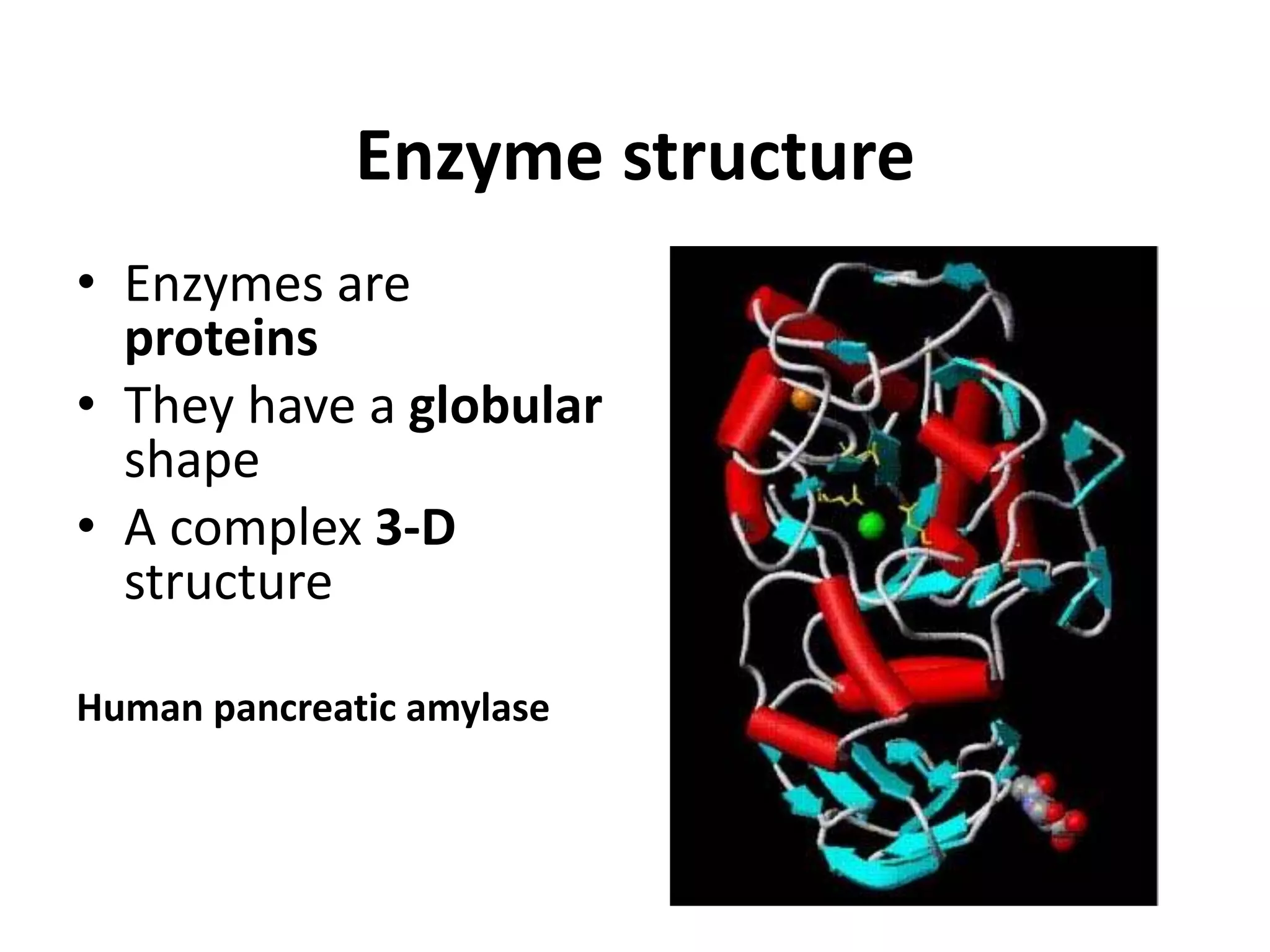
