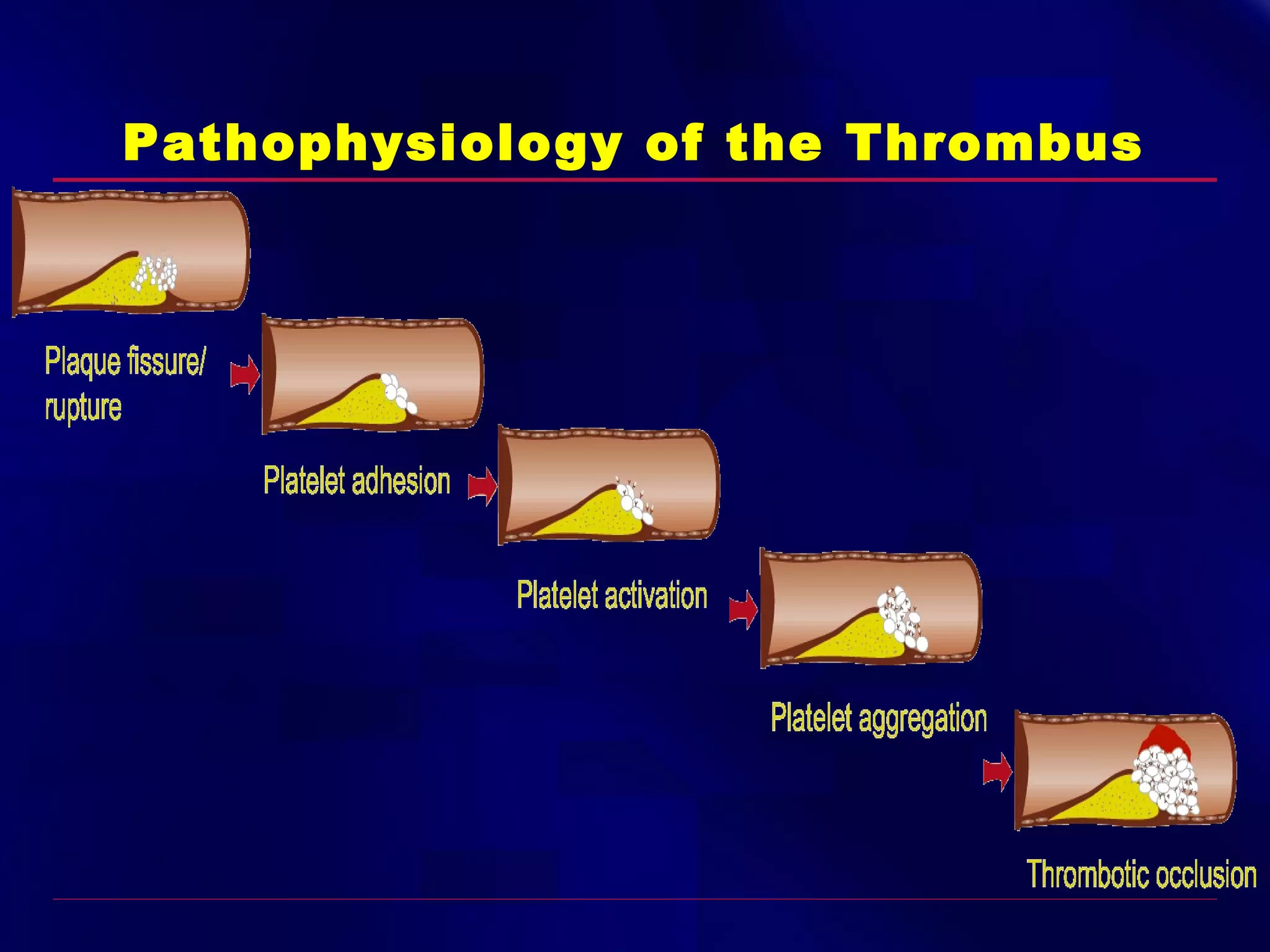
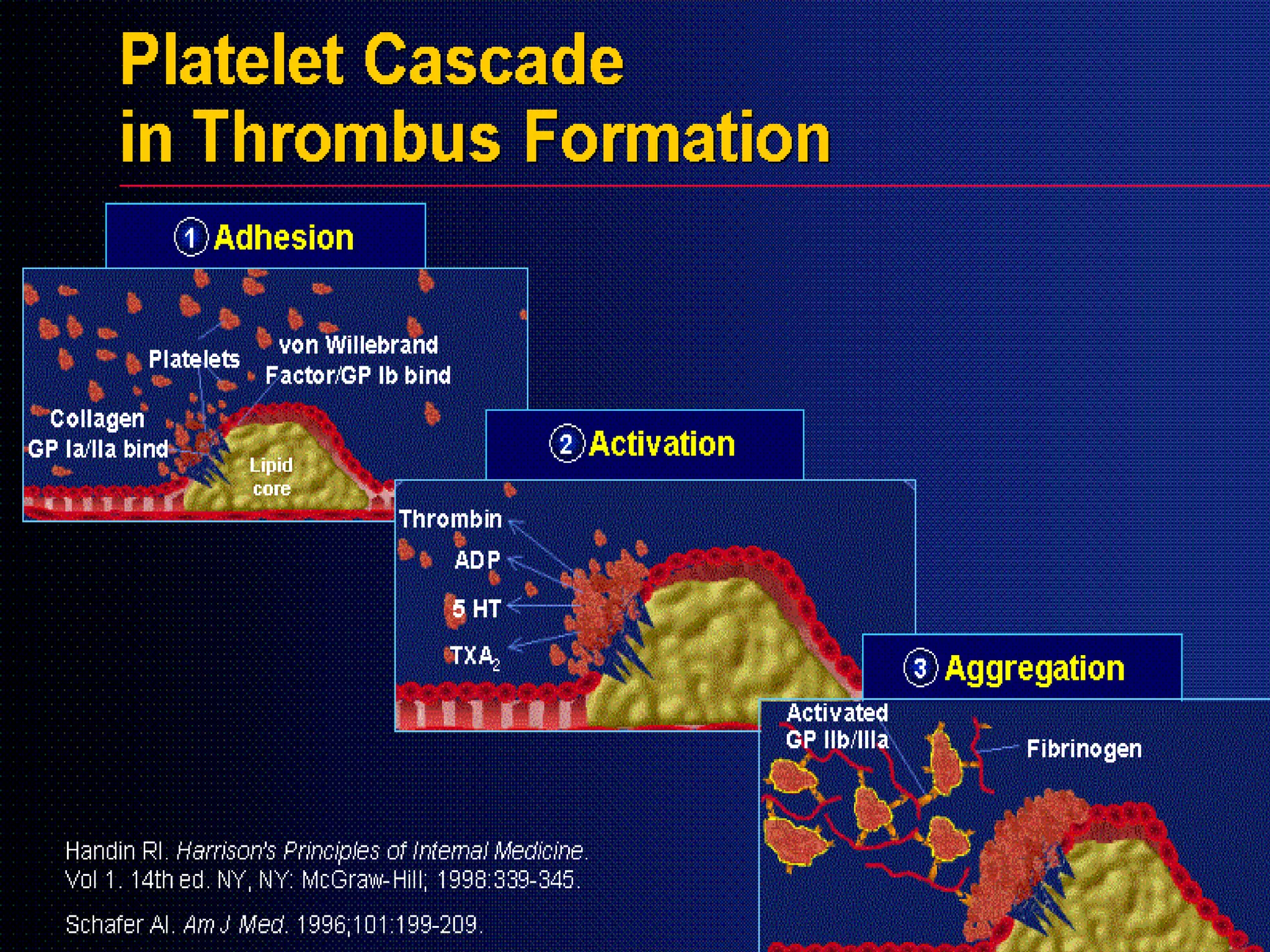
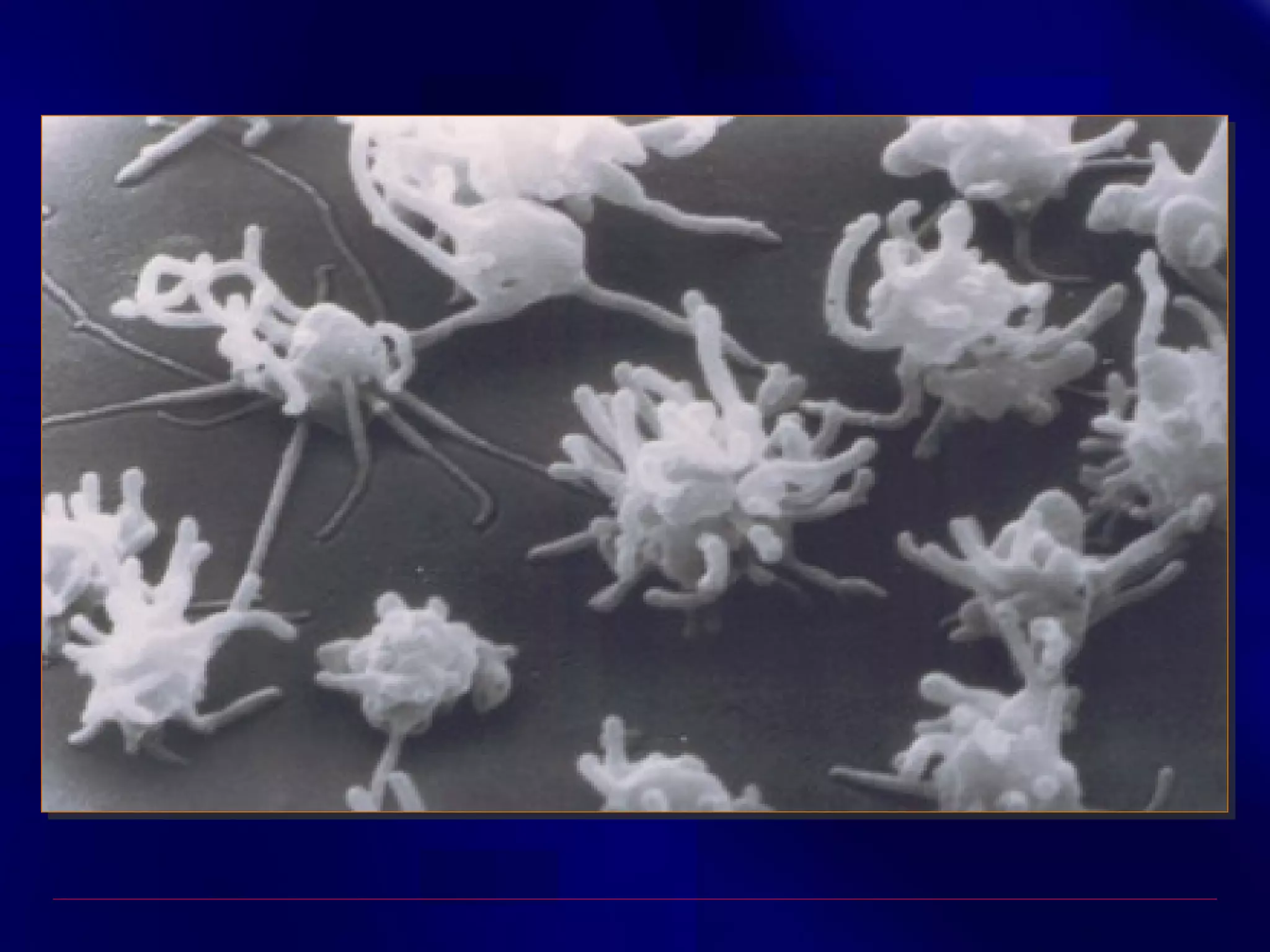
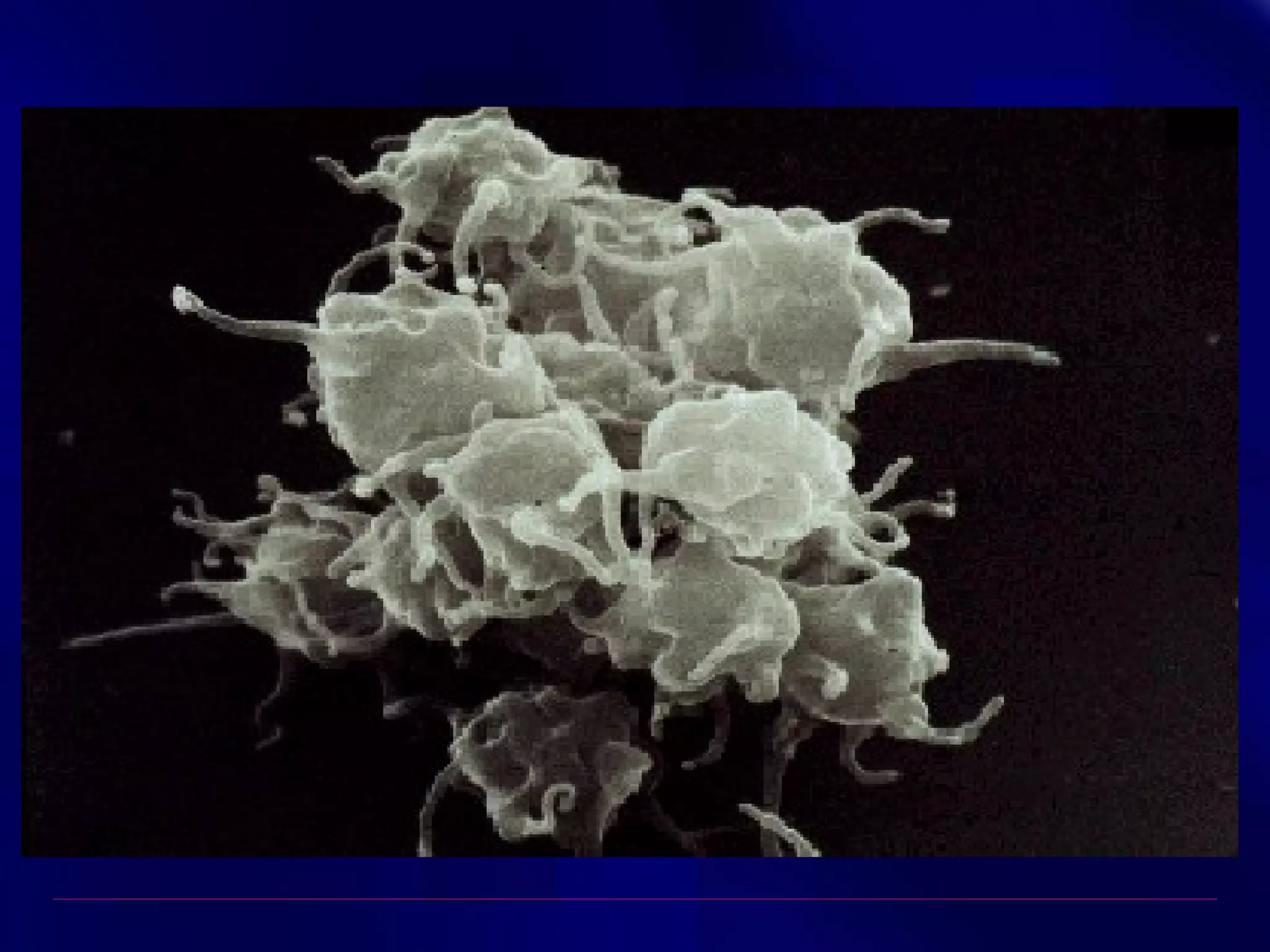
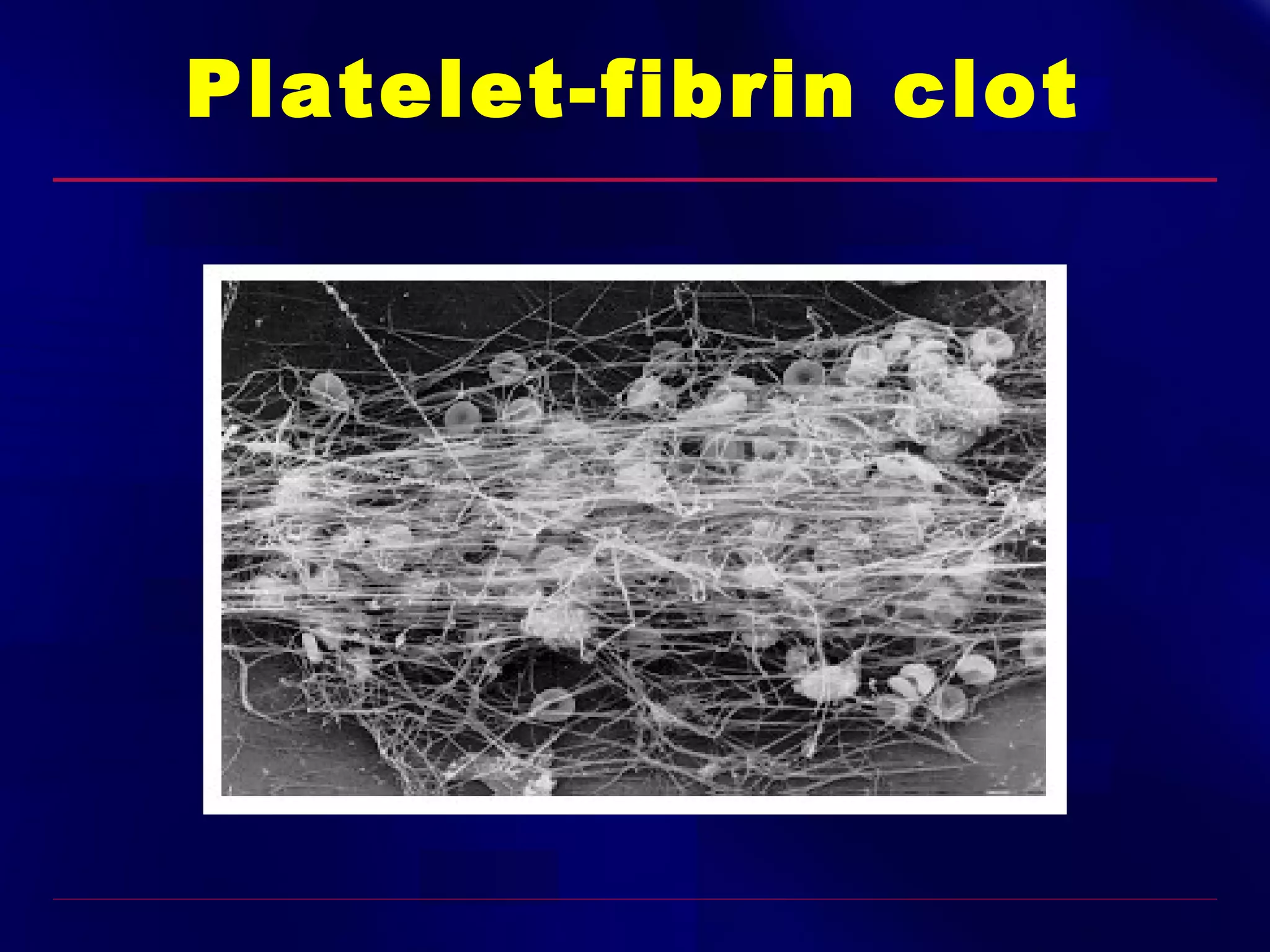
