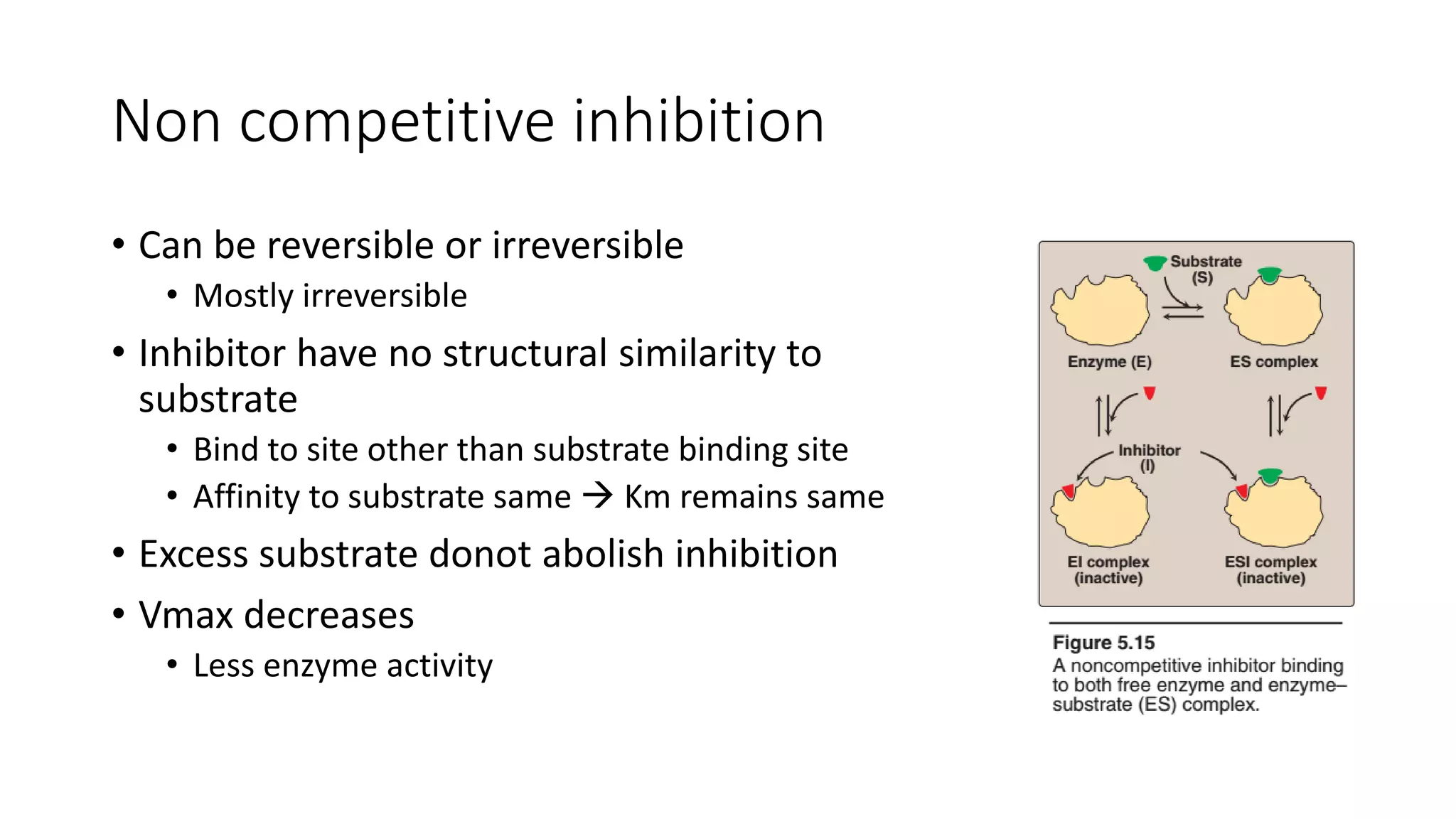
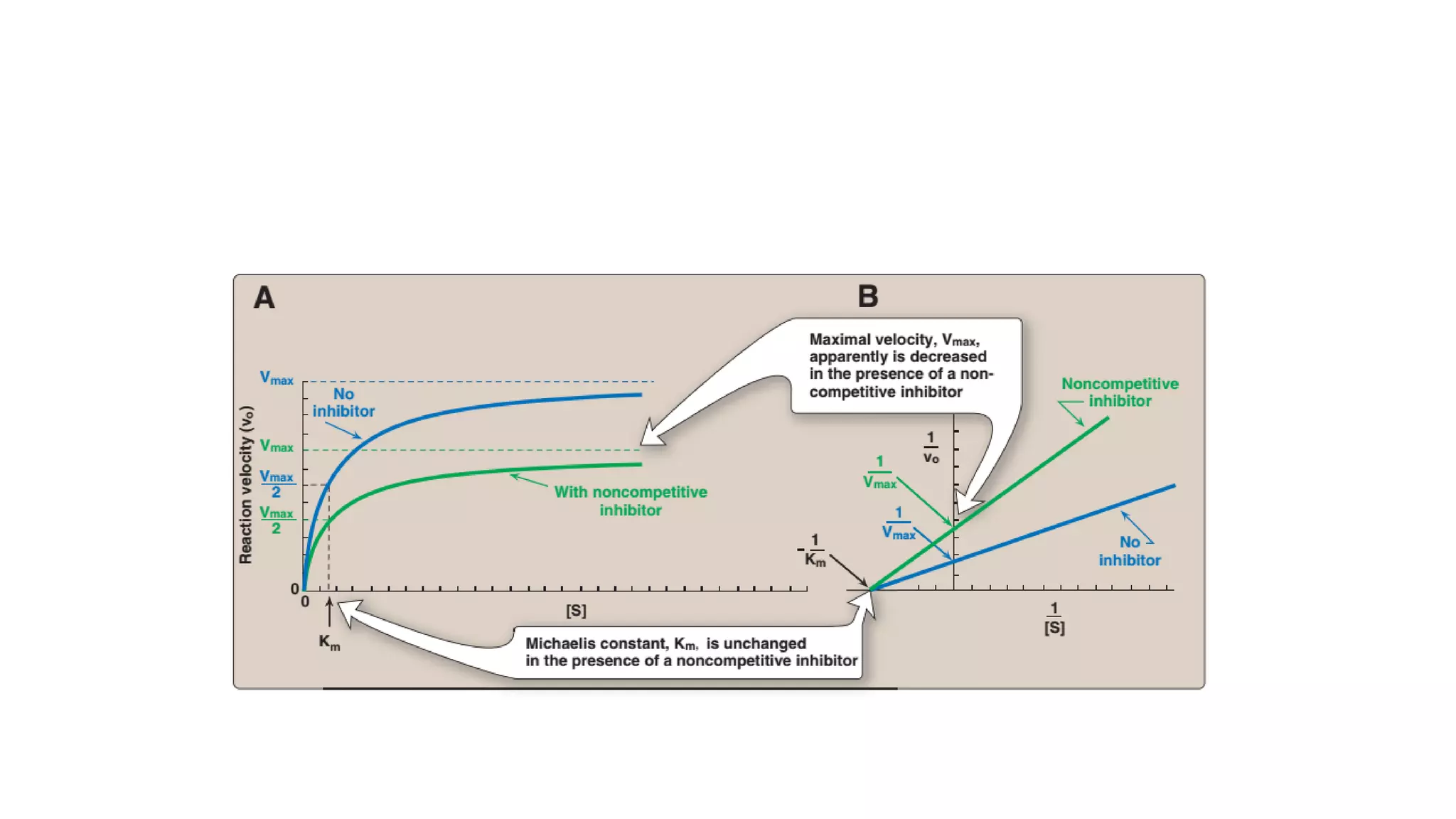
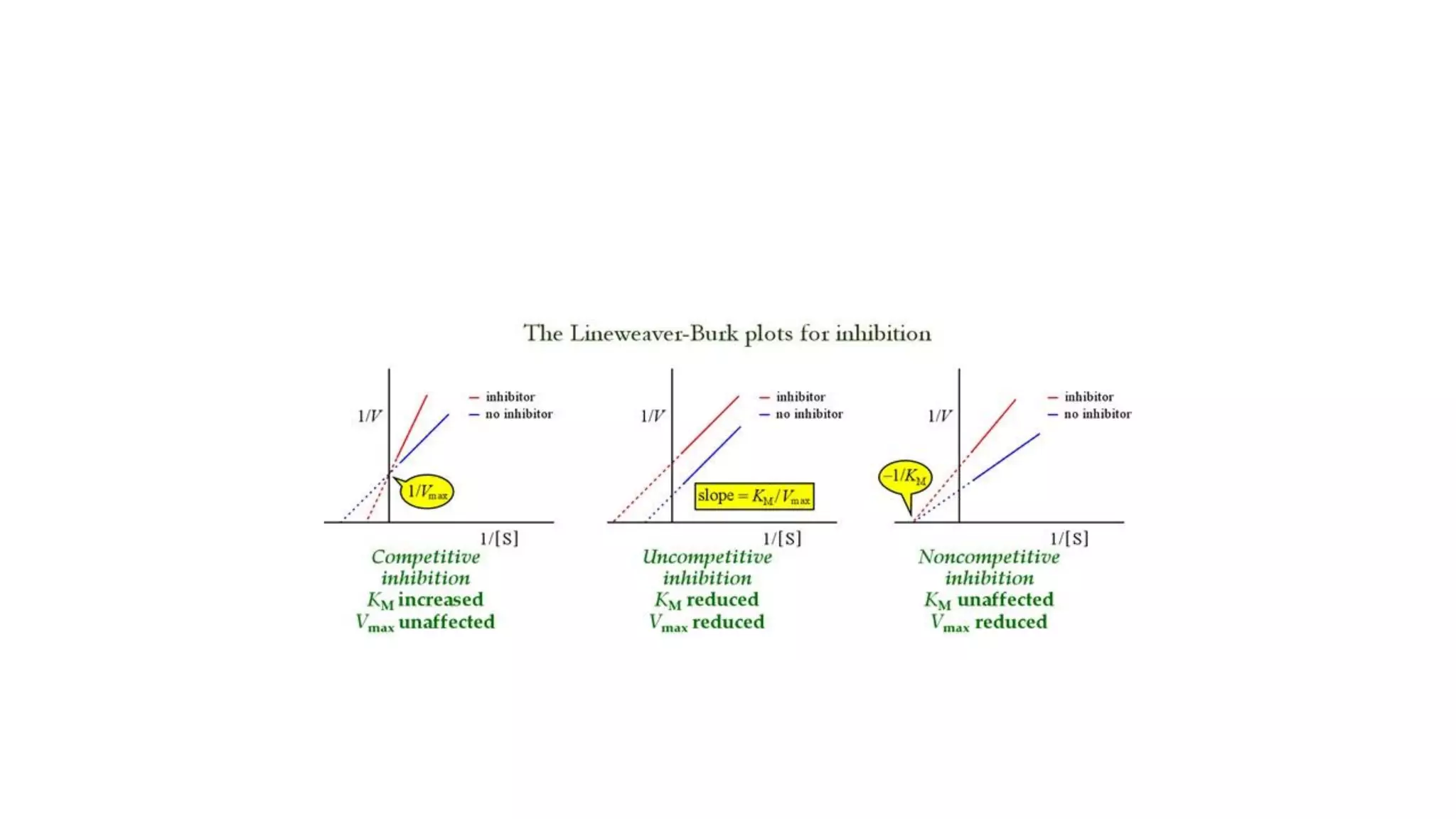
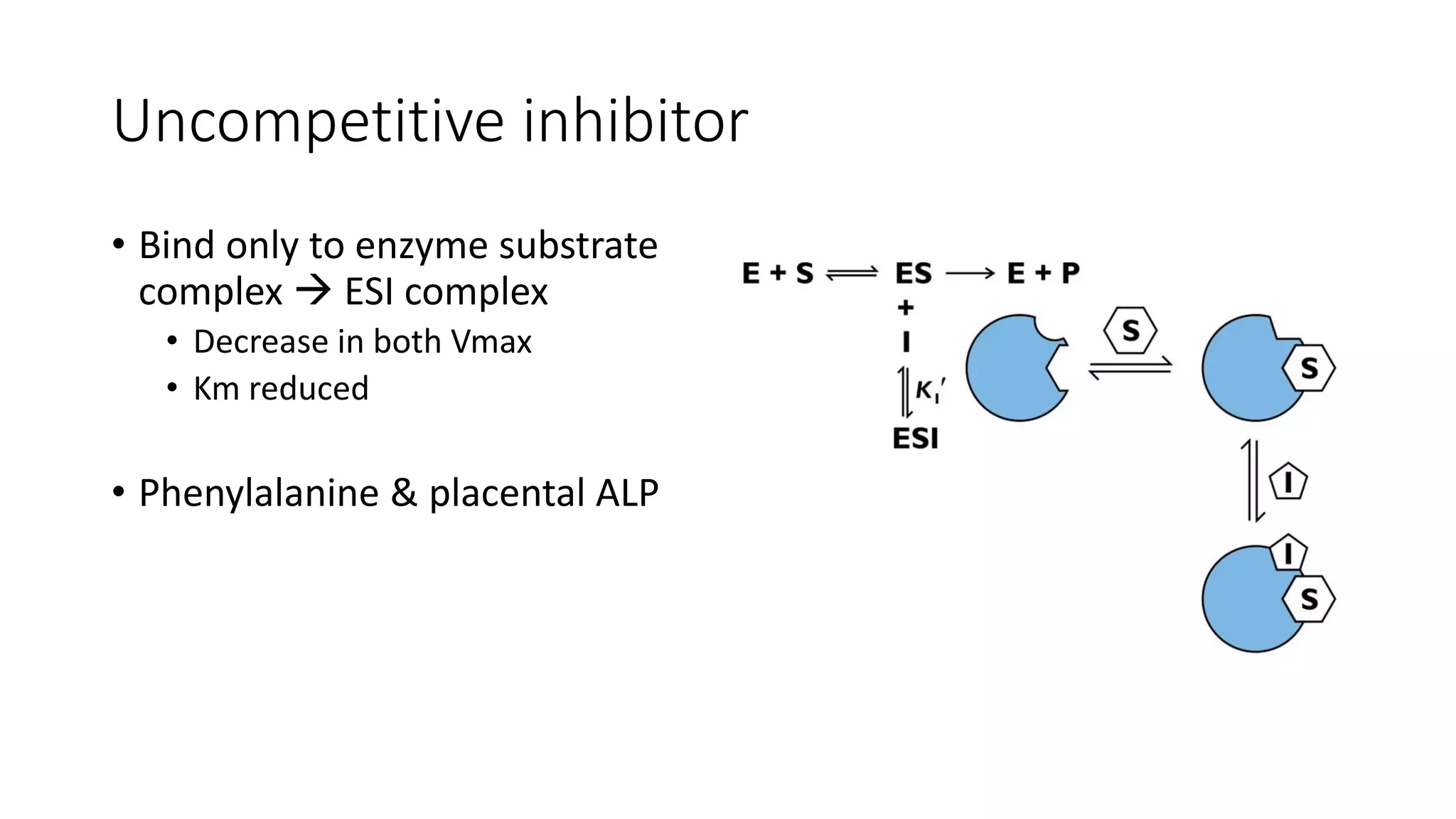
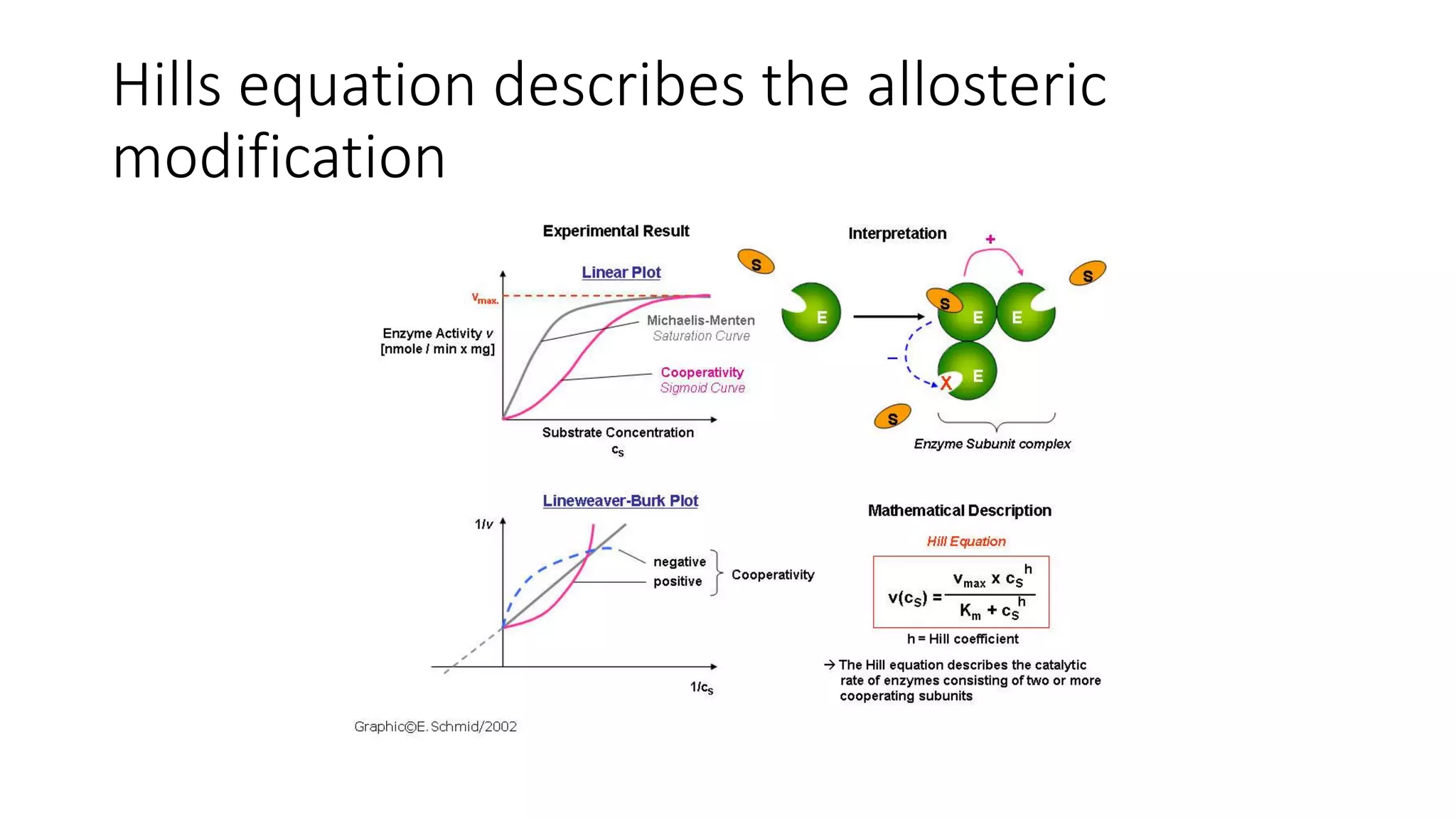
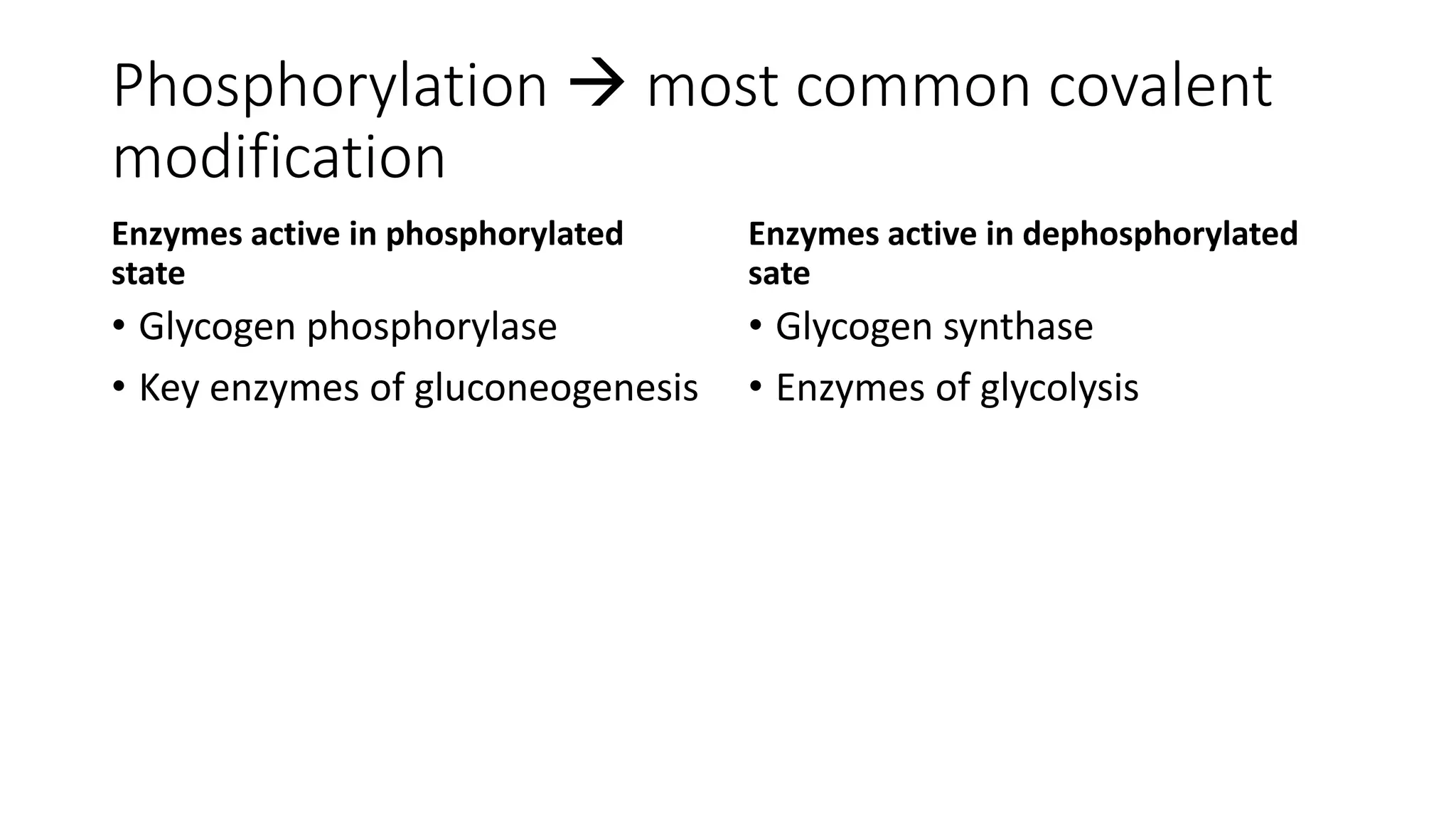
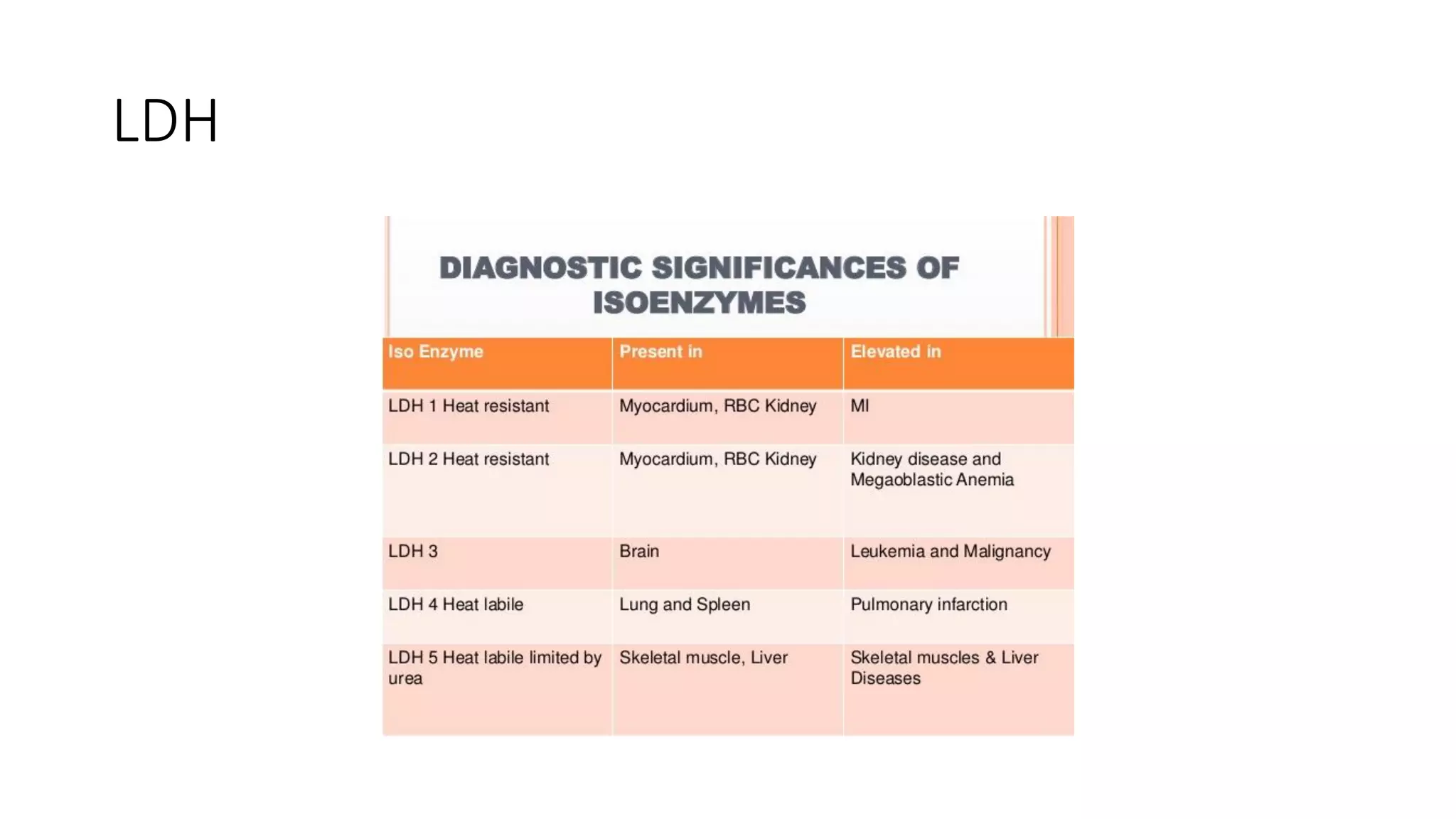