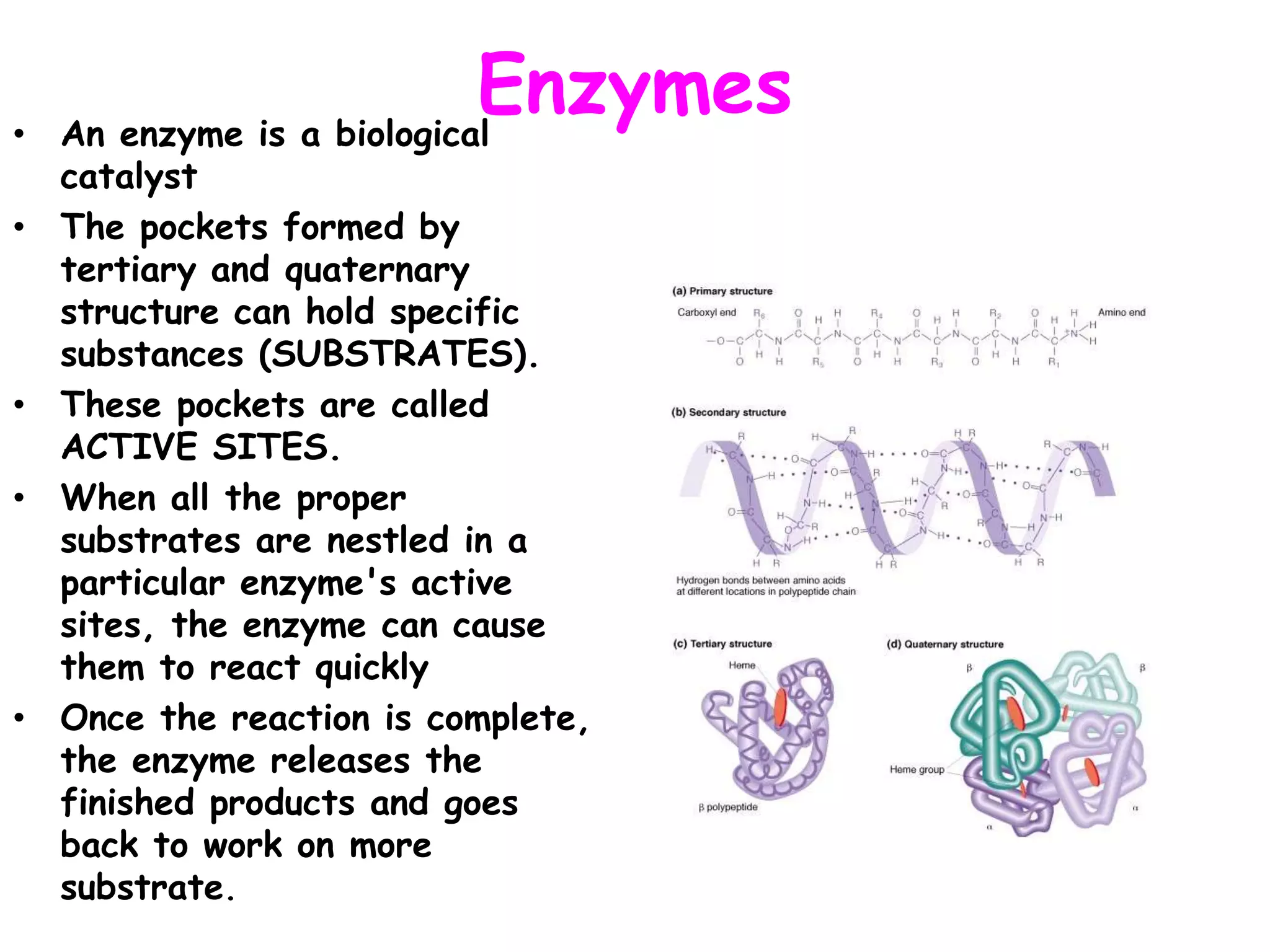