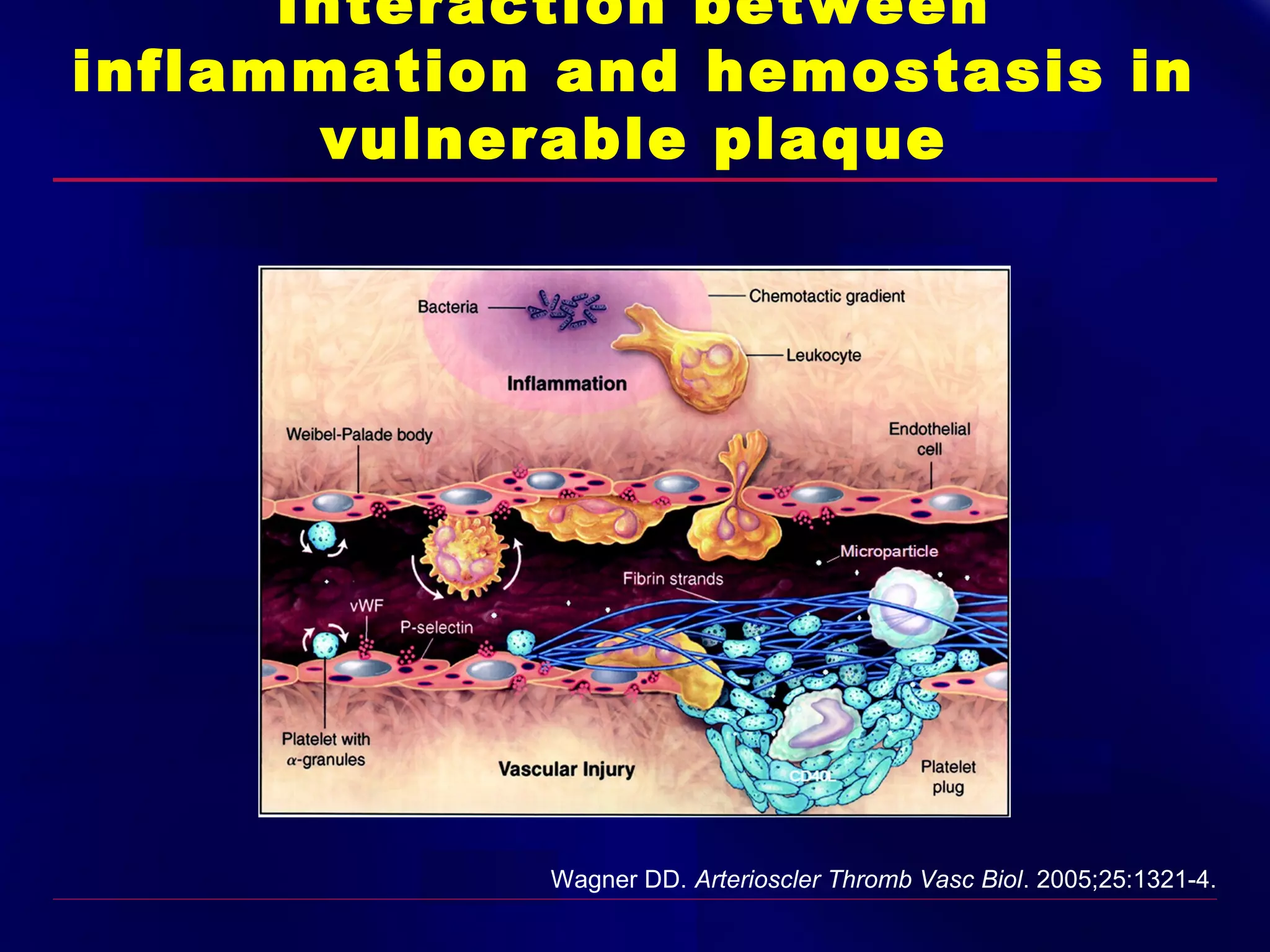
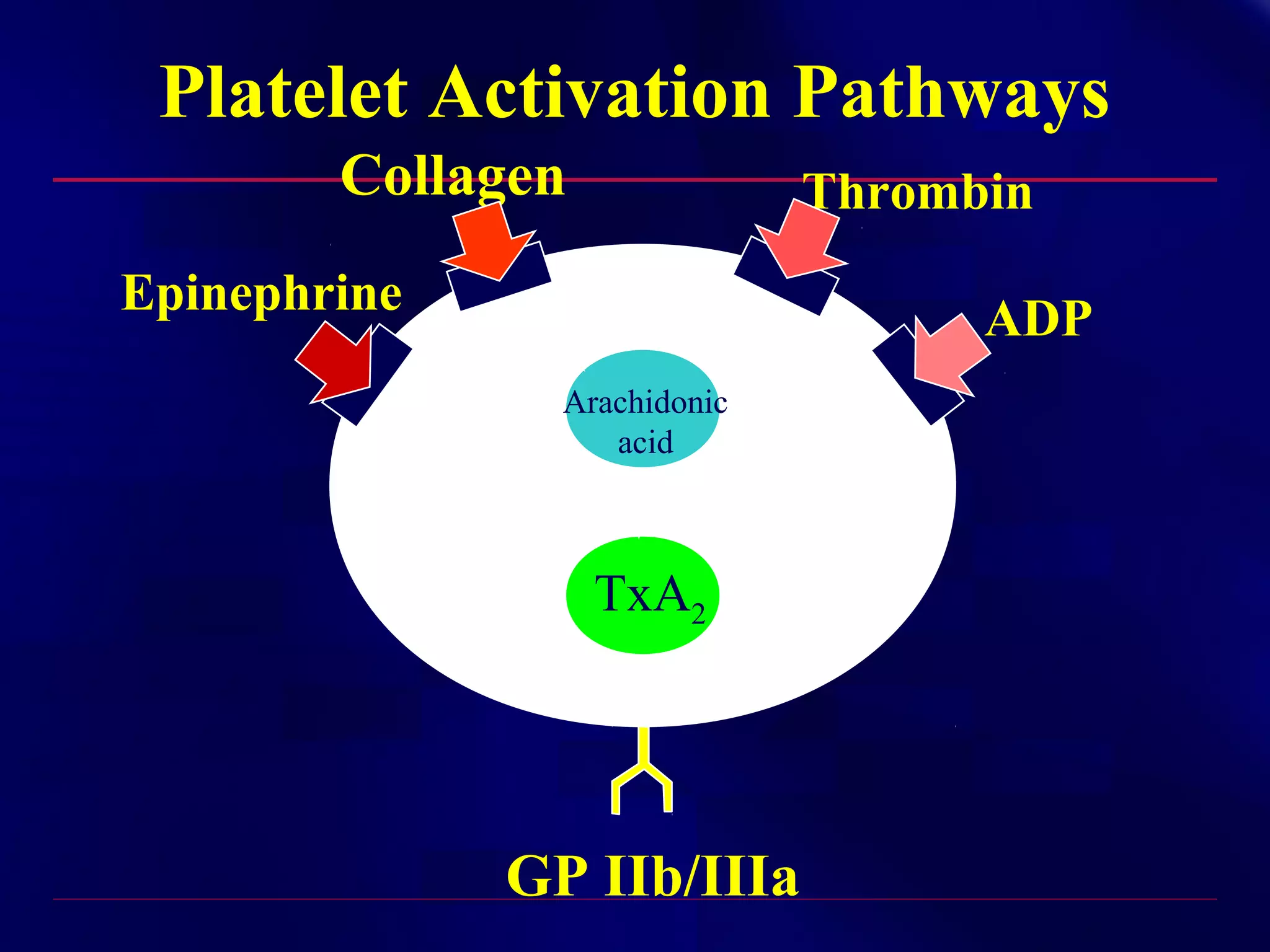
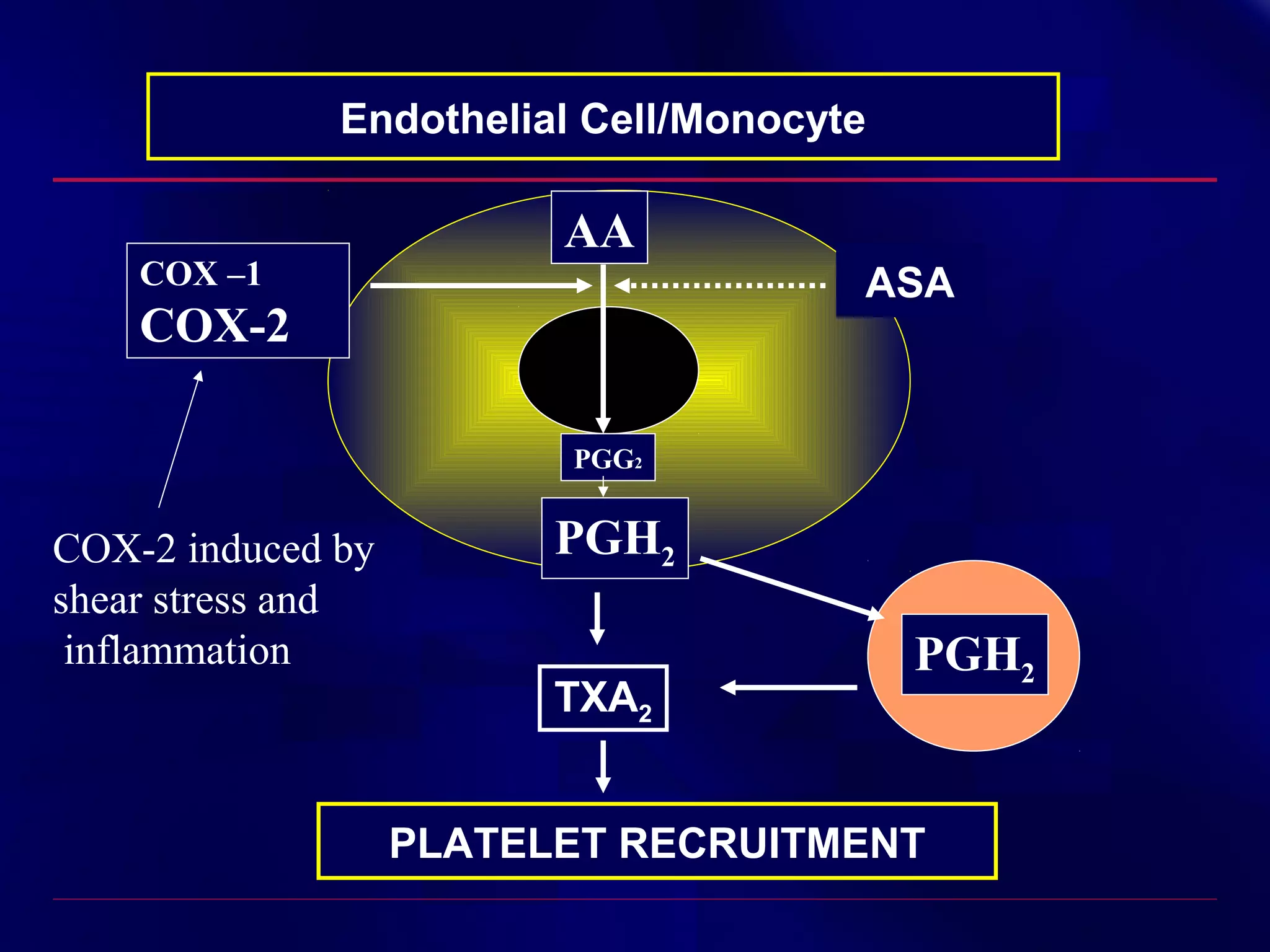
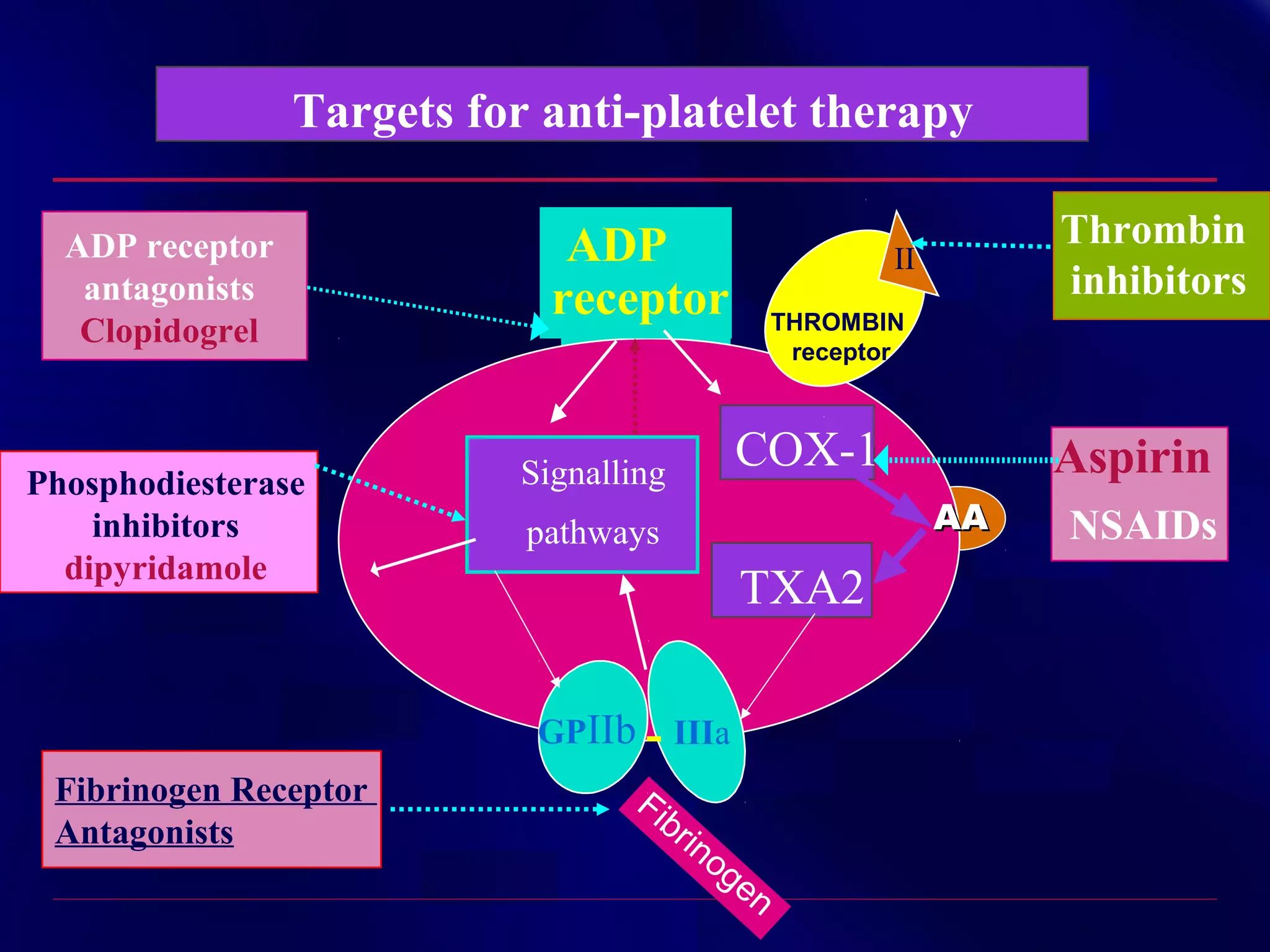
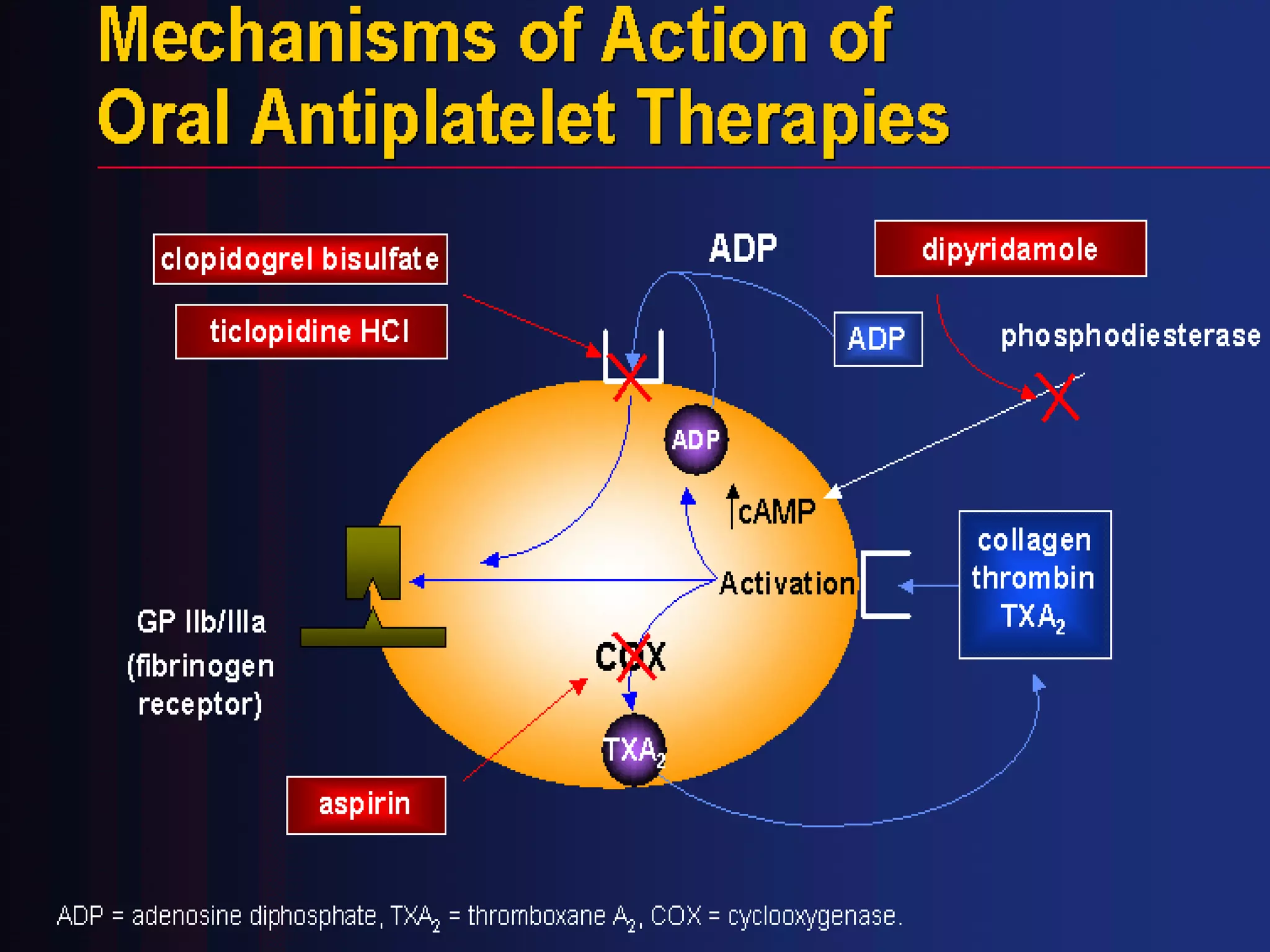
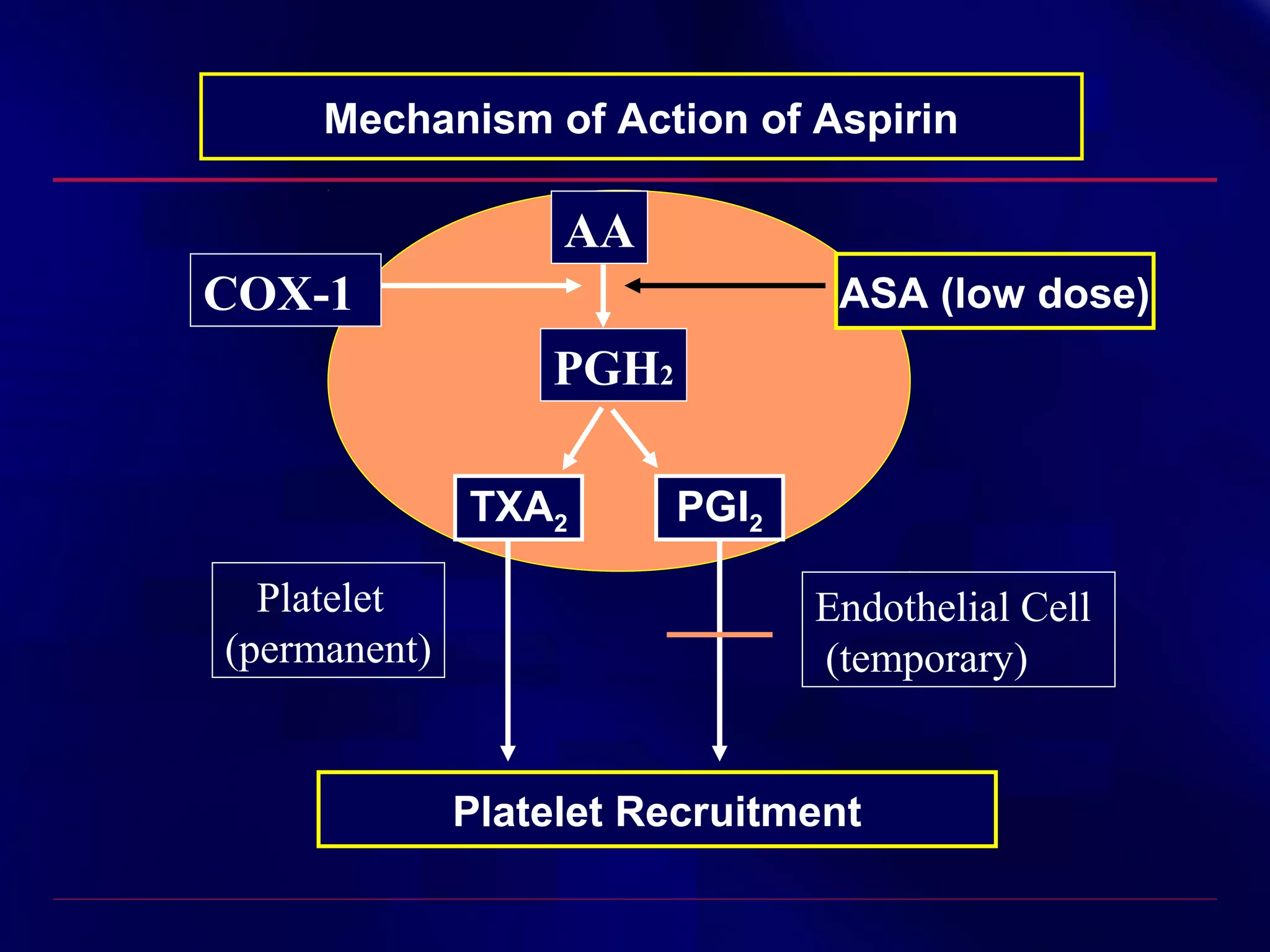
