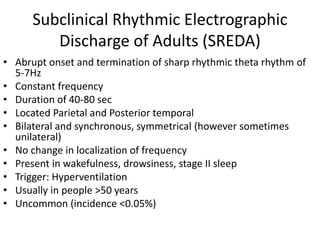
2) The variants are described in terms of their frequency, location, morphology, when they typically occur, and other characteristics. For example, wicket waves occur in the alpha frequency range and are seen unilaterally in the temporal region.
3) Many of the variants are considered normal variants seen in relaxed wakefulness, drowsiness, or different stages of sleep. They are commonly seen in different age groups but are not clinically significant or associated with epilepsy.