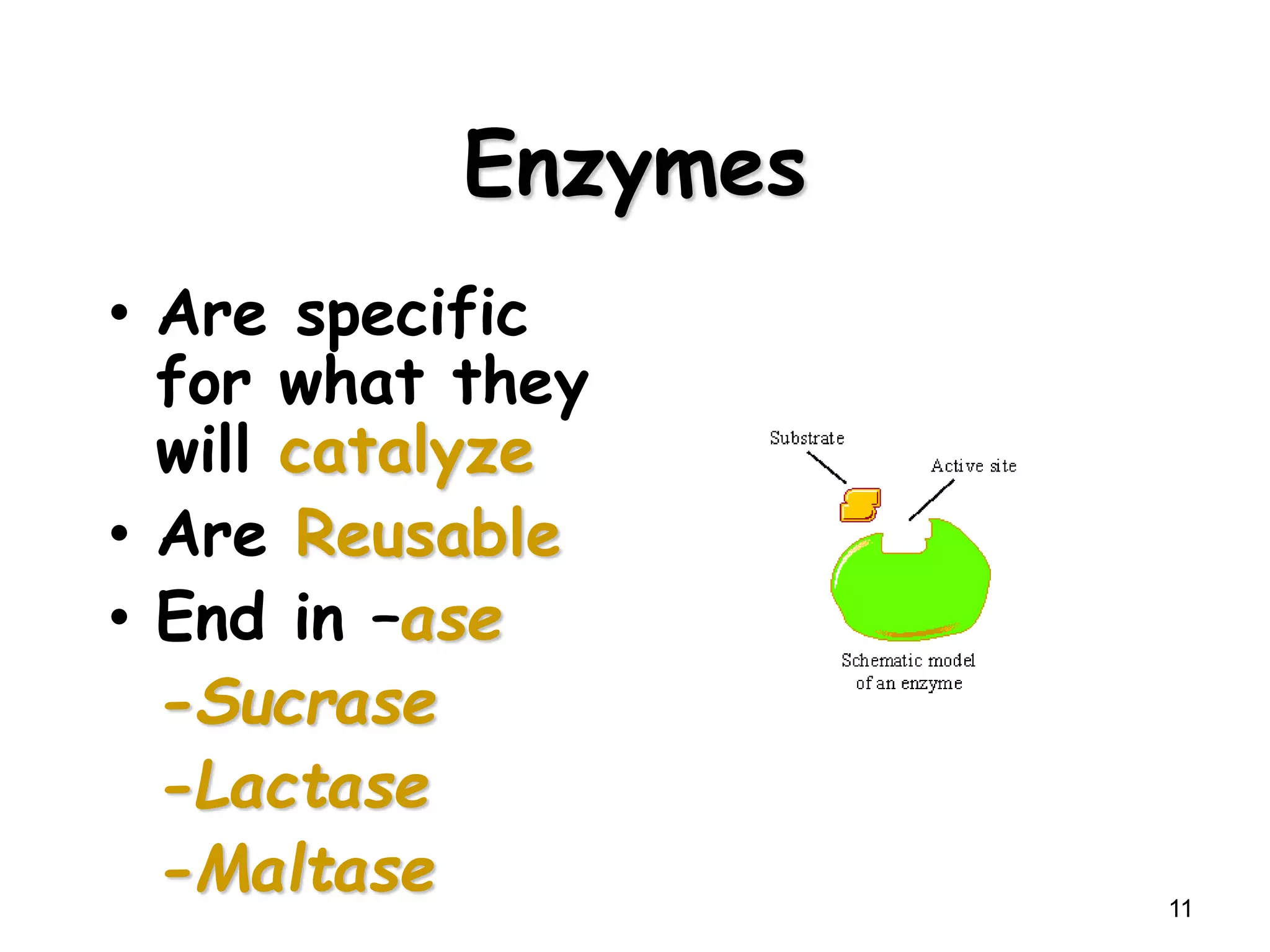
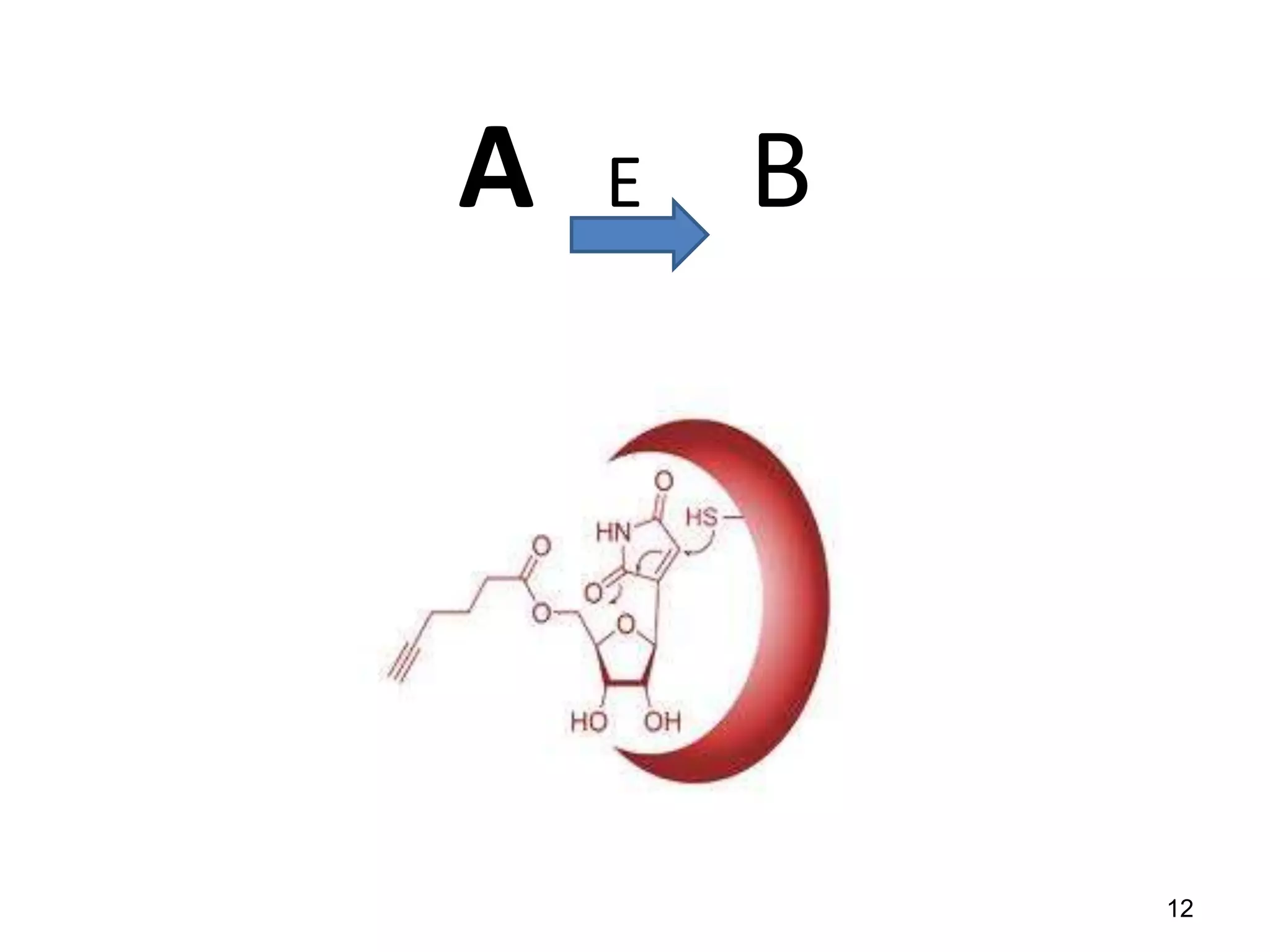
