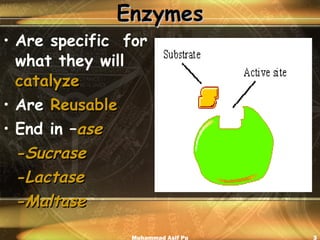
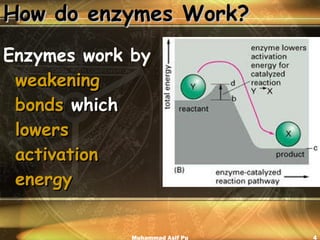
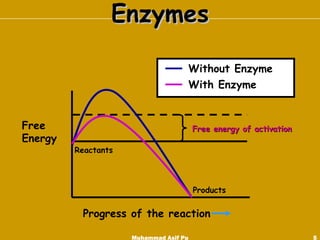
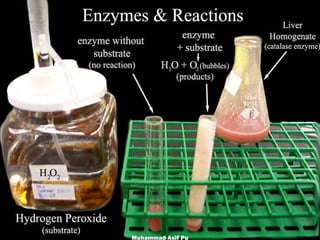
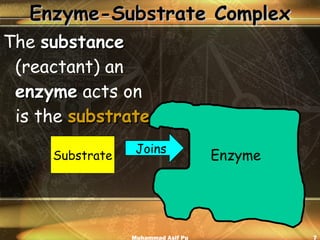
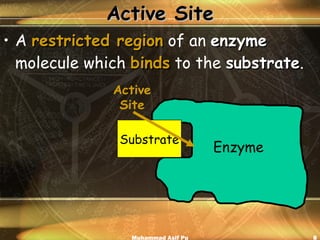
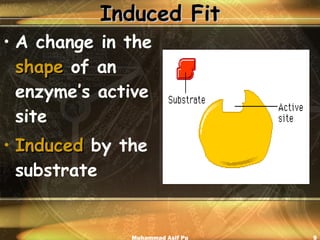
Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are highly specific and only catalyze particular reactions. Enzymes work by weakening the bonds of reactants, reducing the amount of energy needed for the reaction to occur. The substance an enzyme acts on is called the substrate, which binds to the enzyme's active site to induce a shape change that facilitates the reaction. Environmental conditions like temperature and pH can impact enzyme activity, as can cofactors, coenzymes, and enzyme inhibitors.