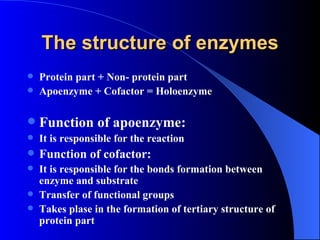
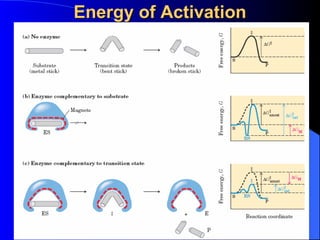
1. Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions in living cells.
2. They are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze such as oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases.
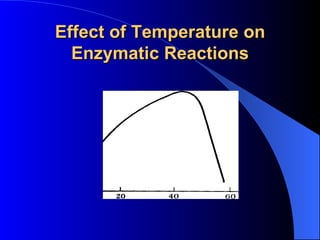
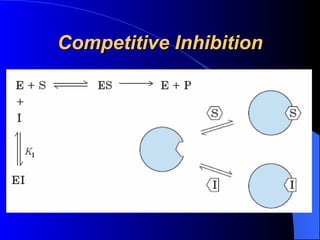
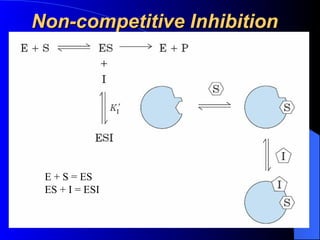
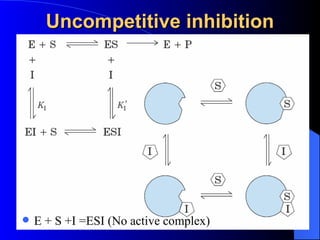
3. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like pH, temperature, and inhibitors. Competitive and non-competitive inhibitors bind at the active site or other regions respectively.