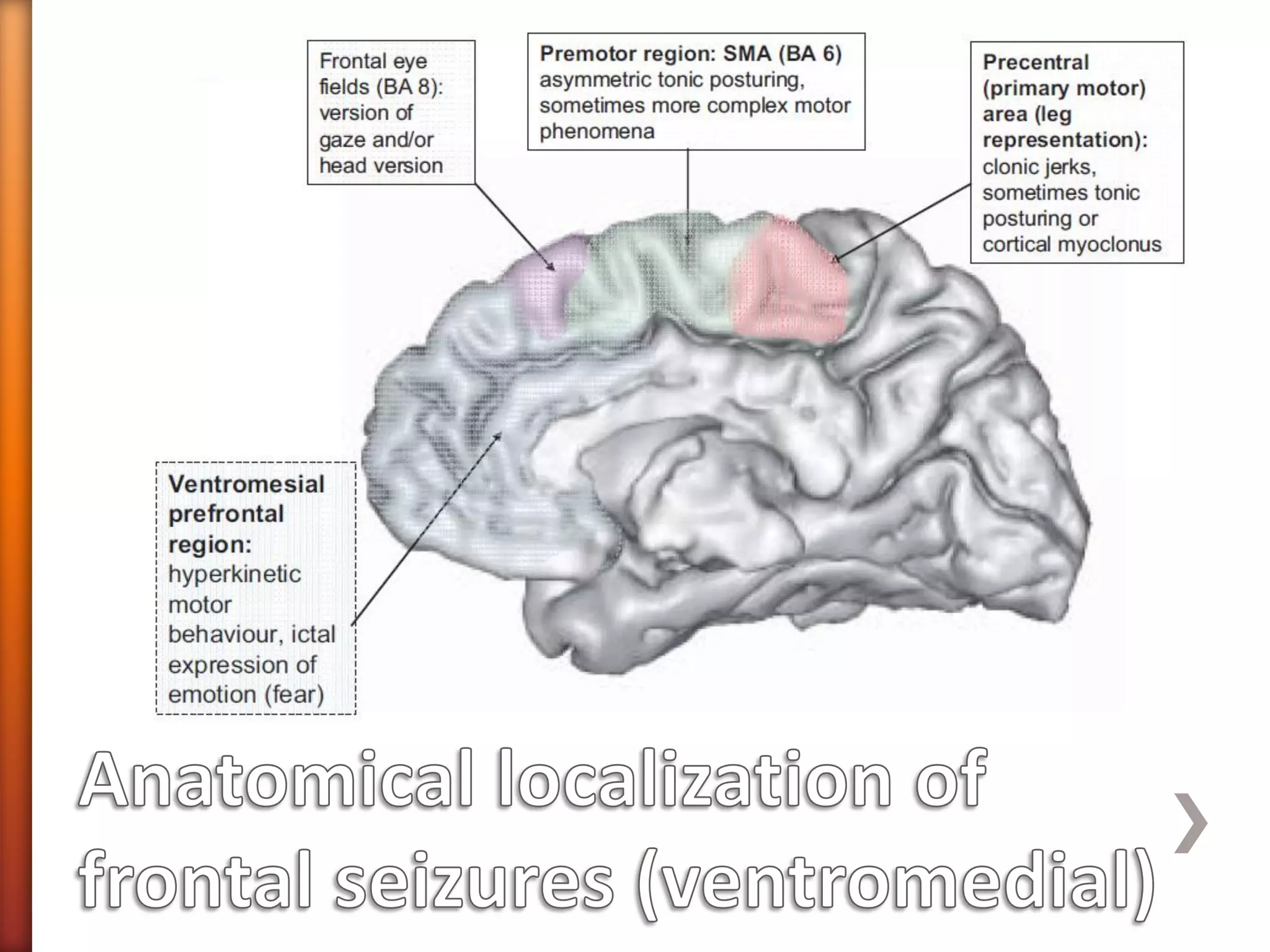
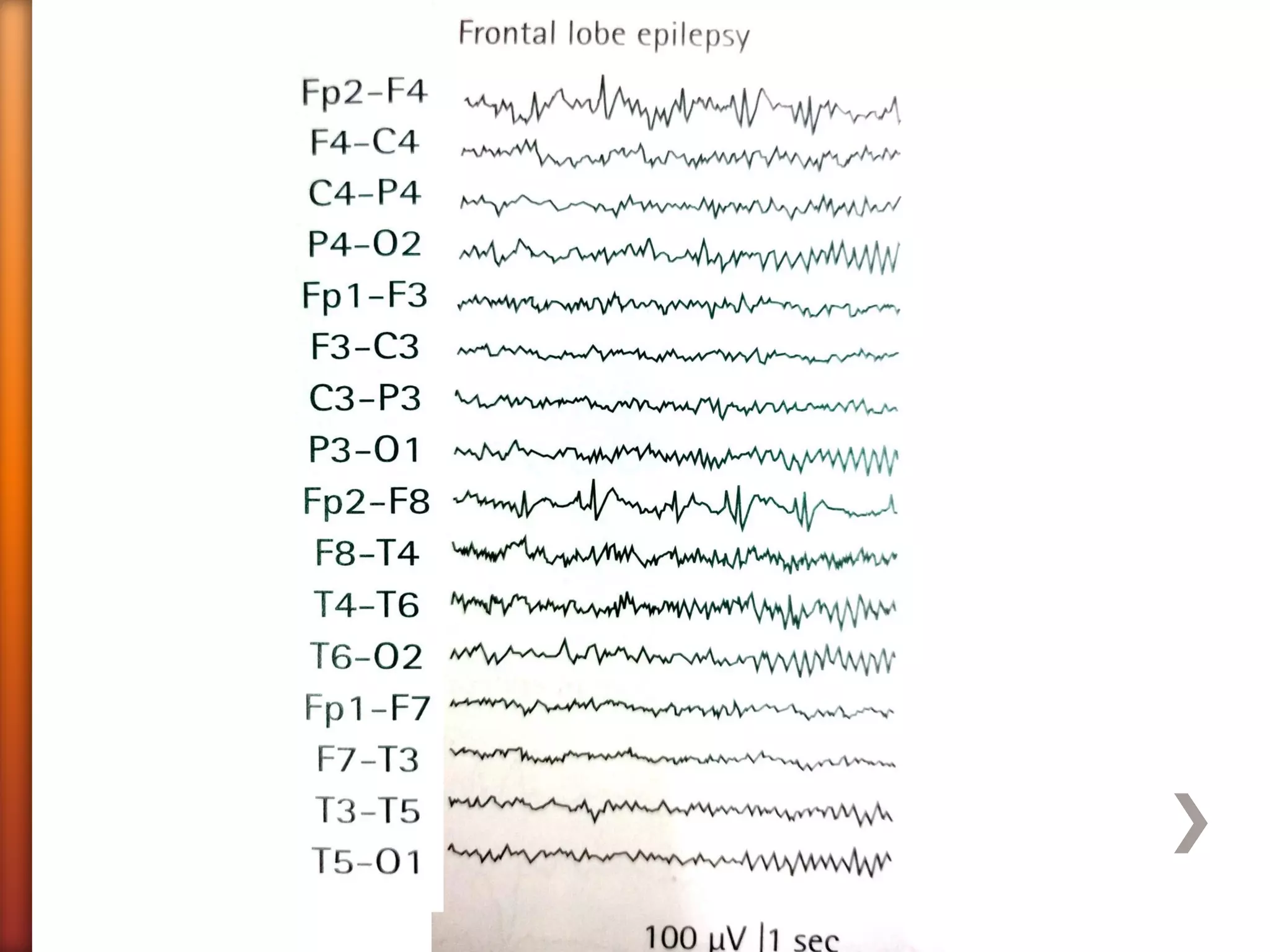
The document discusses frontal lobe epilepsy, including its anatomy and functions, aetiology, diagnosis, and treatment. It covers the different classifications of frontal lobe seizures based on their functional anatomy and manifestations. Some key seizure types mentioned are Rolandic epilepsy, which involves characteristic "Jacksonian march" seizures, and ventromedial and dorsolateral prefrontal seizures, which present with different behavioral and autonomic symptoms. Evaluation involves neuroimaging like MRI and EEG to localize the seizure focus. Treatment options include medications, surgery, diet, and management of impairments.