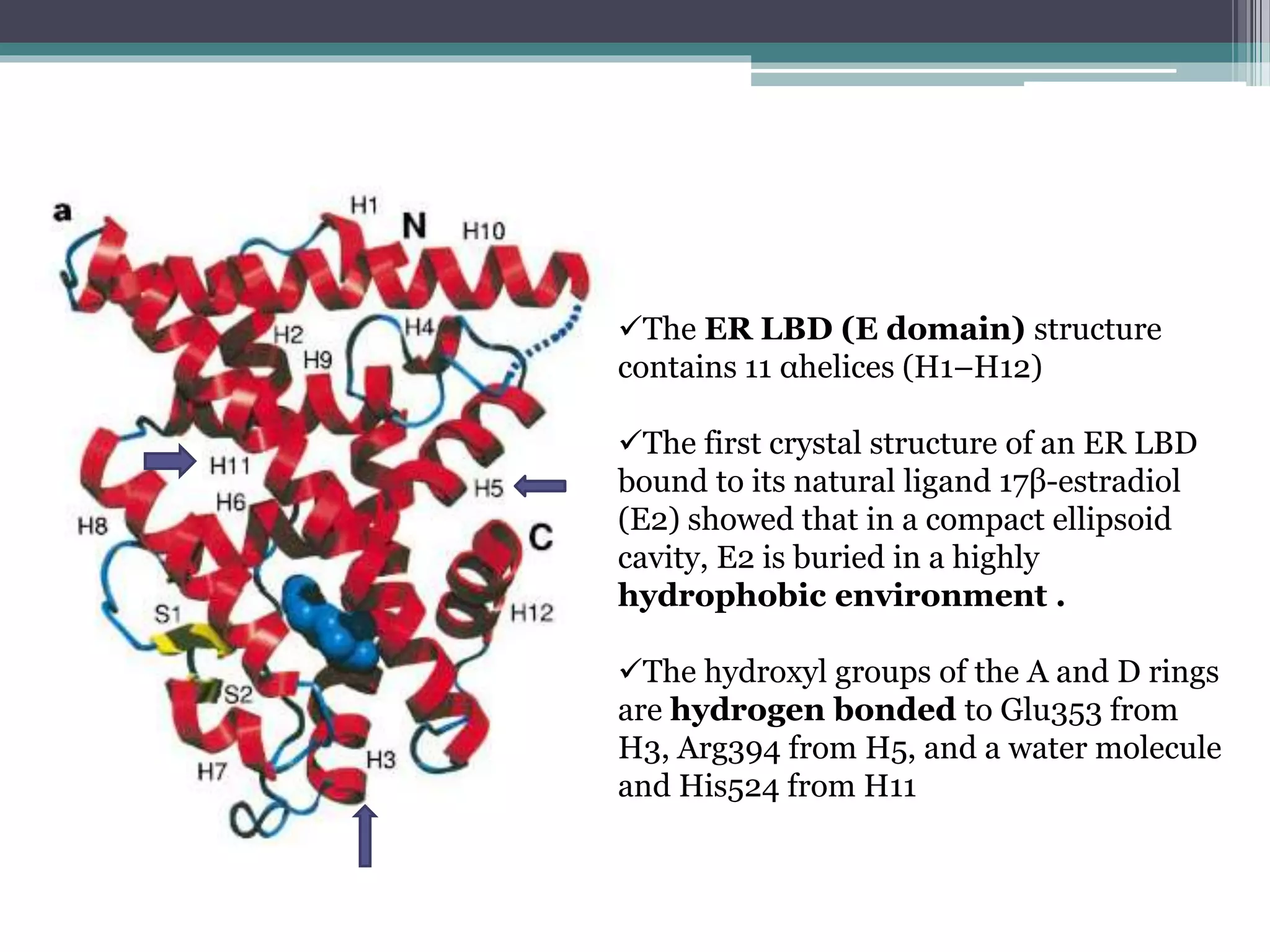
This document discusses ligand-receptor interactions, using estrogen receptor and estrogen as an example. It describes how ligands bind to specific receptors on target cells, inducing a conformational change and cellular response. It then details the domains of estrogen receptors, how estrogen binds and activates the receptors, and the role of the receptor domains in transcription. The discussion includes examples of covalent and non-covalent ligand-receptor interactions.