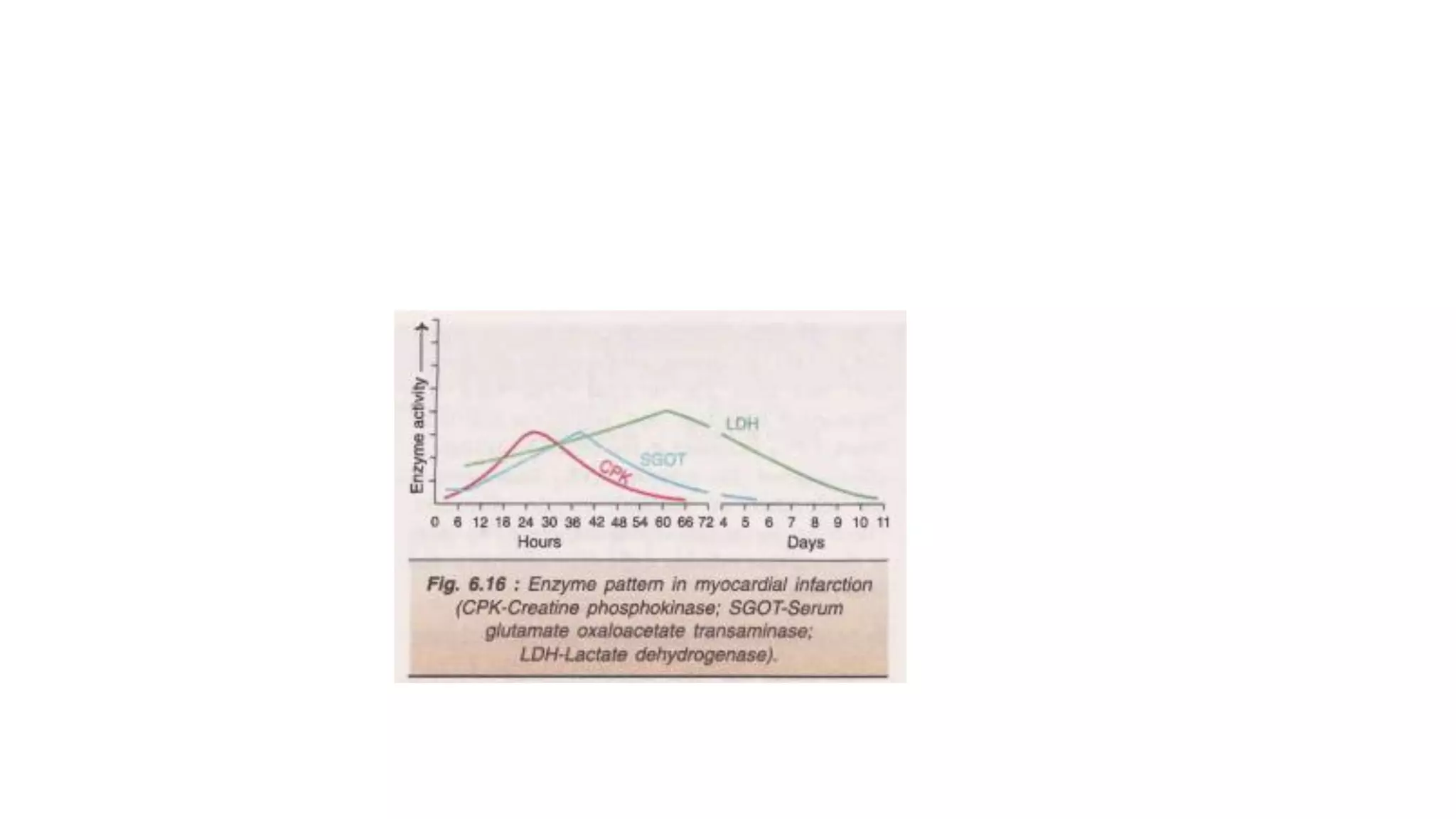
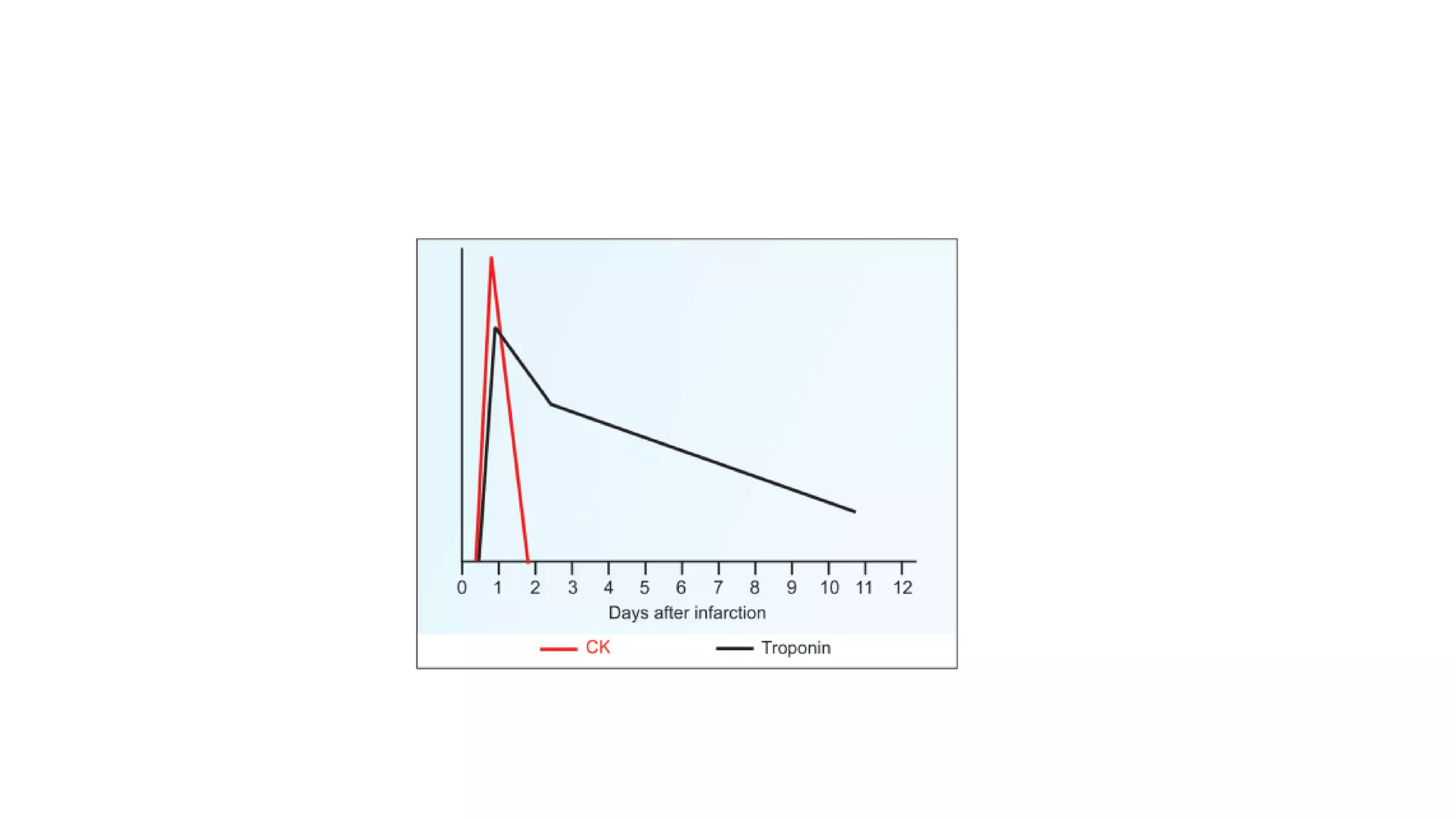
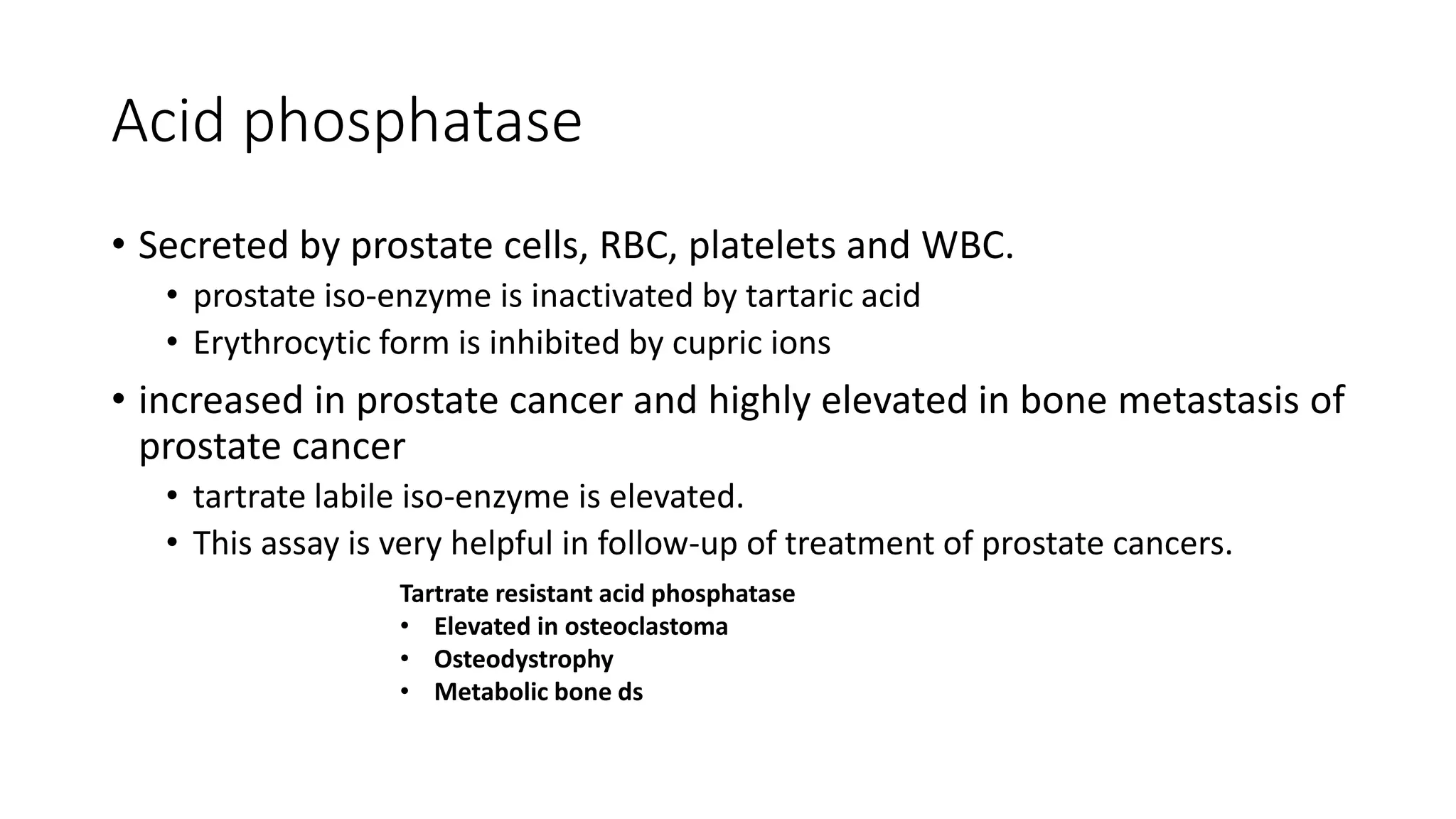
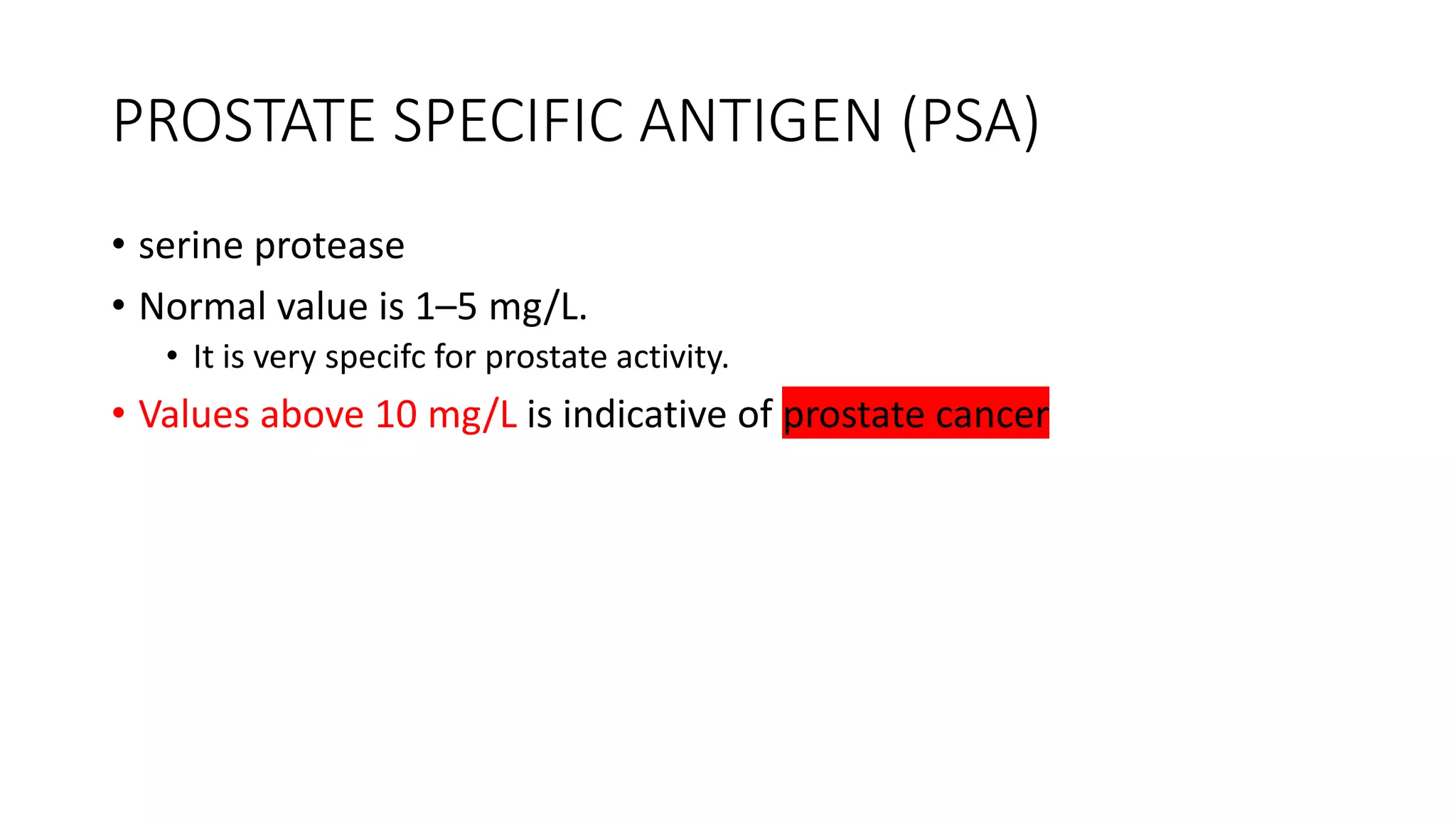
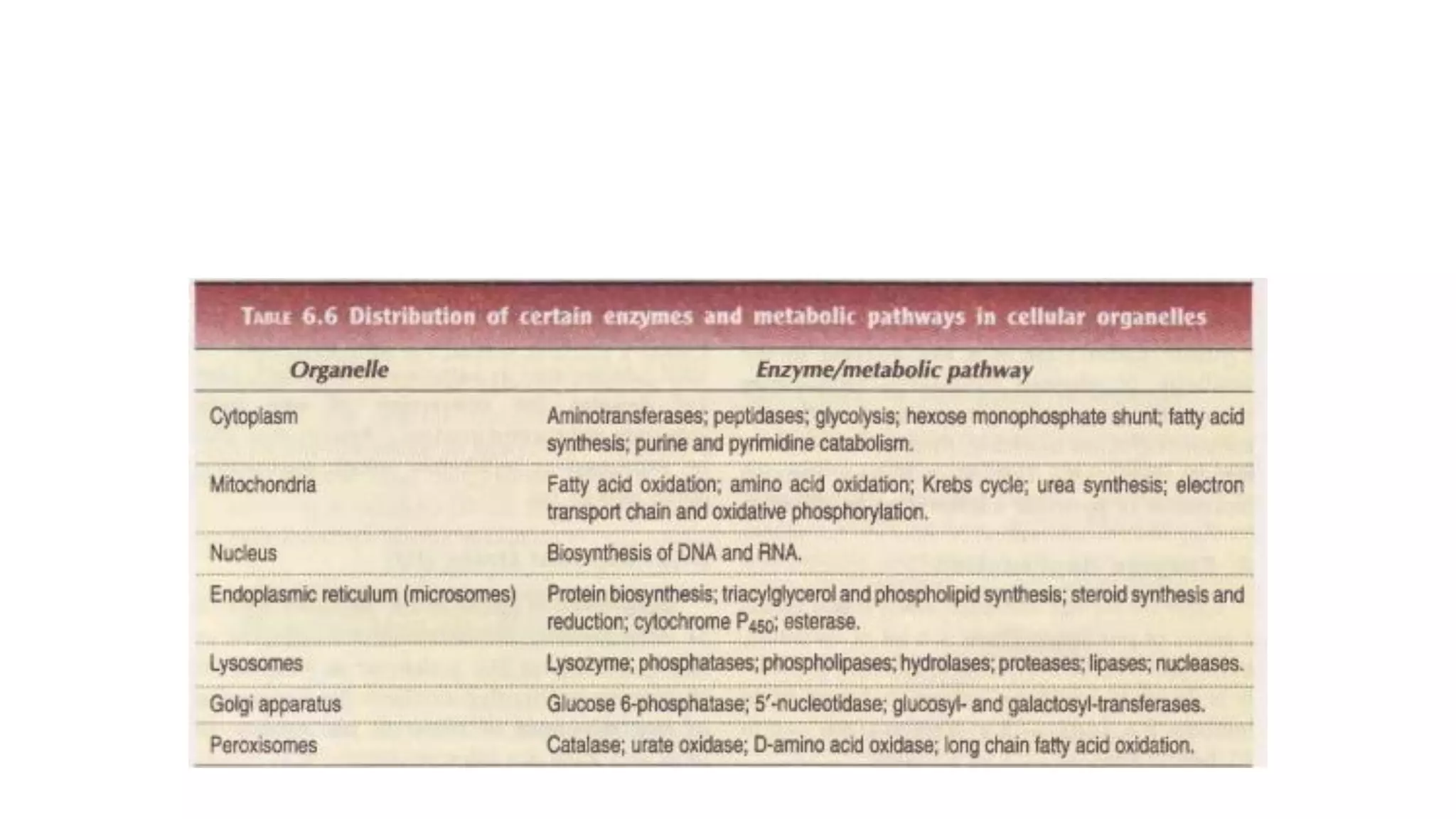
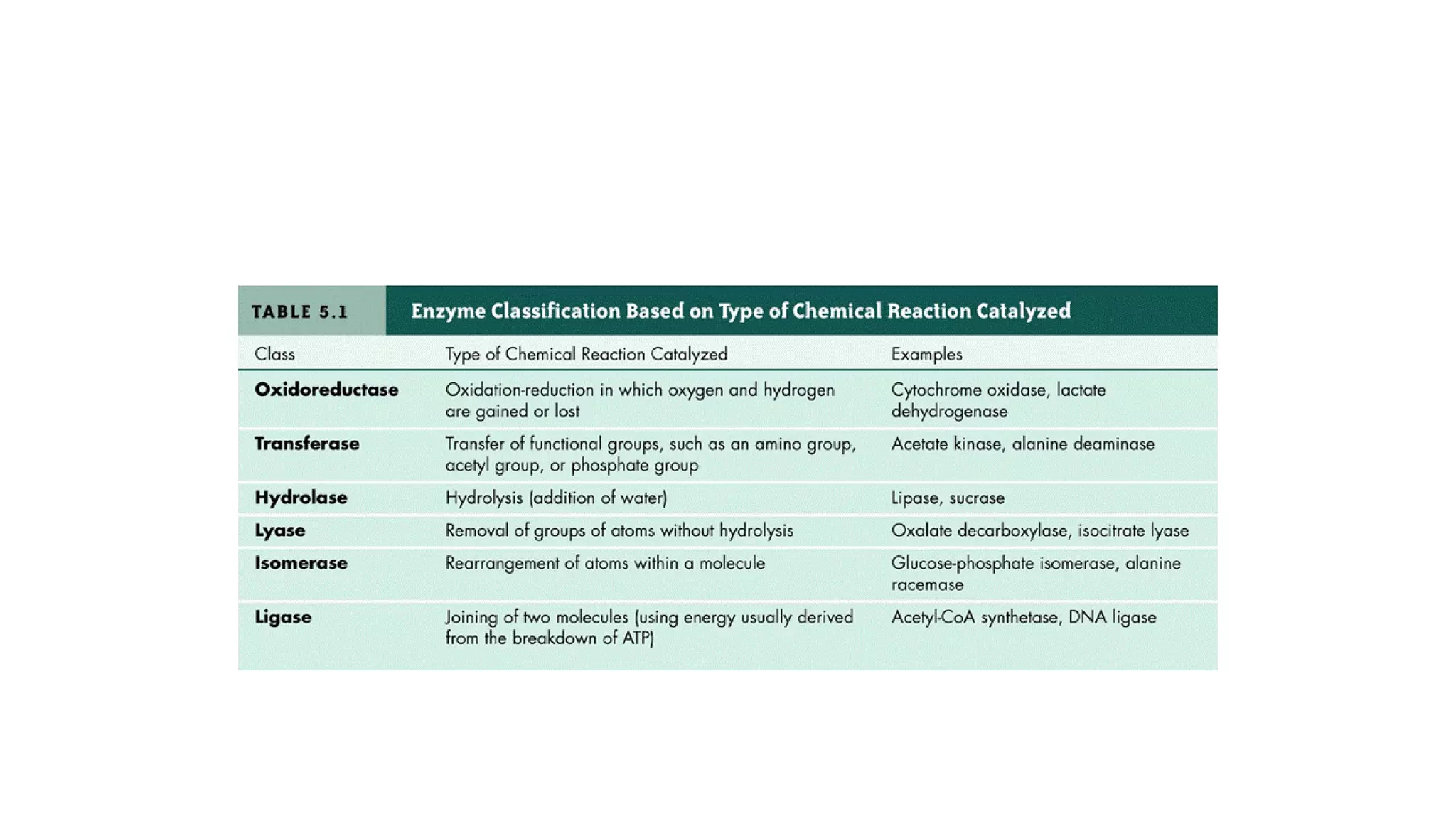
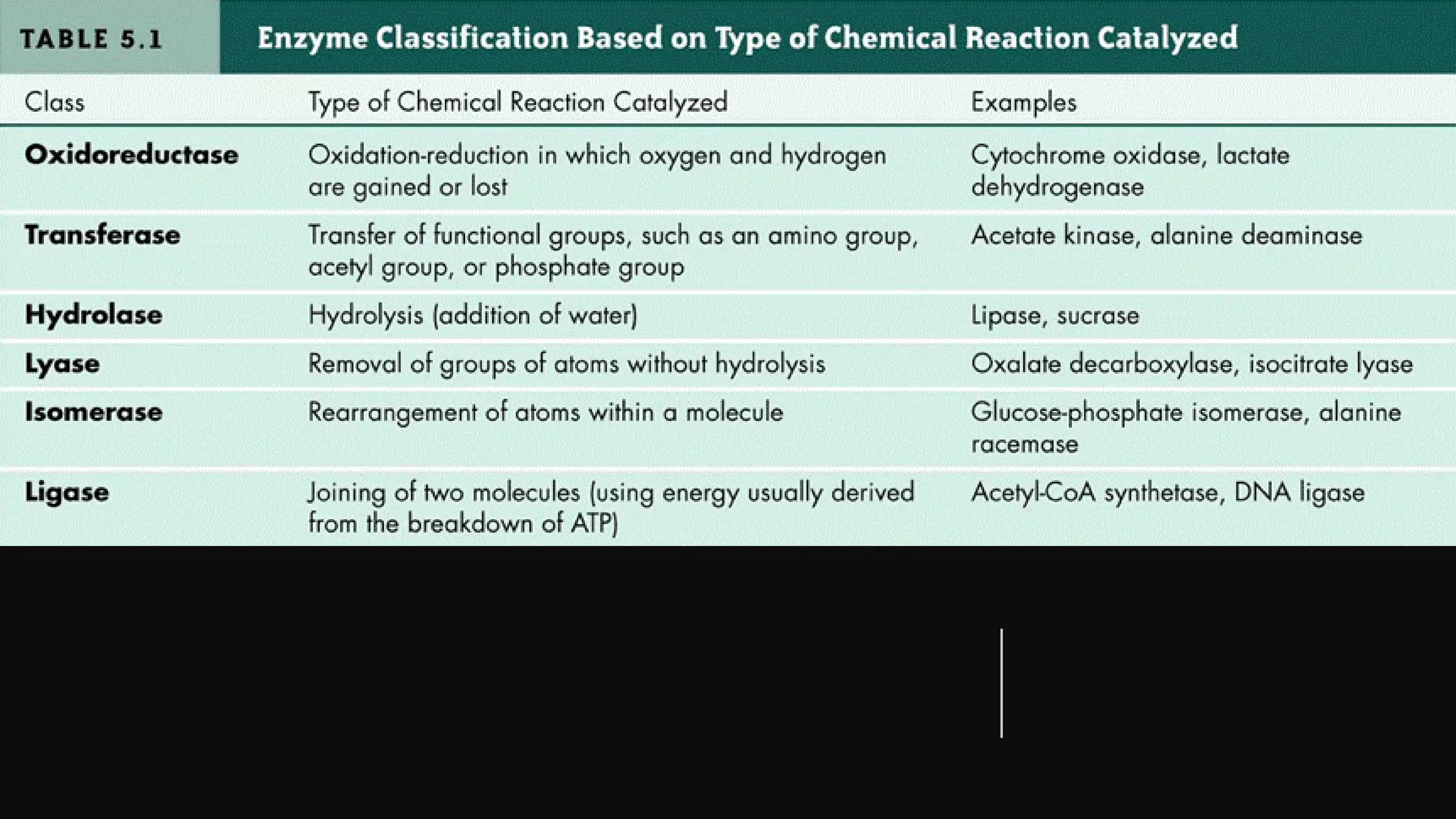
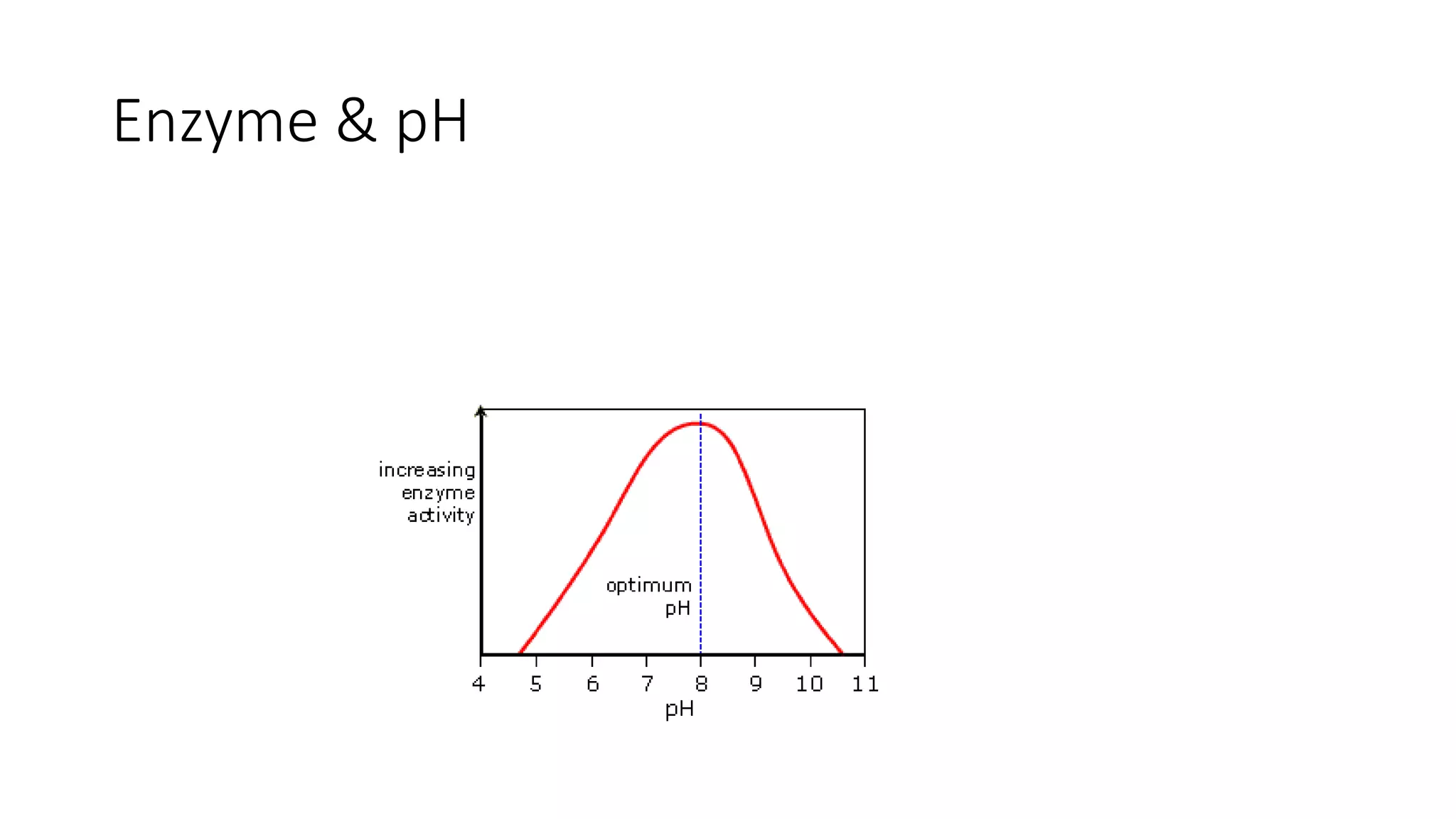