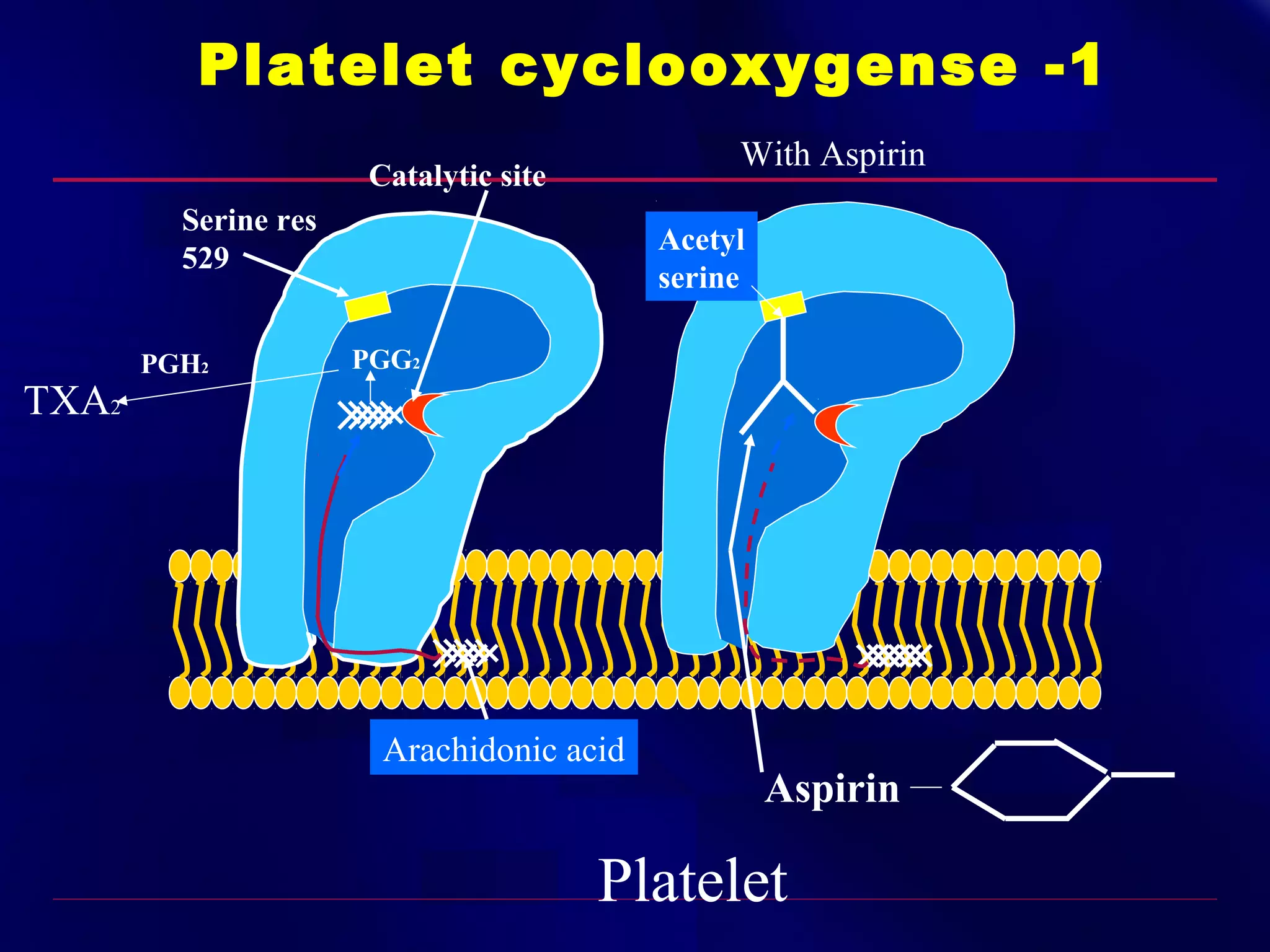
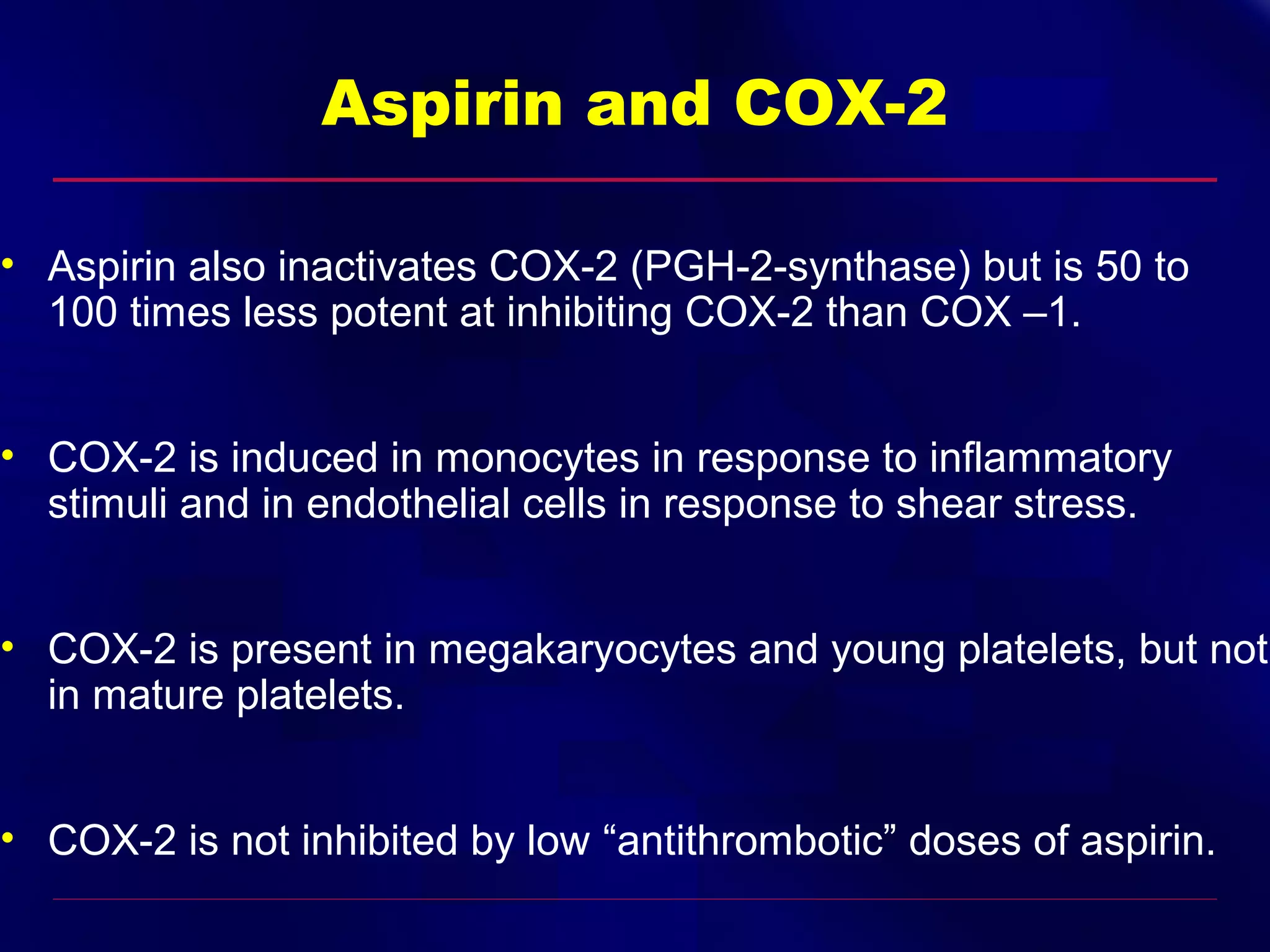
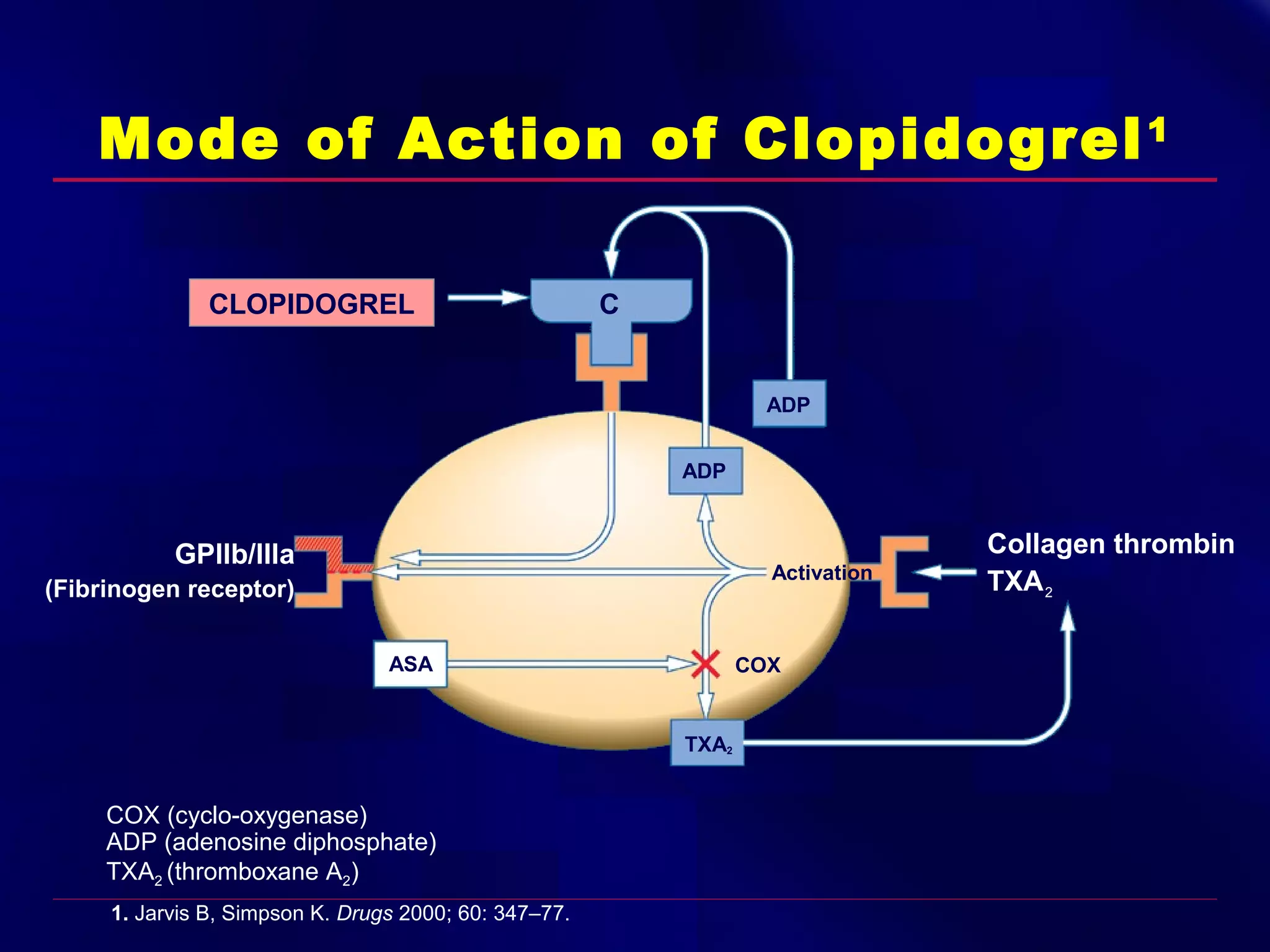
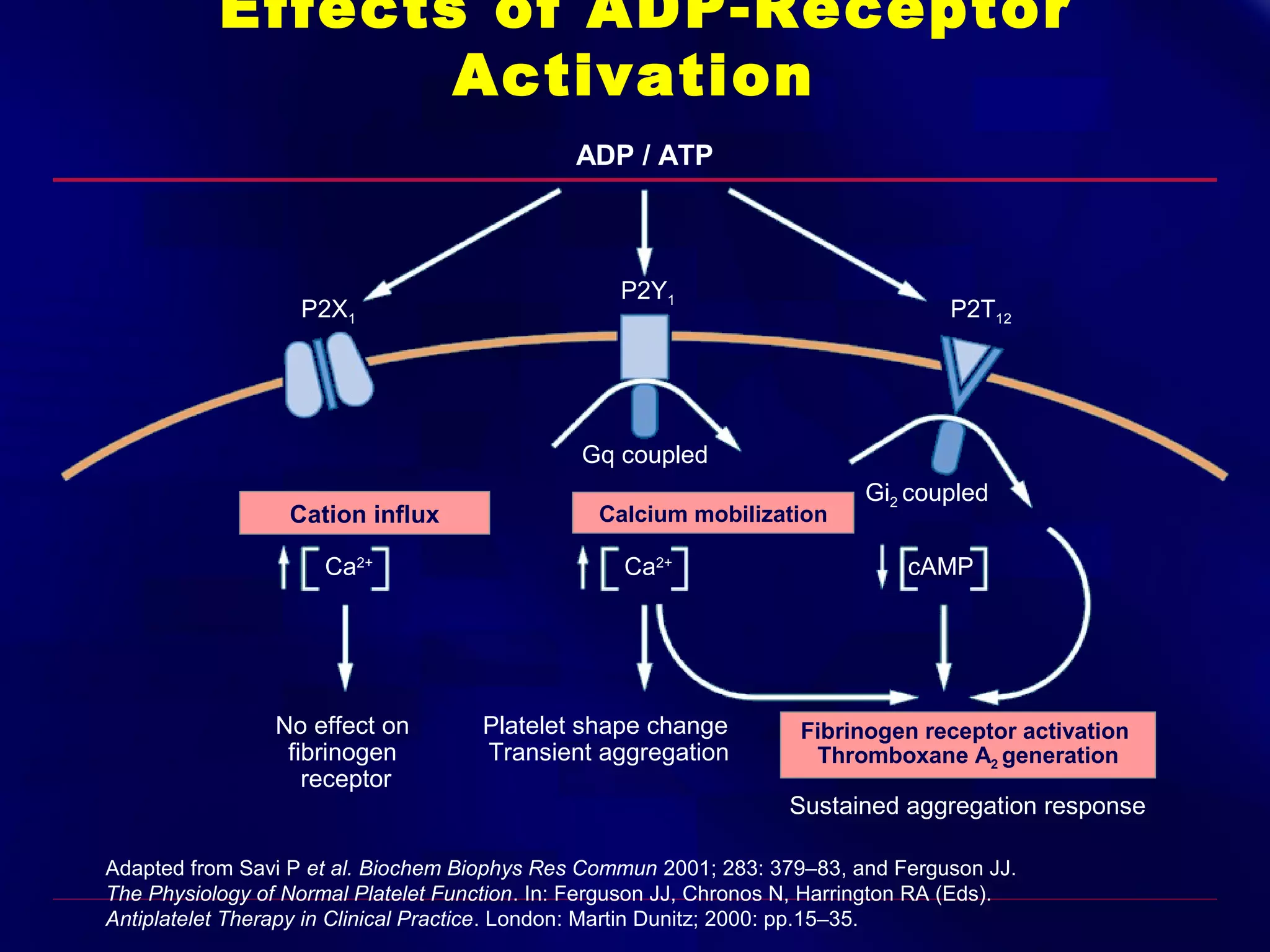
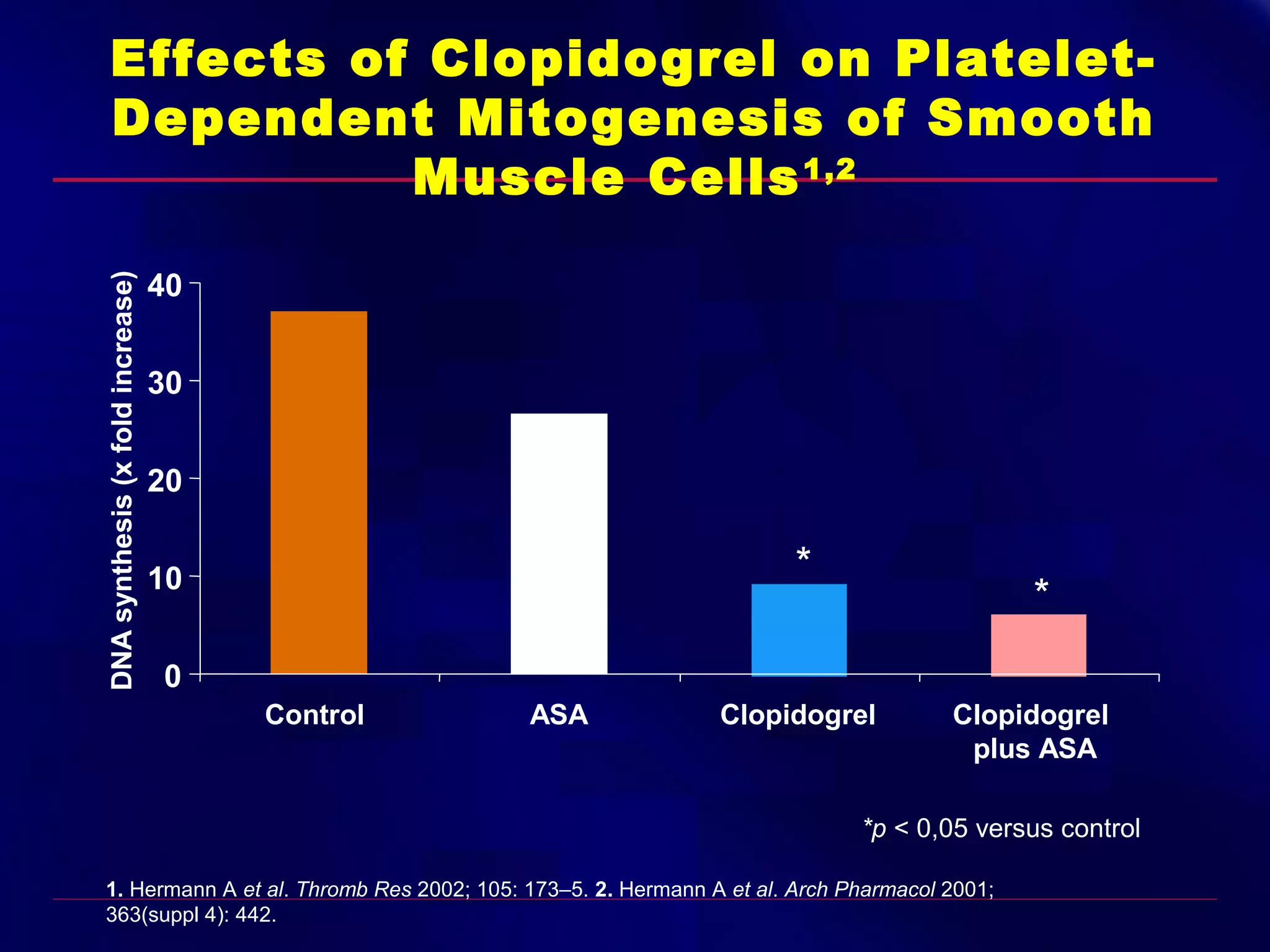