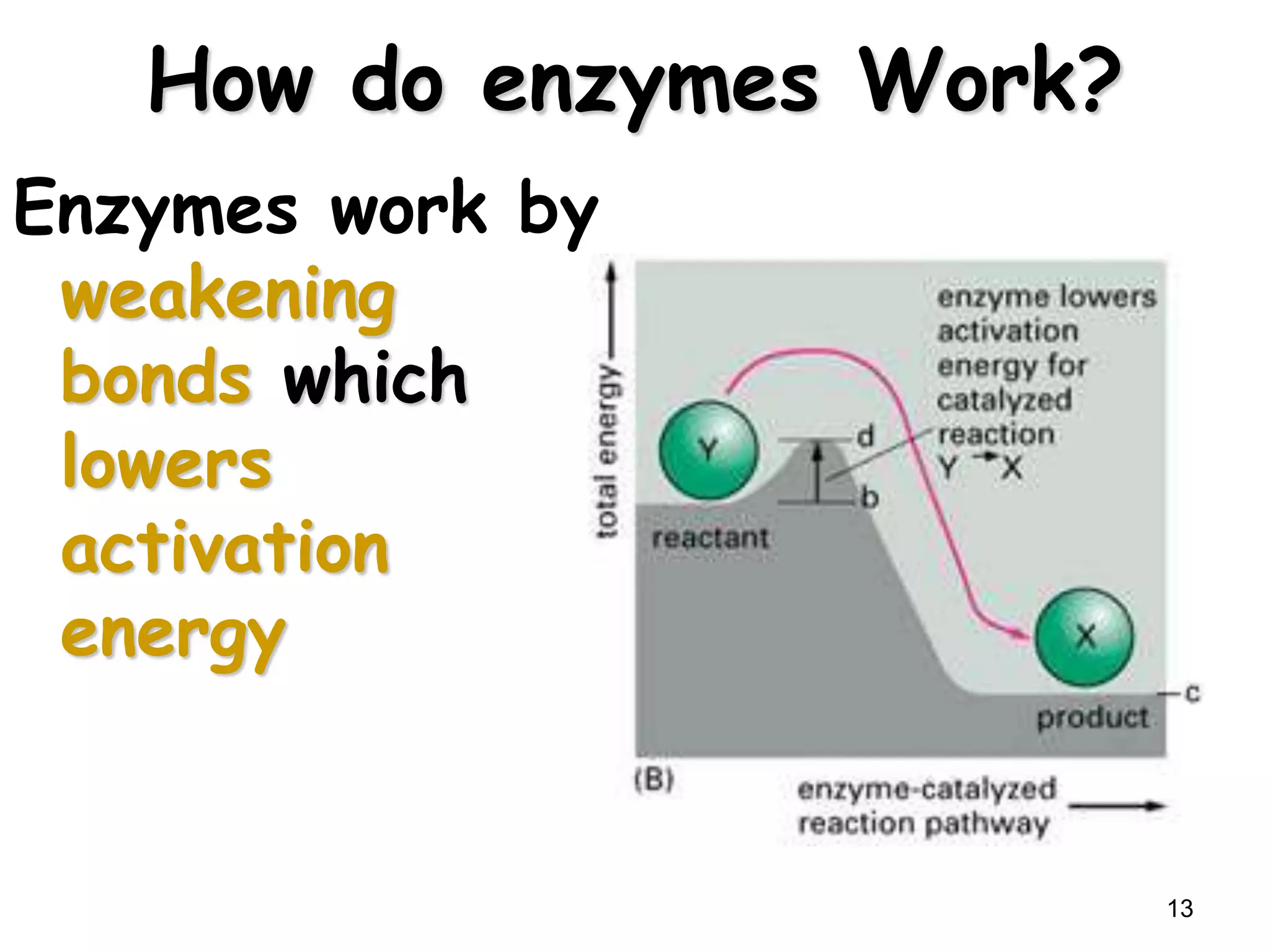
