1. Primary structure of proteins refers to the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain connected by peptide bonds. Peptide bonds are covalent and rigid, adopting a planar trans configuration.
2. Glutathione is a tripeptide that contains a sulfhydryl group and plays an important role in detoxification reactions in the body by conjugating with toxins and metabolites.
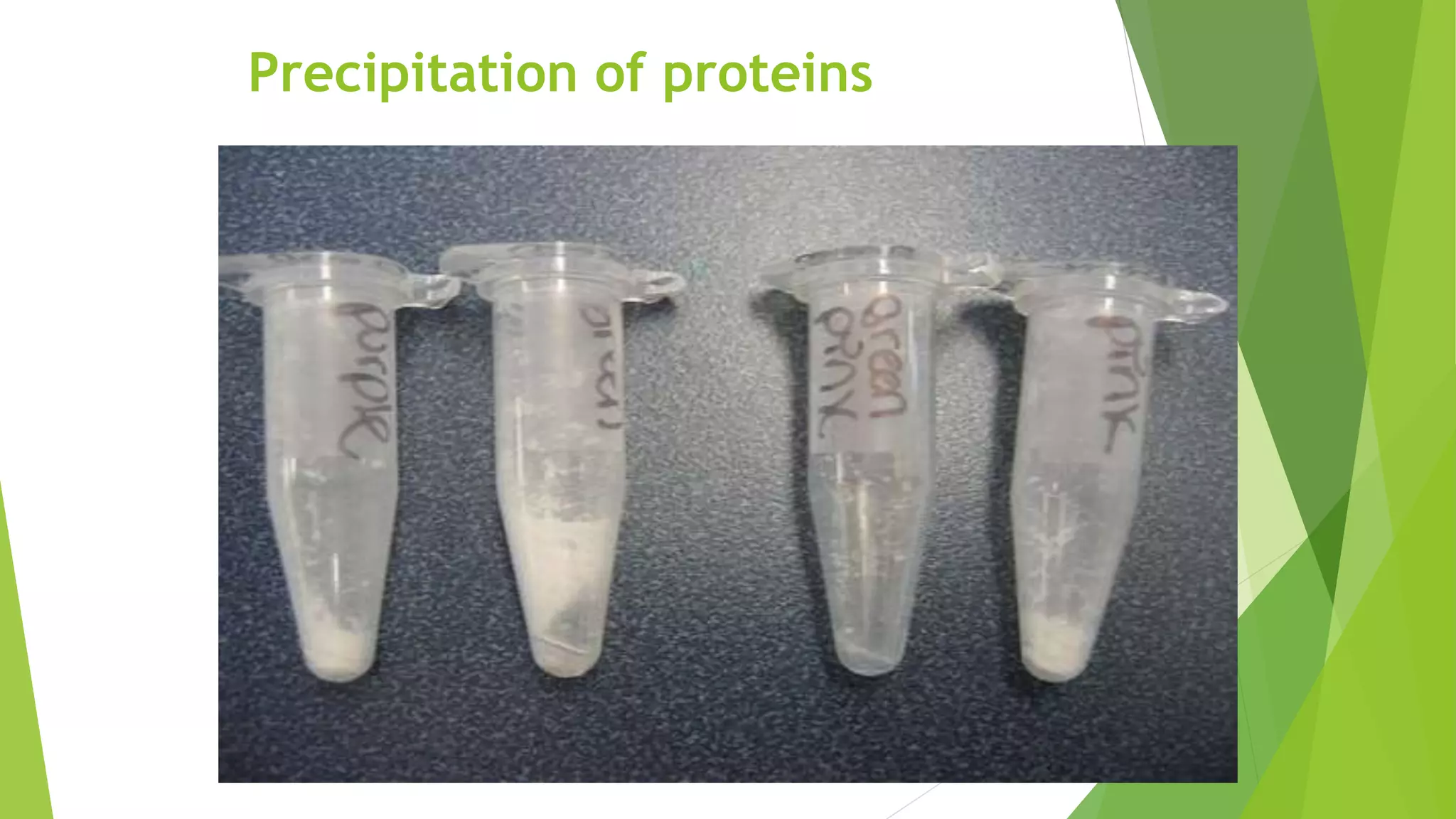
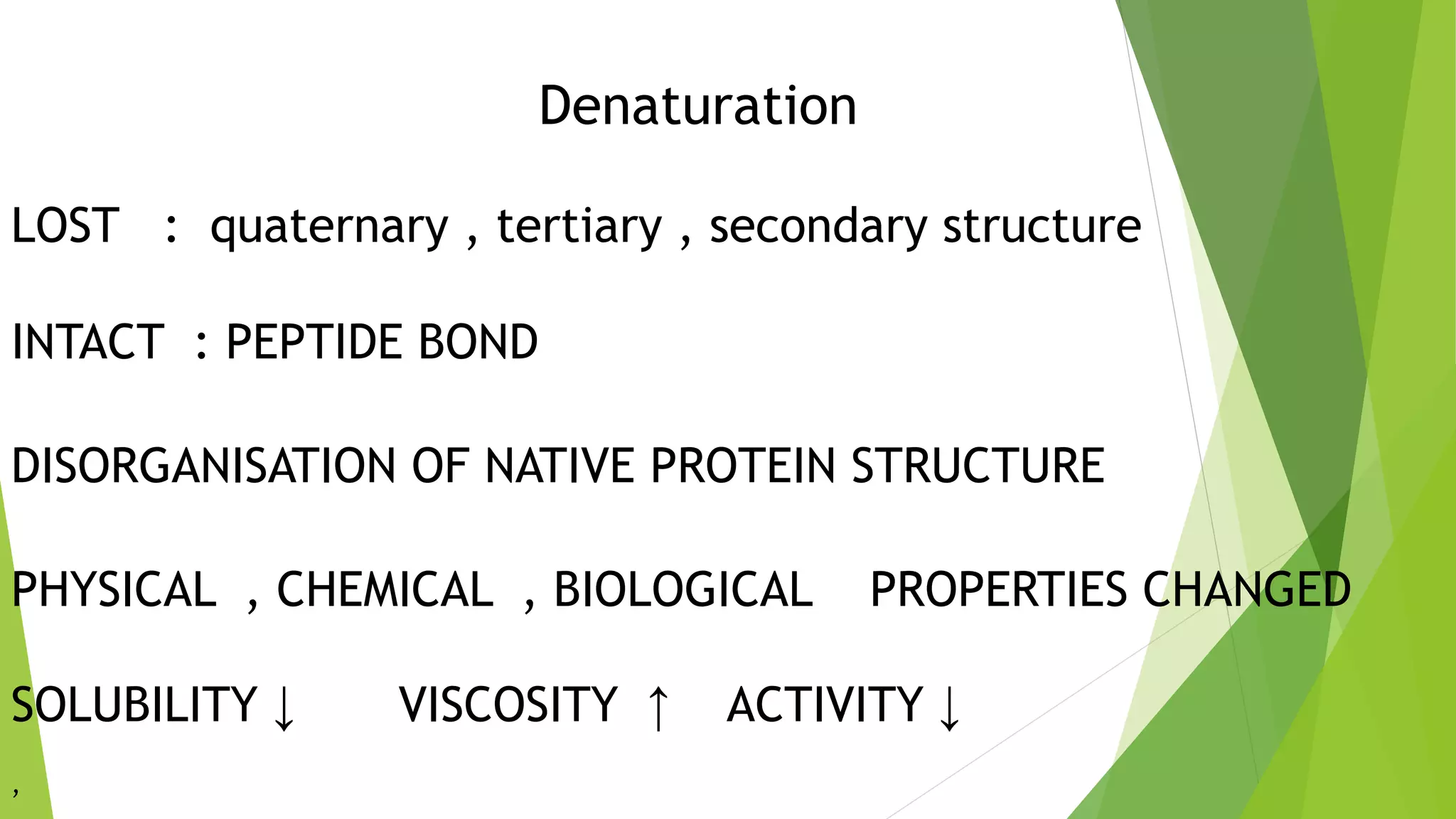
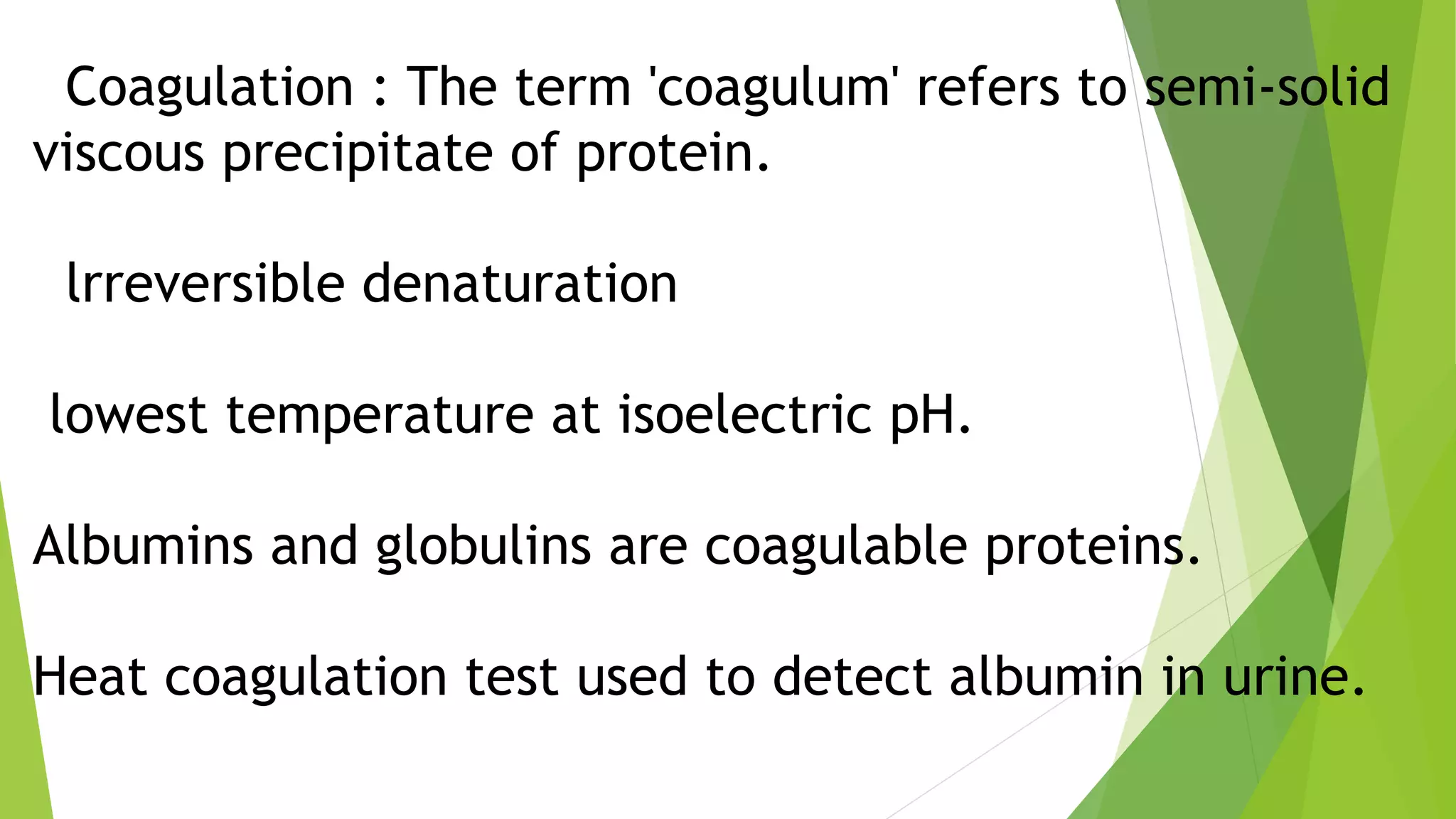
3. Denaturation refers to the loss of tertiary and quaternary structure in a protein resulting in changes to its physical and chemical properties, such as decreased solubility and activity, though the primary structure remains intact. Denaturation can be caused by physical factors like heat or chemicals and is usually irreversible