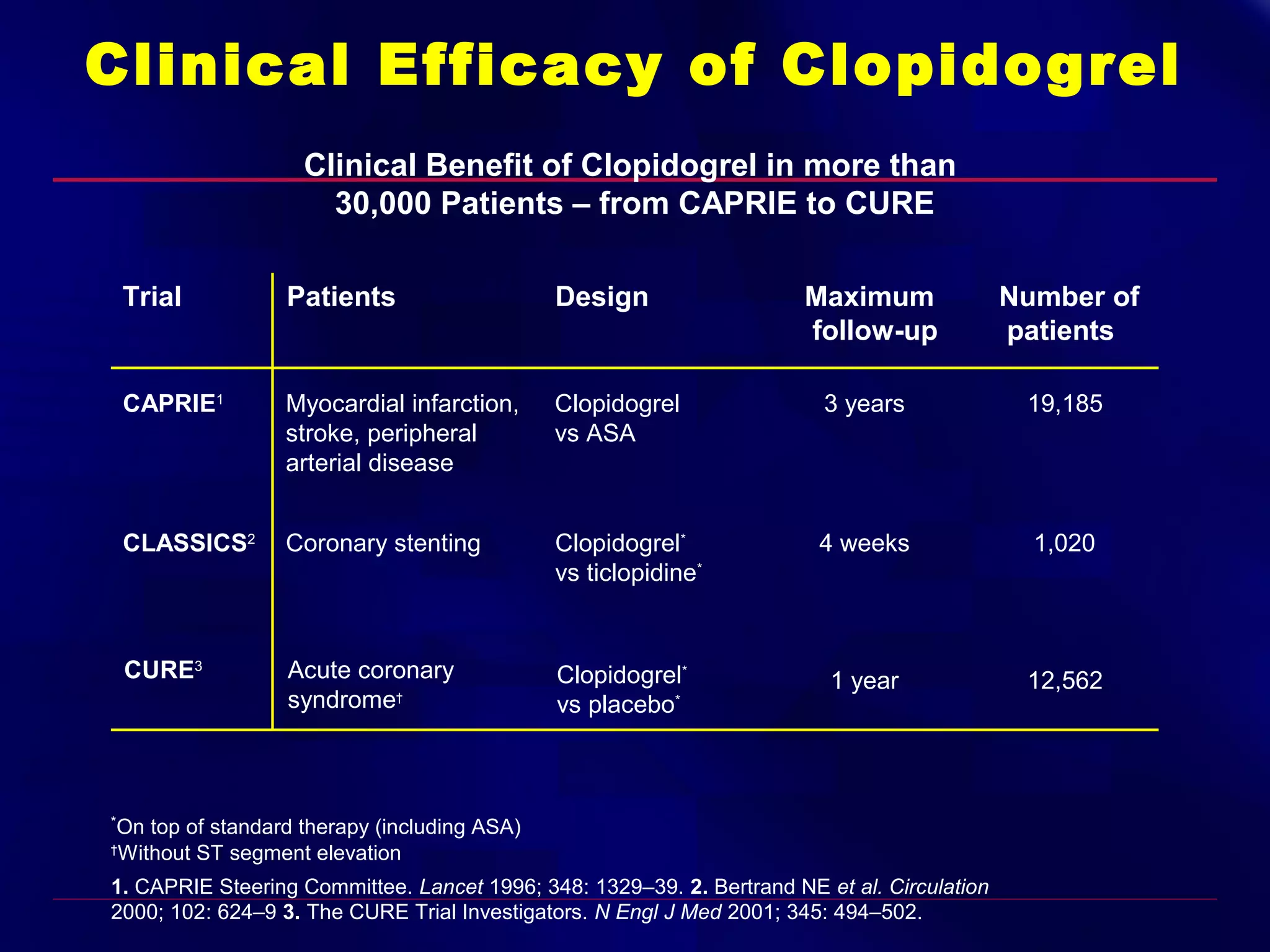
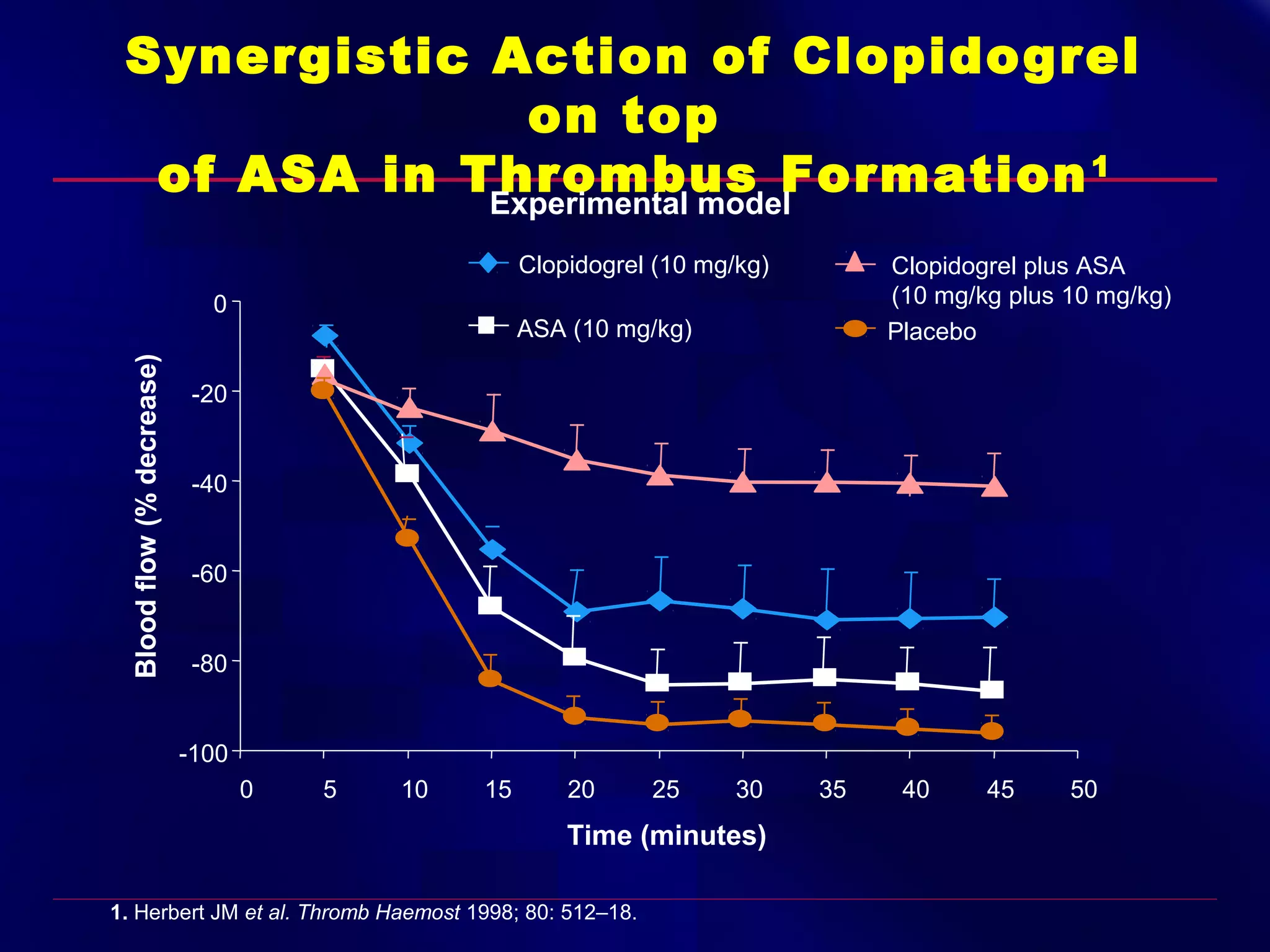
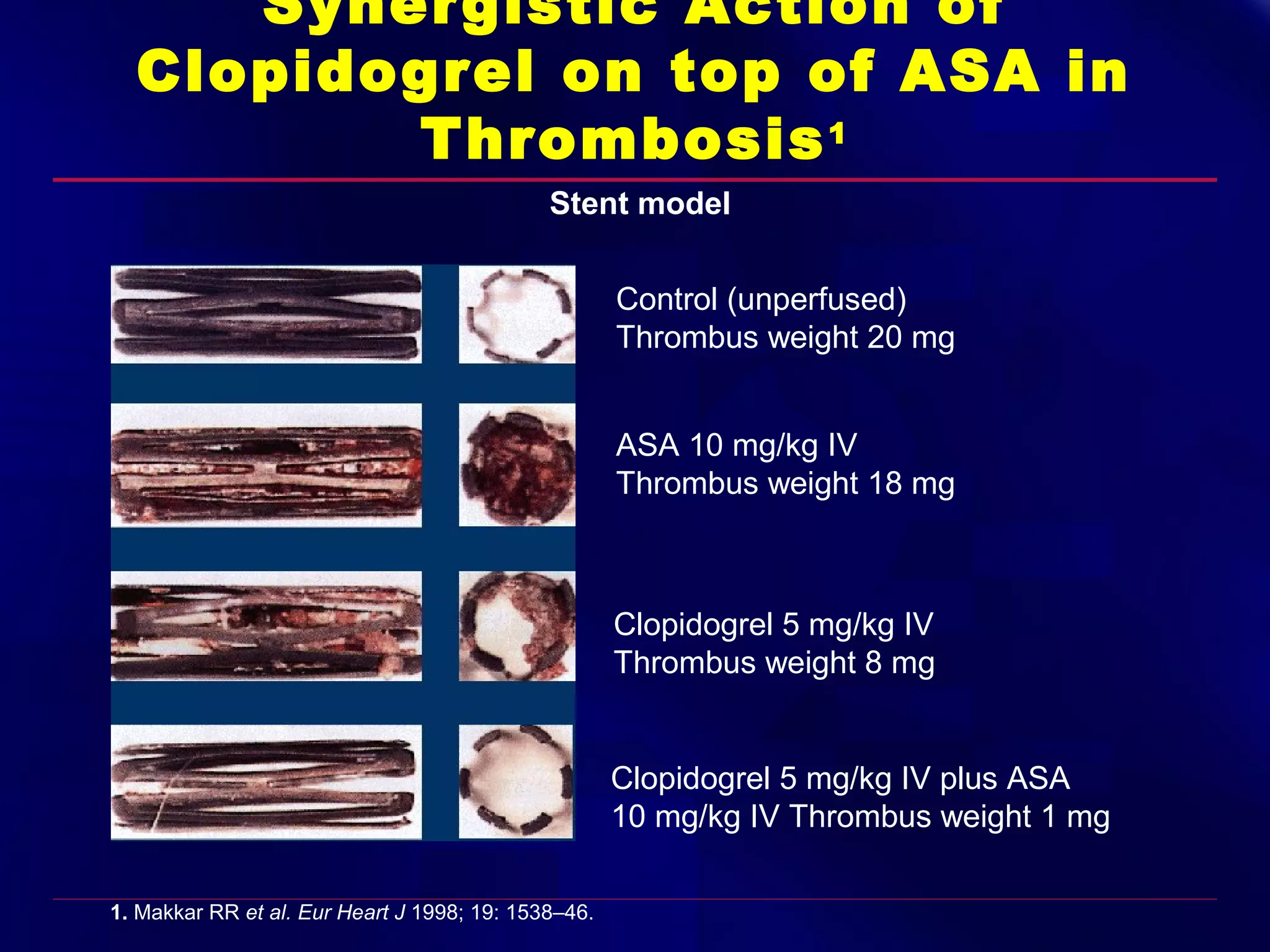
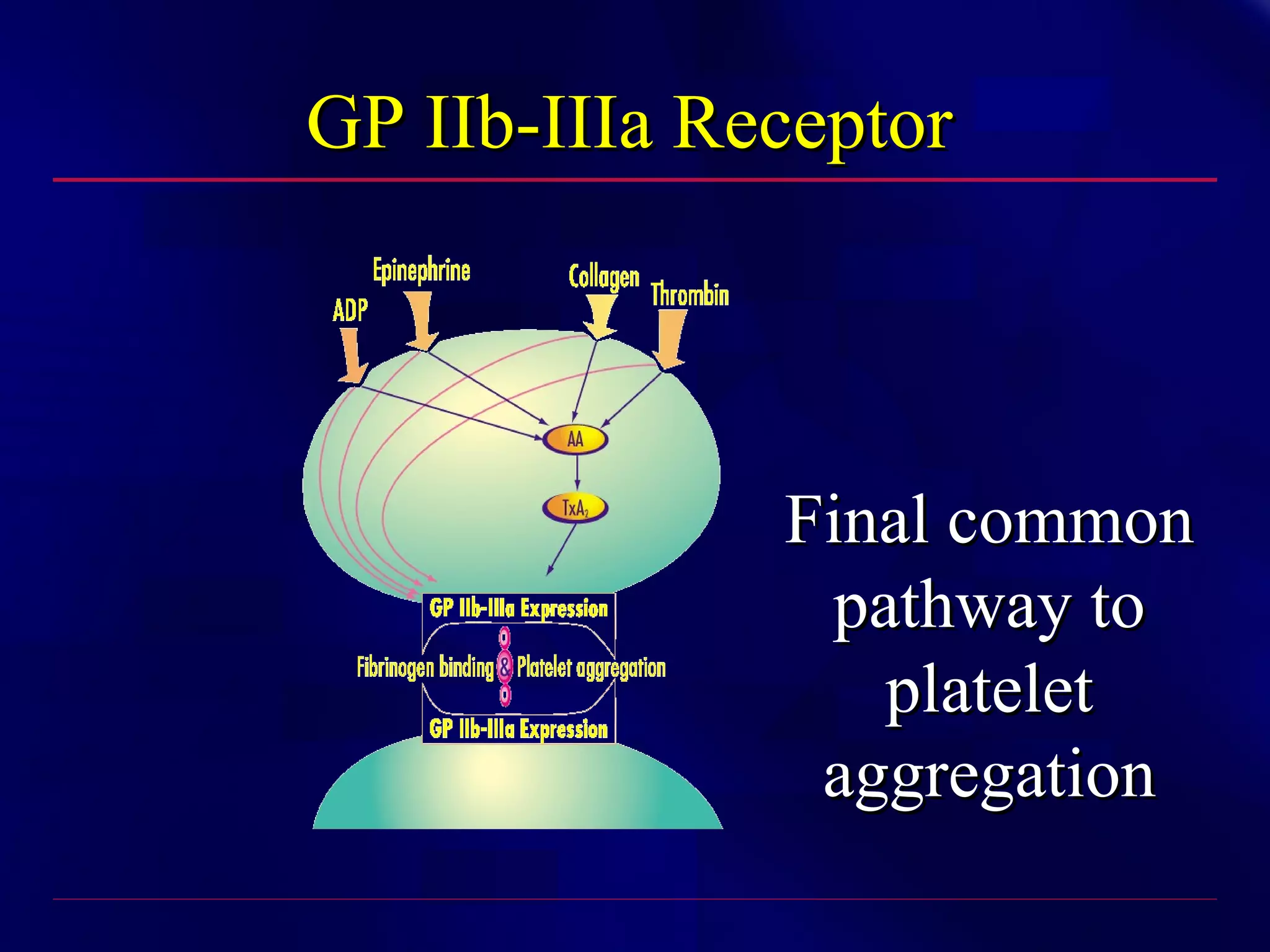
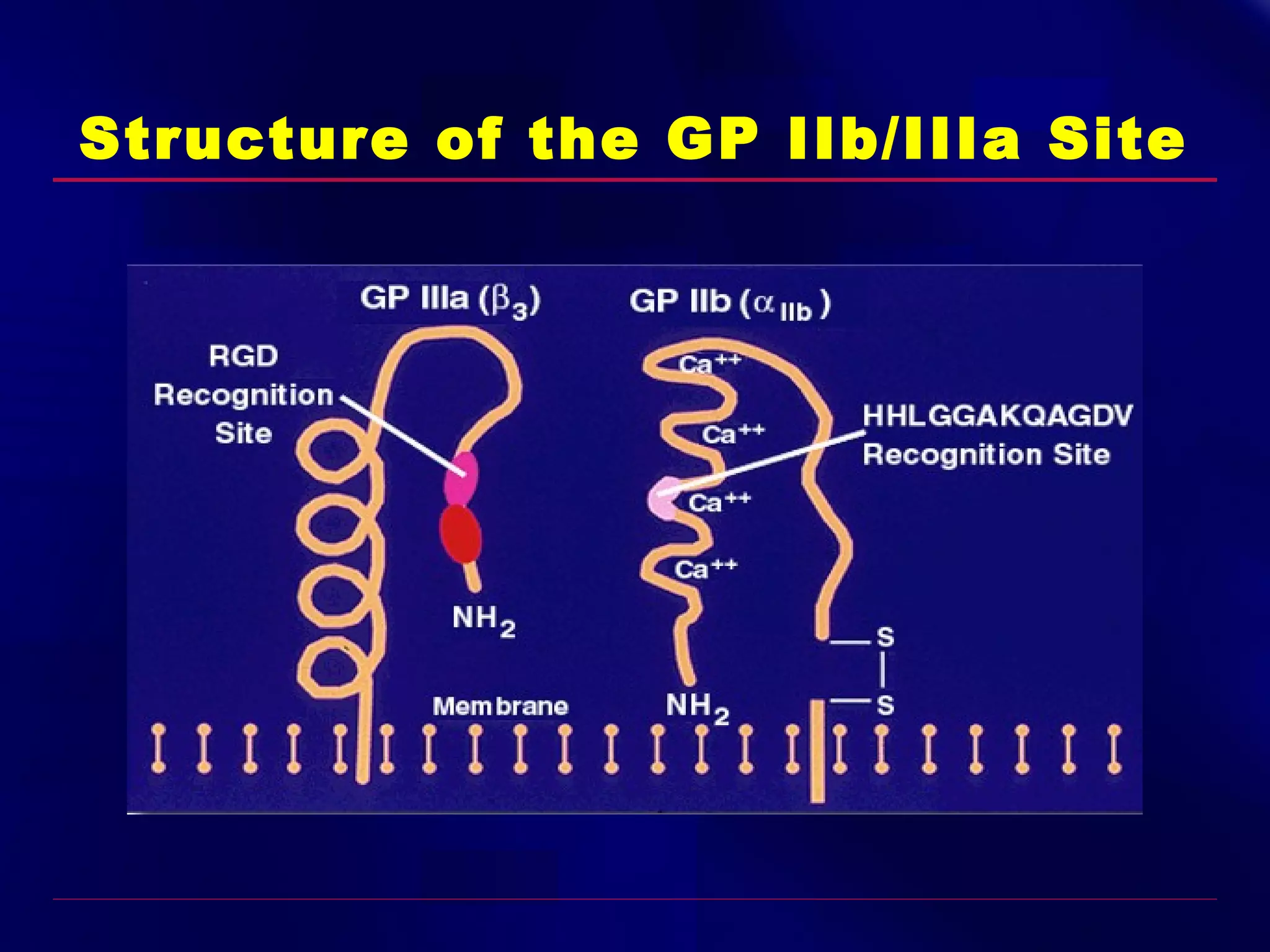
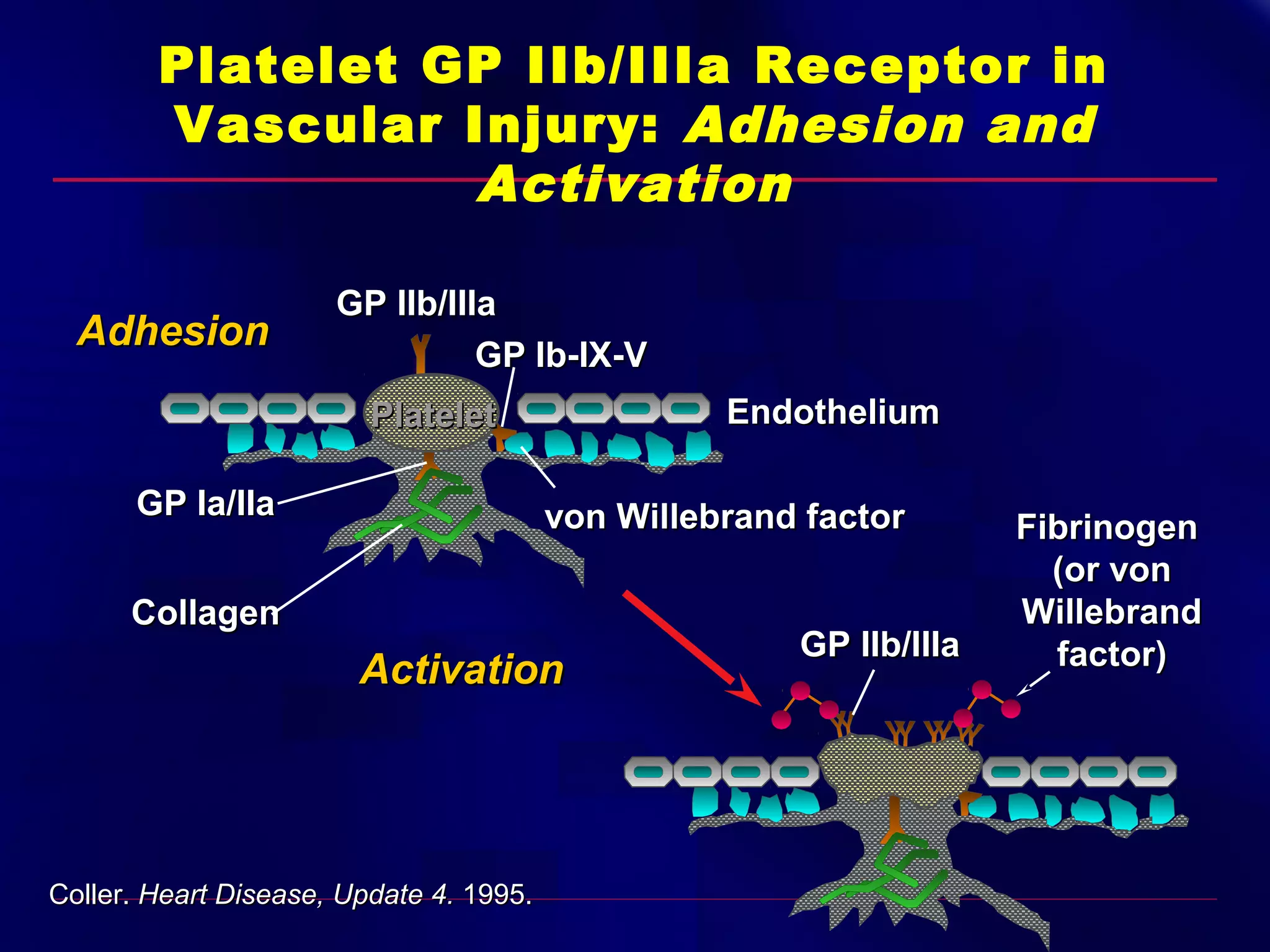