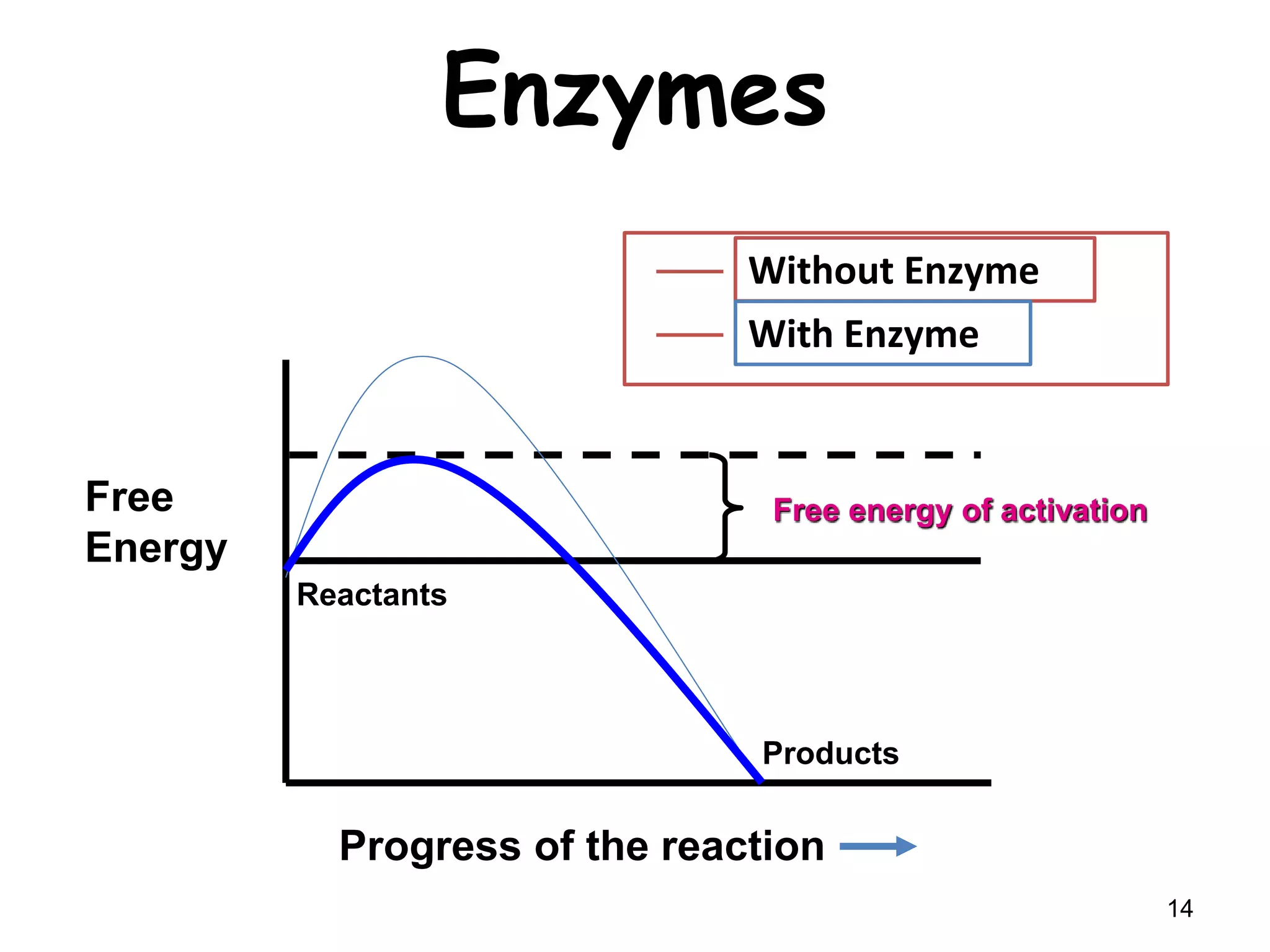
