Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up metabolic reactions by lowering activation energy and remain unchanged after facilitating reactions. They have specific active sites where substrates bind, leading to the formation of products, influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors. The Michaelis-Menten model describes their kinetics, including maximum reaction rates (Vmax) and how enzyme affinity for substrates (Km) is affected by competitive and non-competitive inhibitors.


![What are Enzymes
Biological Catalyst
Specific a certain substrate by its R group
Globular protein – water soluble
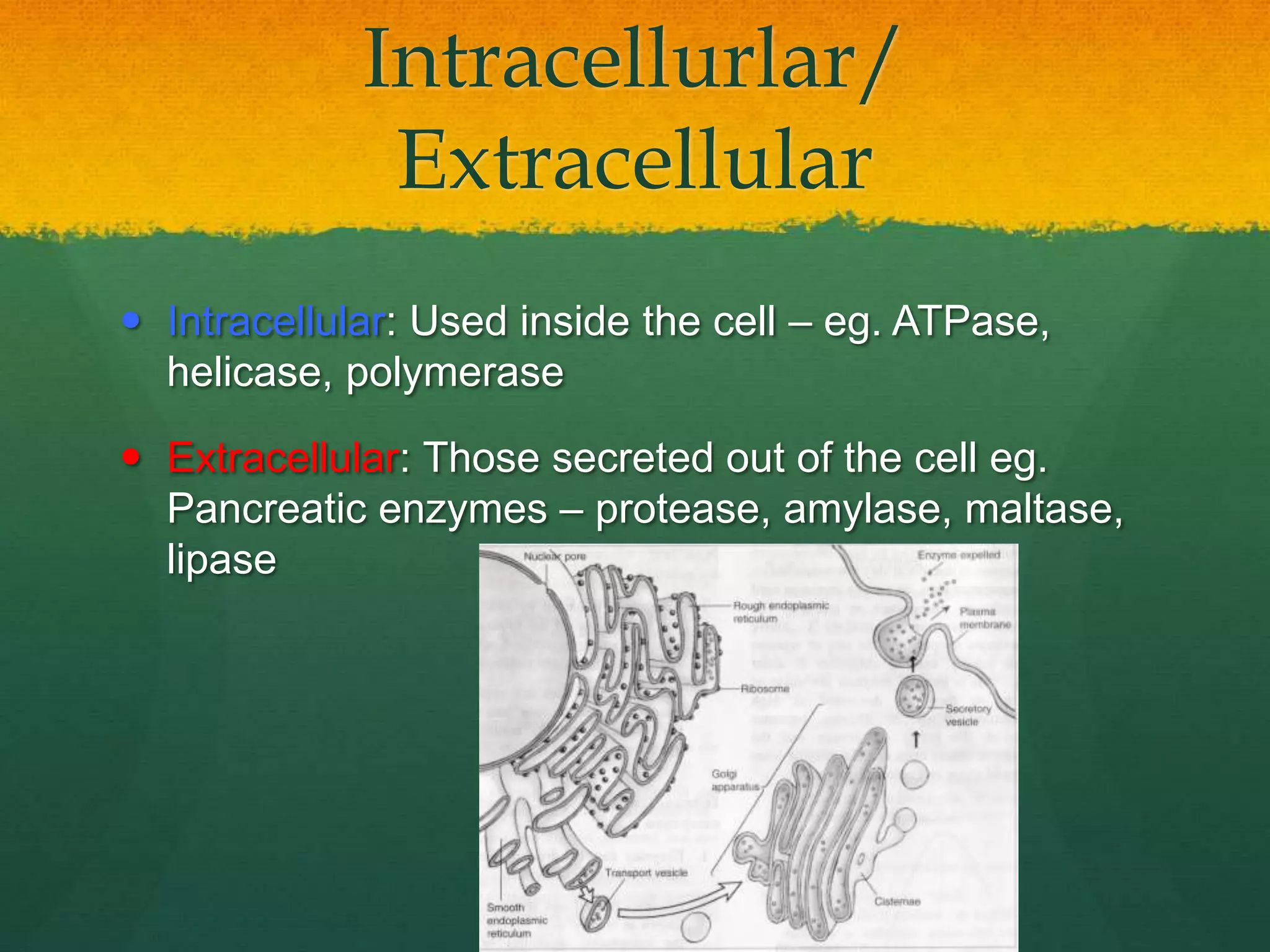
Remain unchanged after the reactions
Enzymes can break and bond!
Nearly all metabolic reaction are enzymes-catalyzed
Enzymes reduce activation energy – increase rate constant
RATE = K[A]*[B}y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1biologyrevisionnotes01-160603054216/75/AS-Level-Biology-3-Enzymes-3-2048.jpg)




























![Competitive
Reduces Enzymes affinity – as it prevents the
substrate from joining with the enzymes
Km increases (don’t forget Km is simply acceleration
expressed in the terms of distance[sub conc.] hence
it is inversely proportional to the enzyme affinity)
Vmax doesn’t change because adding substrate can
still over come the effect
If we add high enough Substrate concentration –
they can overtake inhibitor – and Vmax can still be
reached](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1biologyrevisionnotes01-160603054216/75/AS-Level-Biology-3-Enzymes-33-2048.jpg)