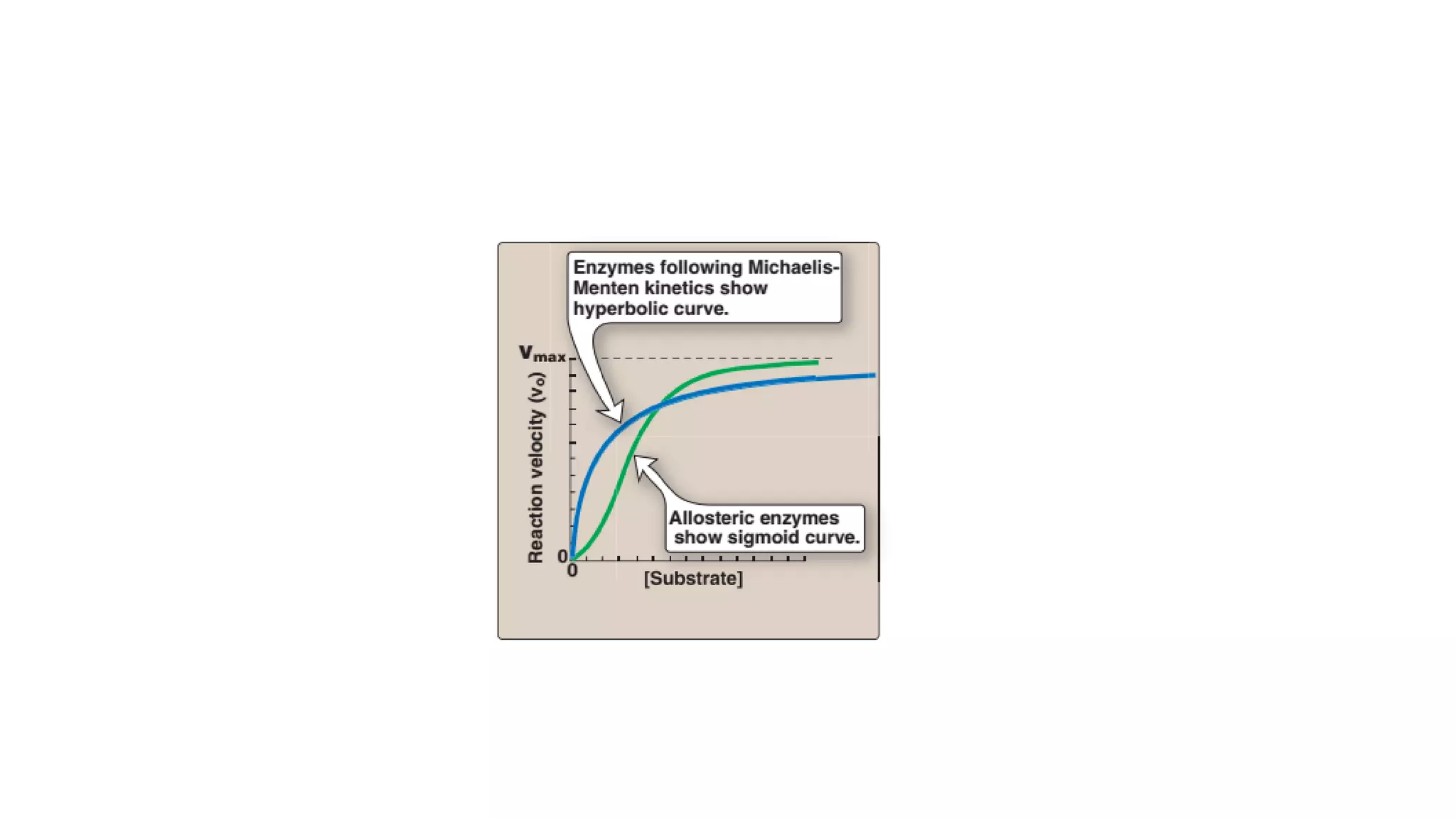
Enzymes are usually proteins that act as catalysts and speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed. They have optimal temperatures and pH levels for activity. The Michaelis-Menten equation describes how reaction velocity varies with substrate