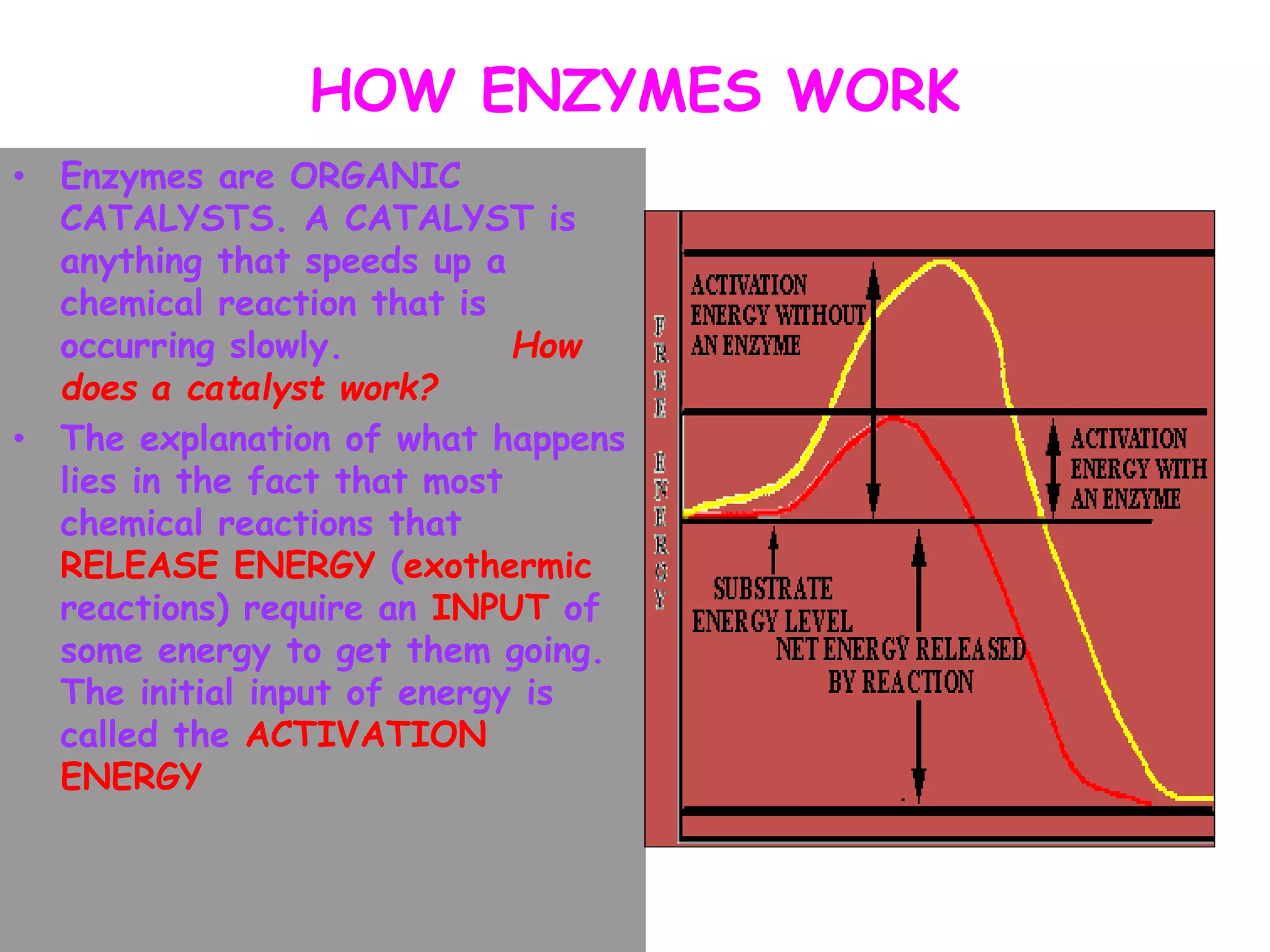
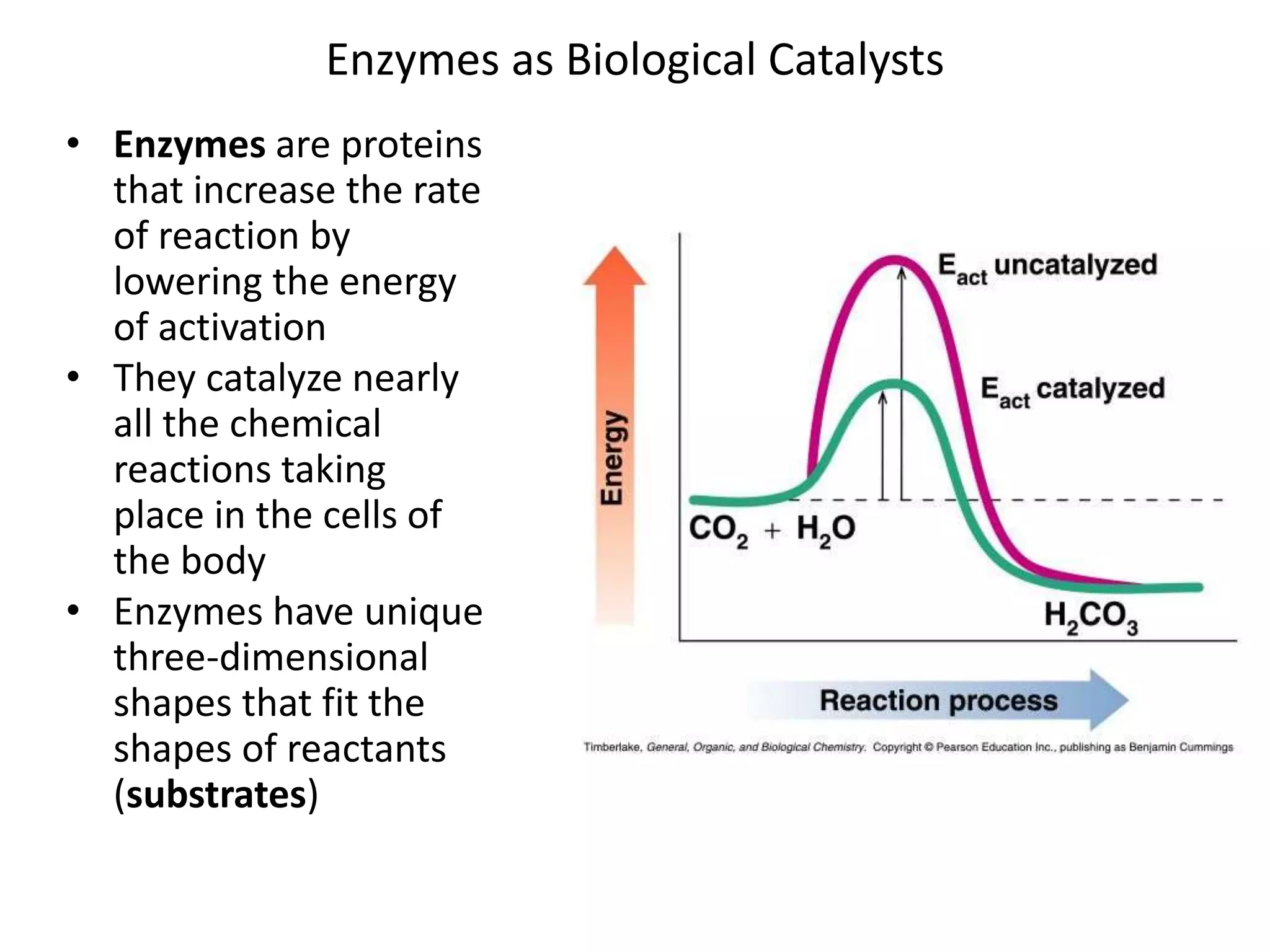
