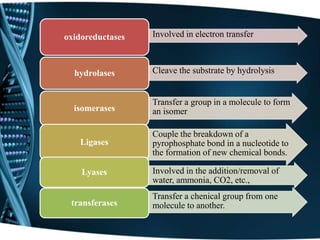
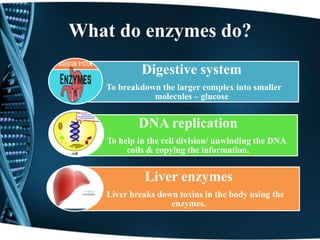
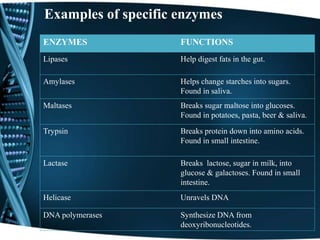
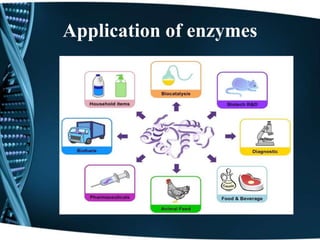
This document discusses enzymes, including their classification, functions, properties, and applications. Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts and are produced by living cells. They speed up biochemical reactions by lowering activation energy. There are six main classes of enzymes including oxidoreductases, hydrolases, isomerases, ligases, lyases, and transferases. Enzymes work via the lock and key or induced fit models and have high specificity. They are affected by factors like temperature, pH, and inhibitors. Examples of enzymes and their functions in digestion and other processes are provided. Common applications of enzymes include in food production, cleaning products, and medicine.