concentration. Competitive inhibitors bind the enzyme's active site, increasing Km; noncompetitive inhibitors bind elsewhere, decreasing Vmax. Enzymes are important clinically as markers of tissue damage - creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase indicate heart attacks, while alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase and alkaline phosphatase detect liver disease. Troponin is a very specific marker for myocardial infarction.

























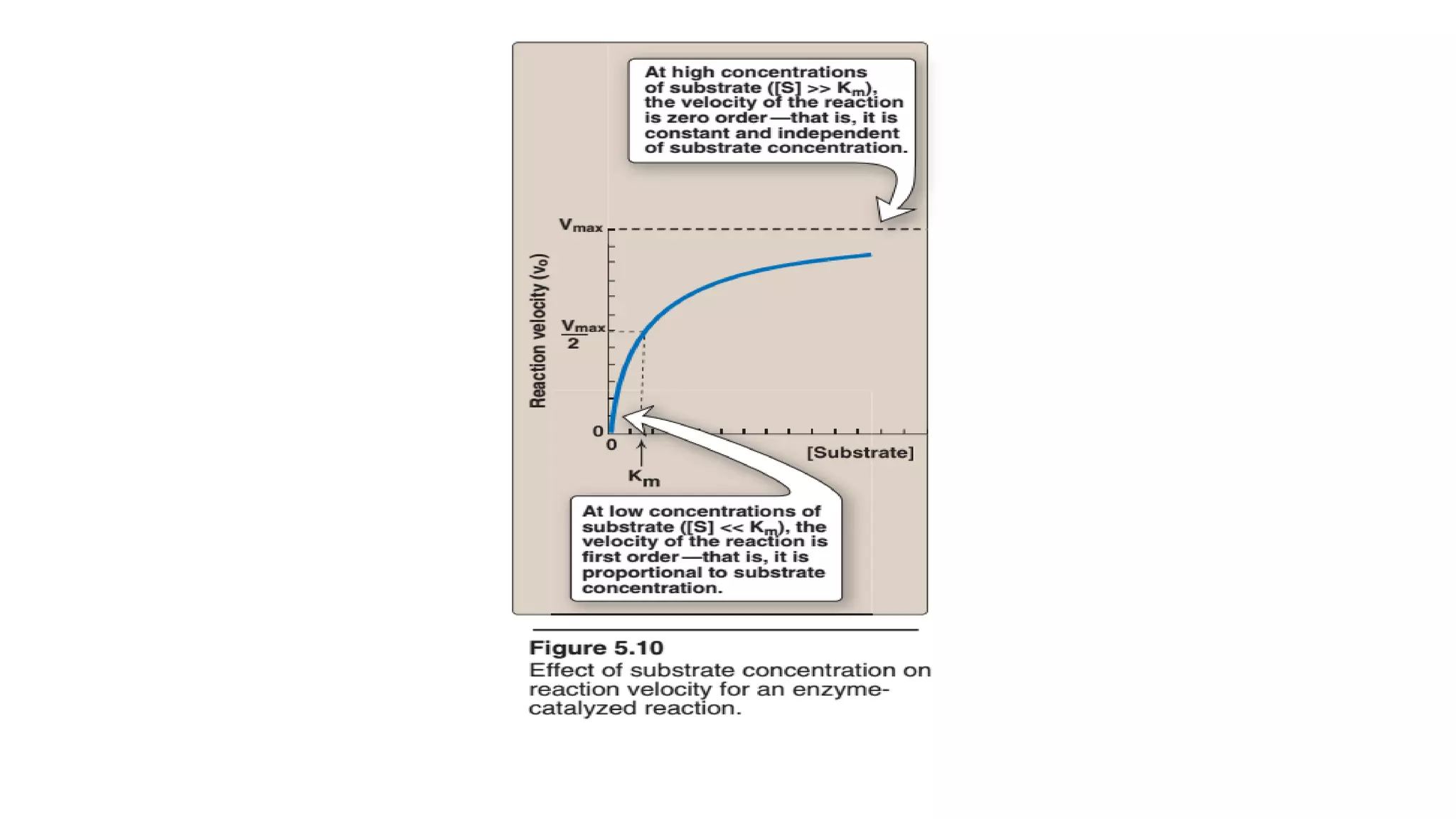
![Michaelis menten equation
• Reaction velocity varies with substrate
concentration