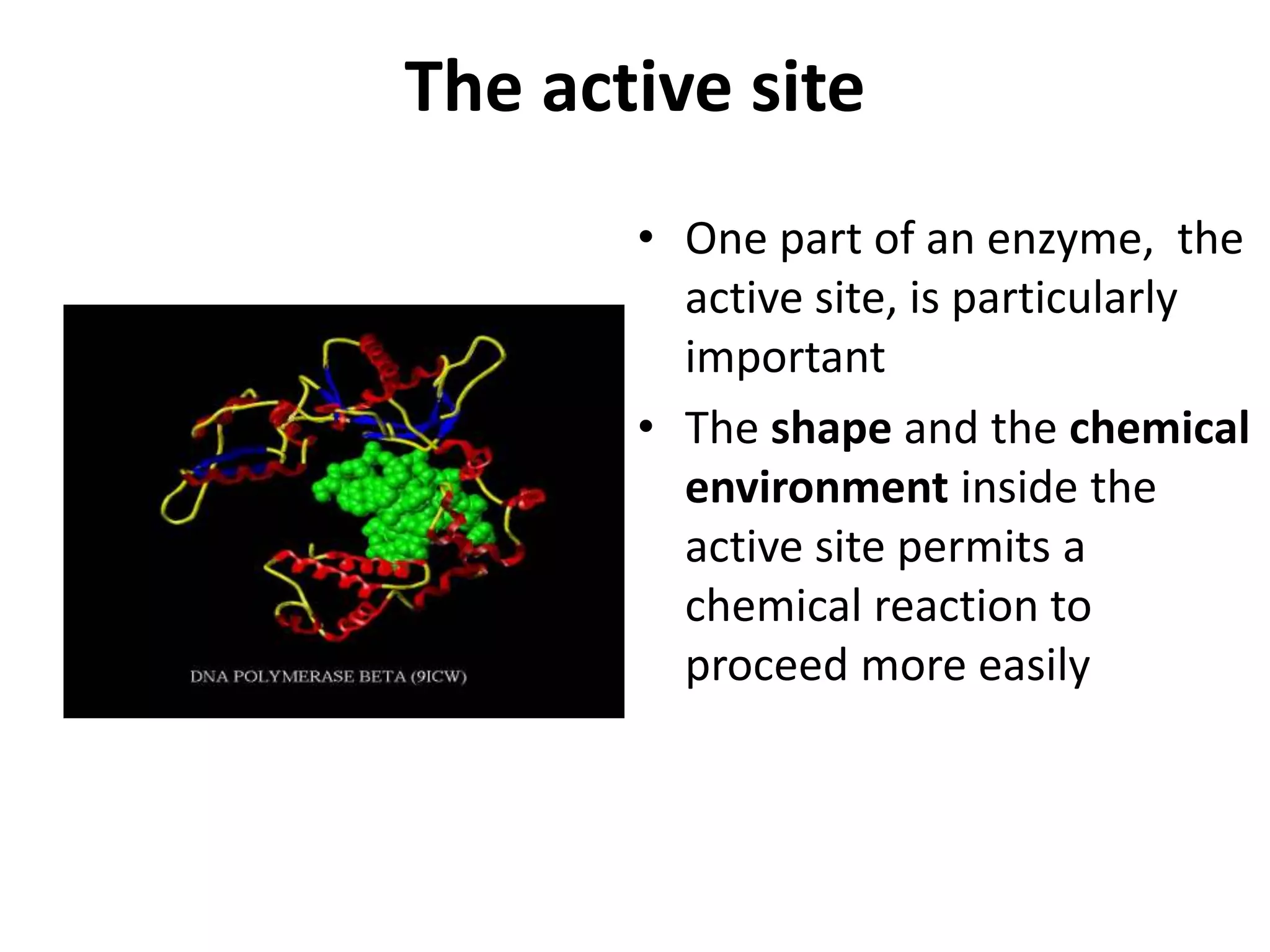