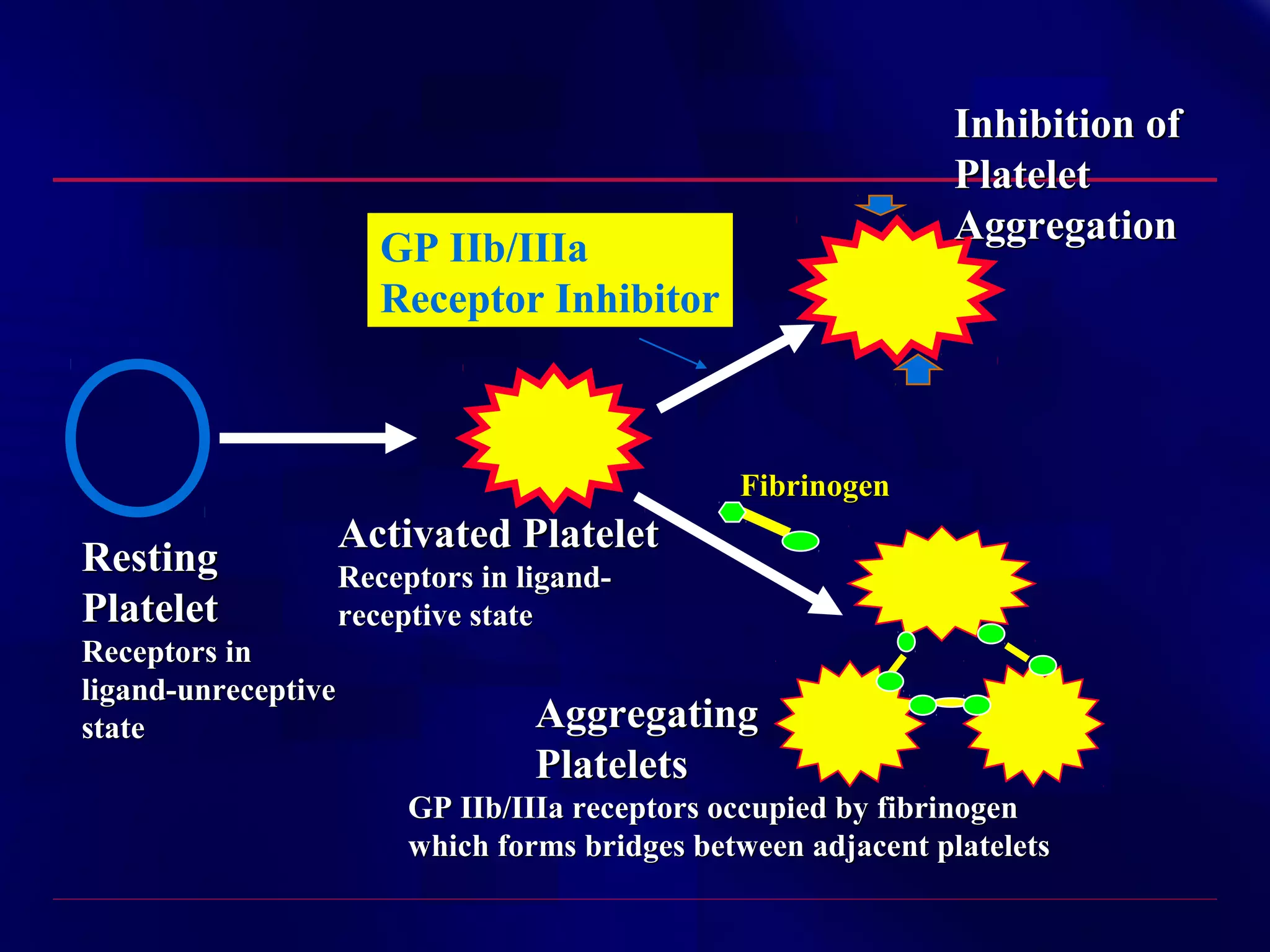
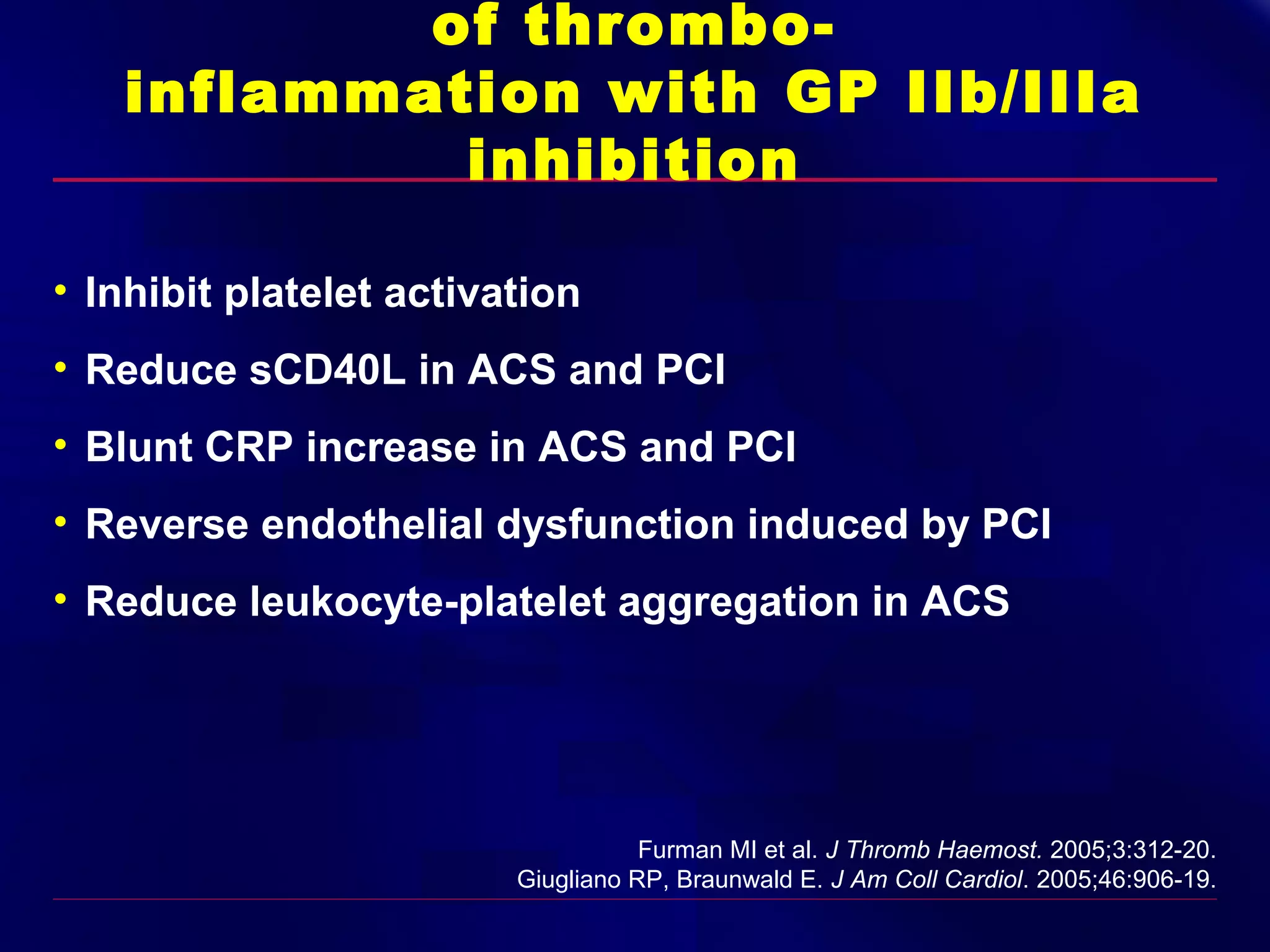
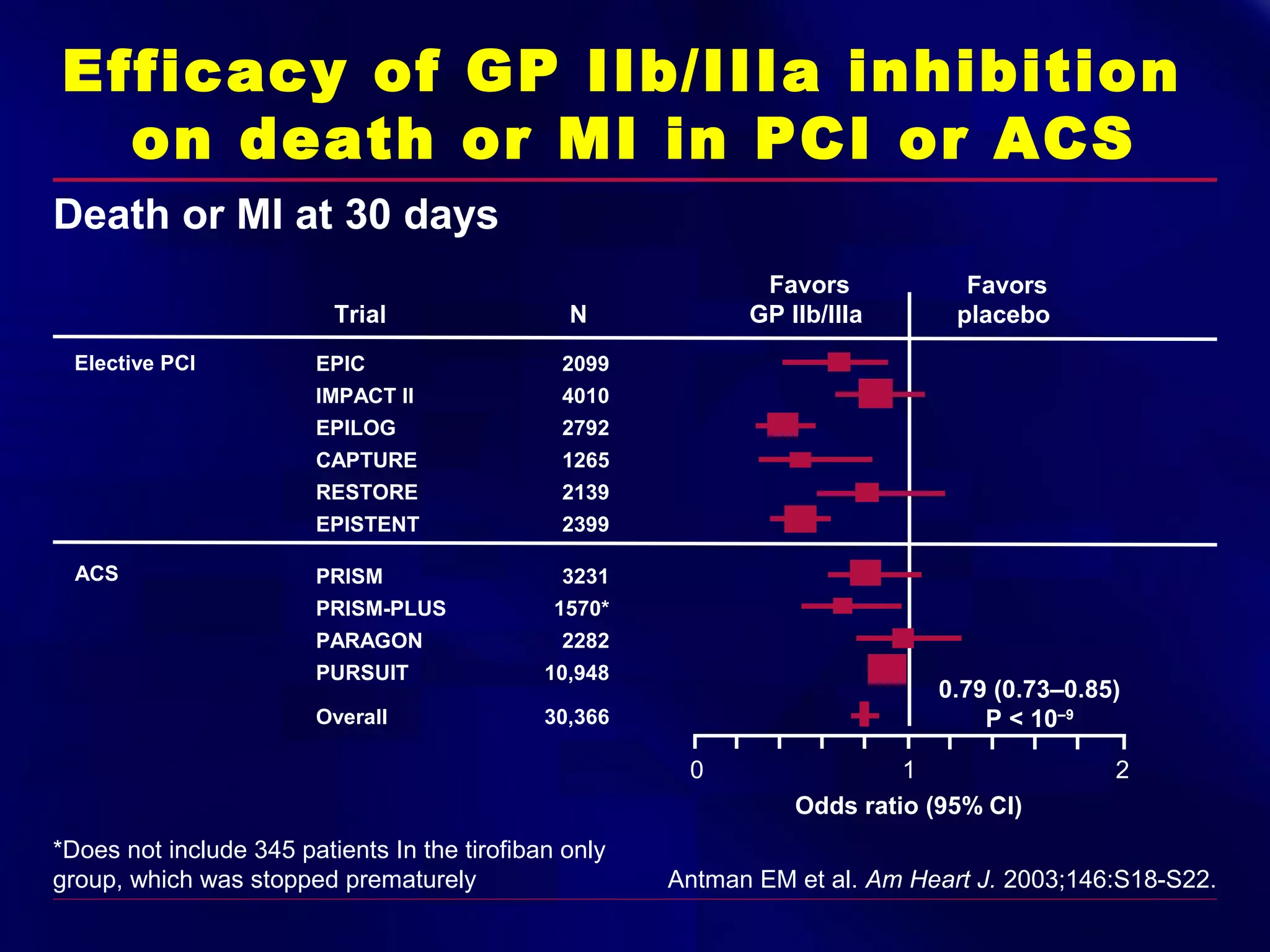
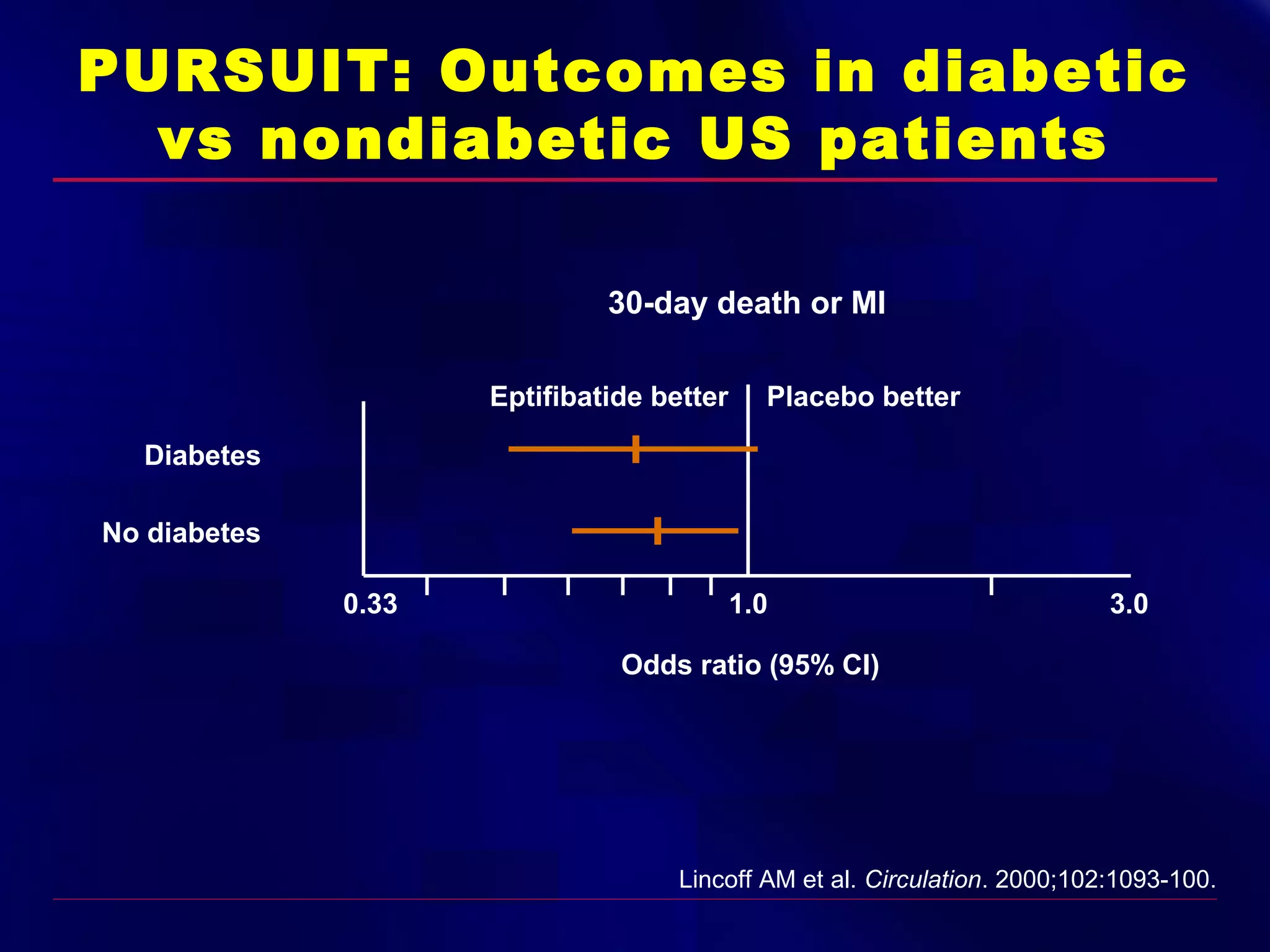
This document summarizes anti-platelet agents and their mechanisms of action. It discusses the pathophysiology of thrombus formation and platelet activation pathways. Targets for anti-platelet therapy include blocking ADP receptors, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, cyclooxygenase-1, and the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor. Aspirin irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase-1, preventing thromboxane A2 production. Clopidogrel inhibits the P2Y12 ADP receptor. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists like abciximab, tirofiban, and eptifibatide prevent fibrinogen binding. Clinical trials demonstrate the efficacy of these agents in