• V0initial velocity
• Vmax maximum velocity
• Km michaelis menten constant
• [S] substrate concentration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymology-180416091859/75/Enzymology-BIOCHEMISTRY-REVISION-NOTES-32-2048.jpg)


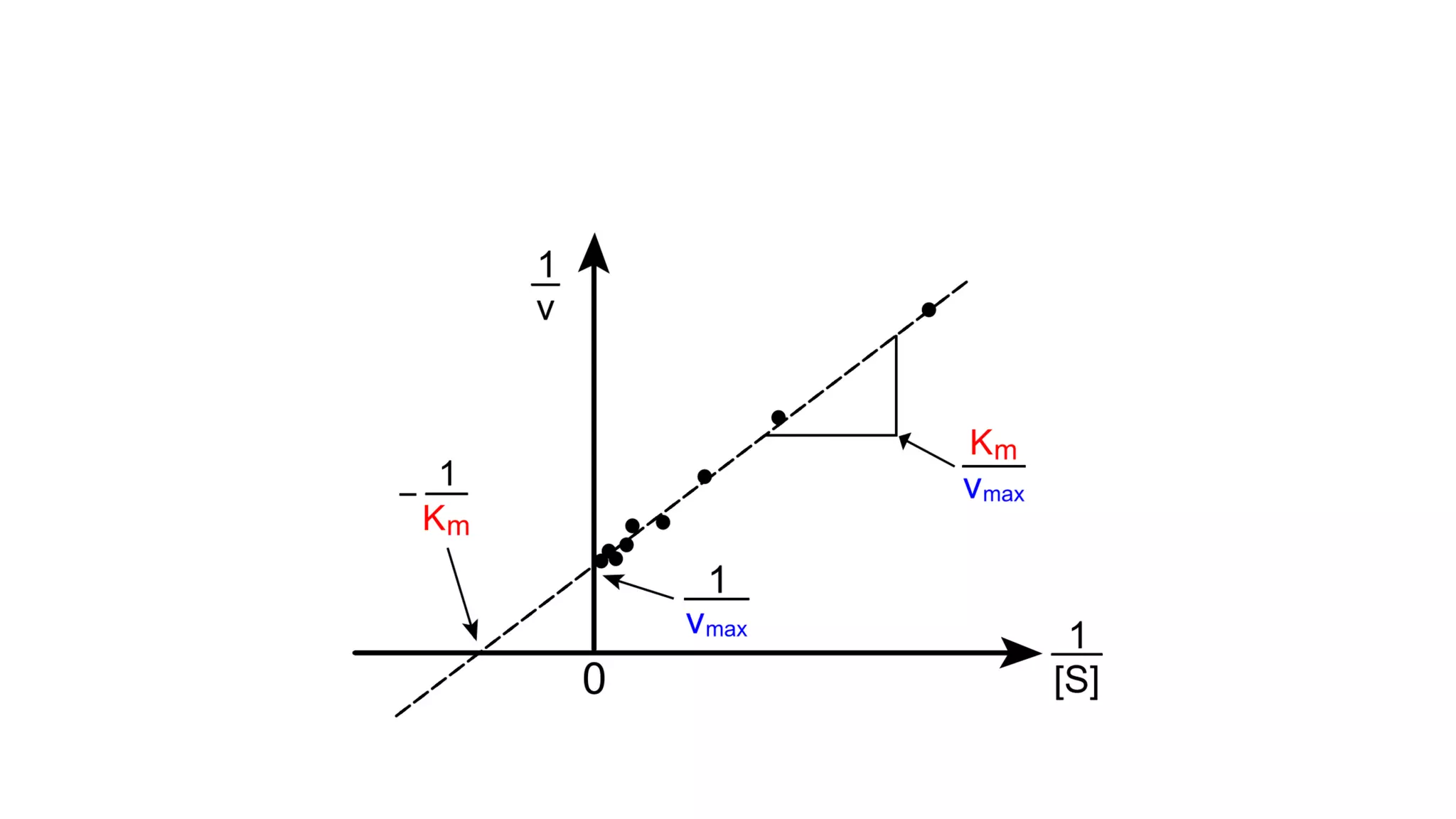
