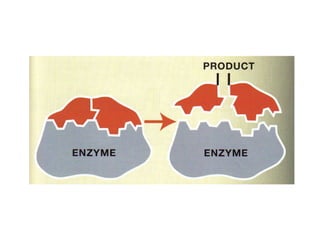
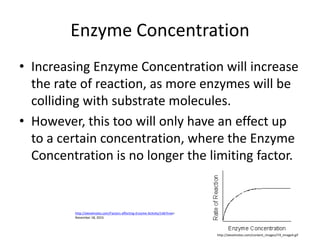
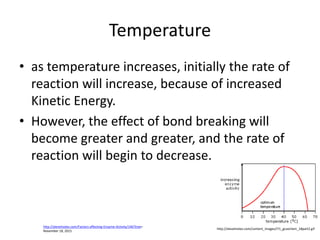
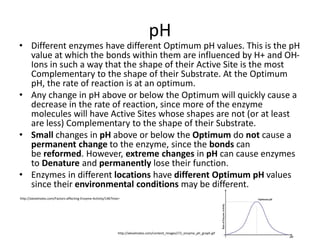
Enzymes are biological molecules that catalyze chemical reactions and increase their rates. They are selective for specific substrates and only catalyze a few reactions. Enzymes work by lowering activation energy and can accelerate reactions by millions of times. They are not consumed in reactions and do not alter equilibrium. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like temperature, pH, inhibitors, and more. The lock and key and induced fit models describe how enzymes and substrates interact specifically in the active site. Cofactors like metal ions and coenzymes are required for some enzyme activity. Enzymes perform critical functions in cell signaling, movement, and metabolism and are targets of drugs and involved in diseases.