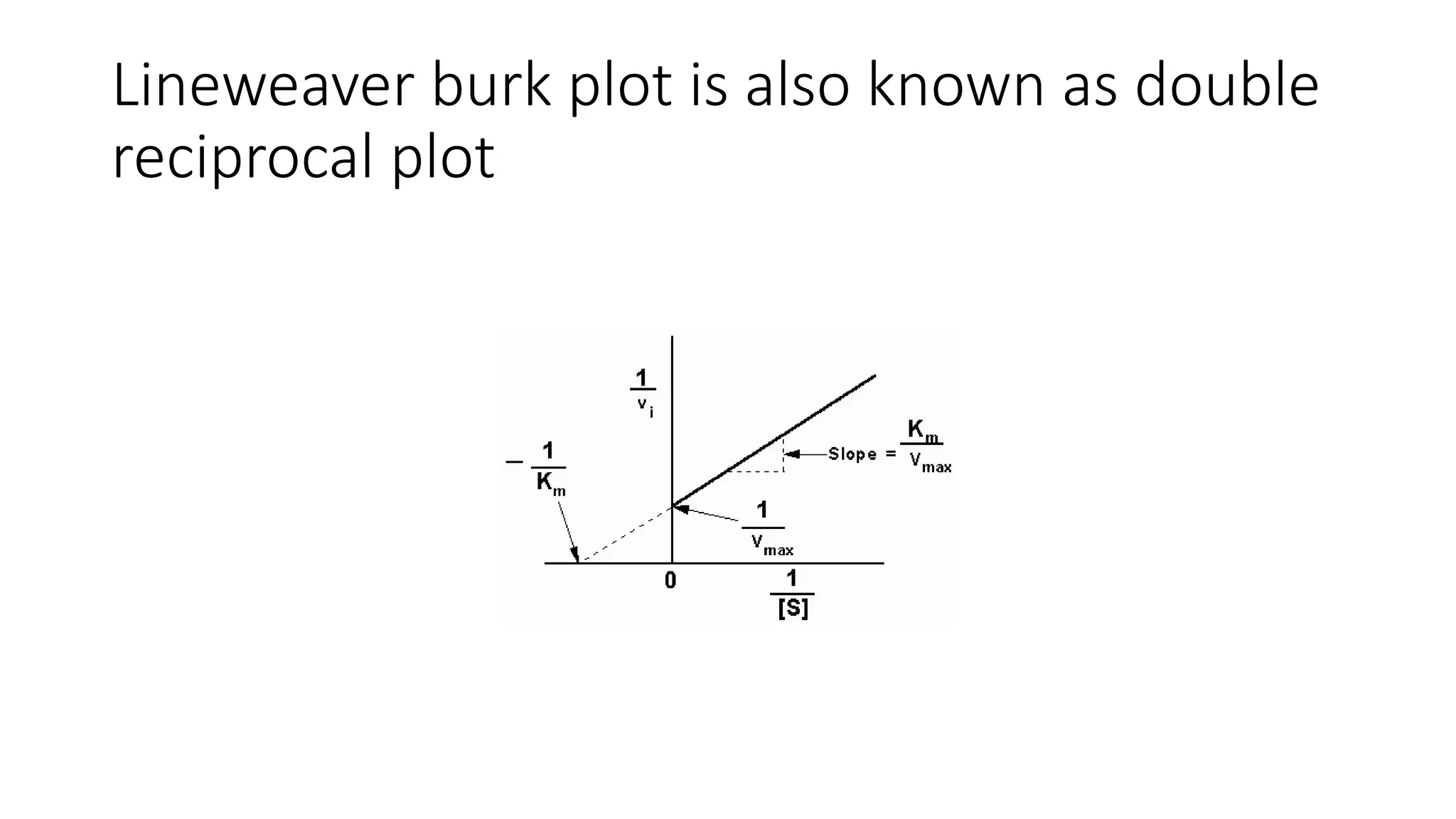






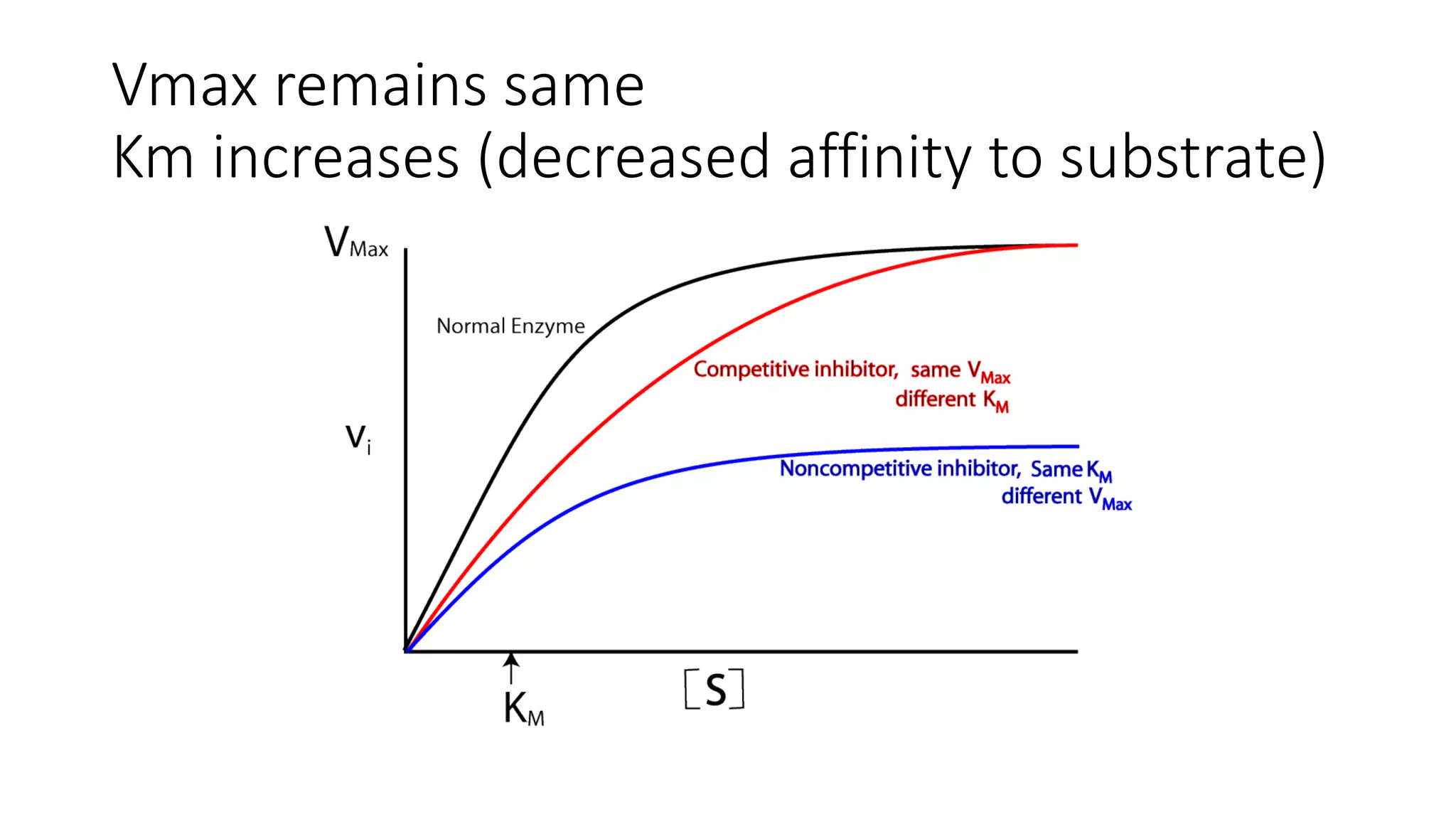


![• Effect on Vmax:
• The effect of a competitive inhibitor is reversed by increasing [S]. At a
sufficiently high substrate concentration, the reaction velocity reaches the
Vmax observed in the absence of inhibitor .
• Effect on Km:
• A competitive inhibitor increases the apparent Km for a given substrate. This
means that, in the presence of a competitive inhibitor, more substrate is
needed to achieve 1⁄2Vmax.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymology-180416091859/75/Enzymology-BIOCHEMISTRY-REVISION-NOTES-47-2048.jpg)