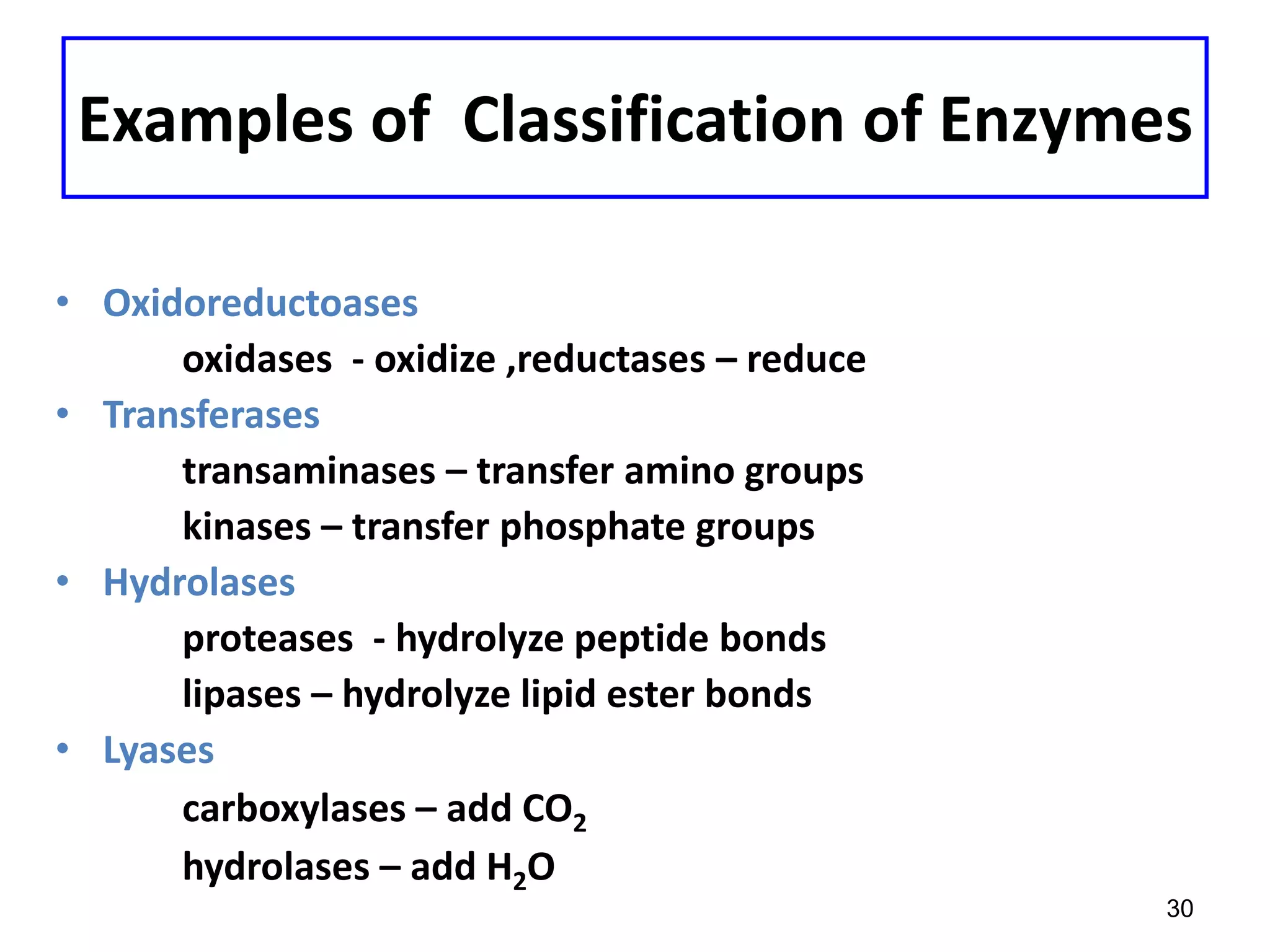
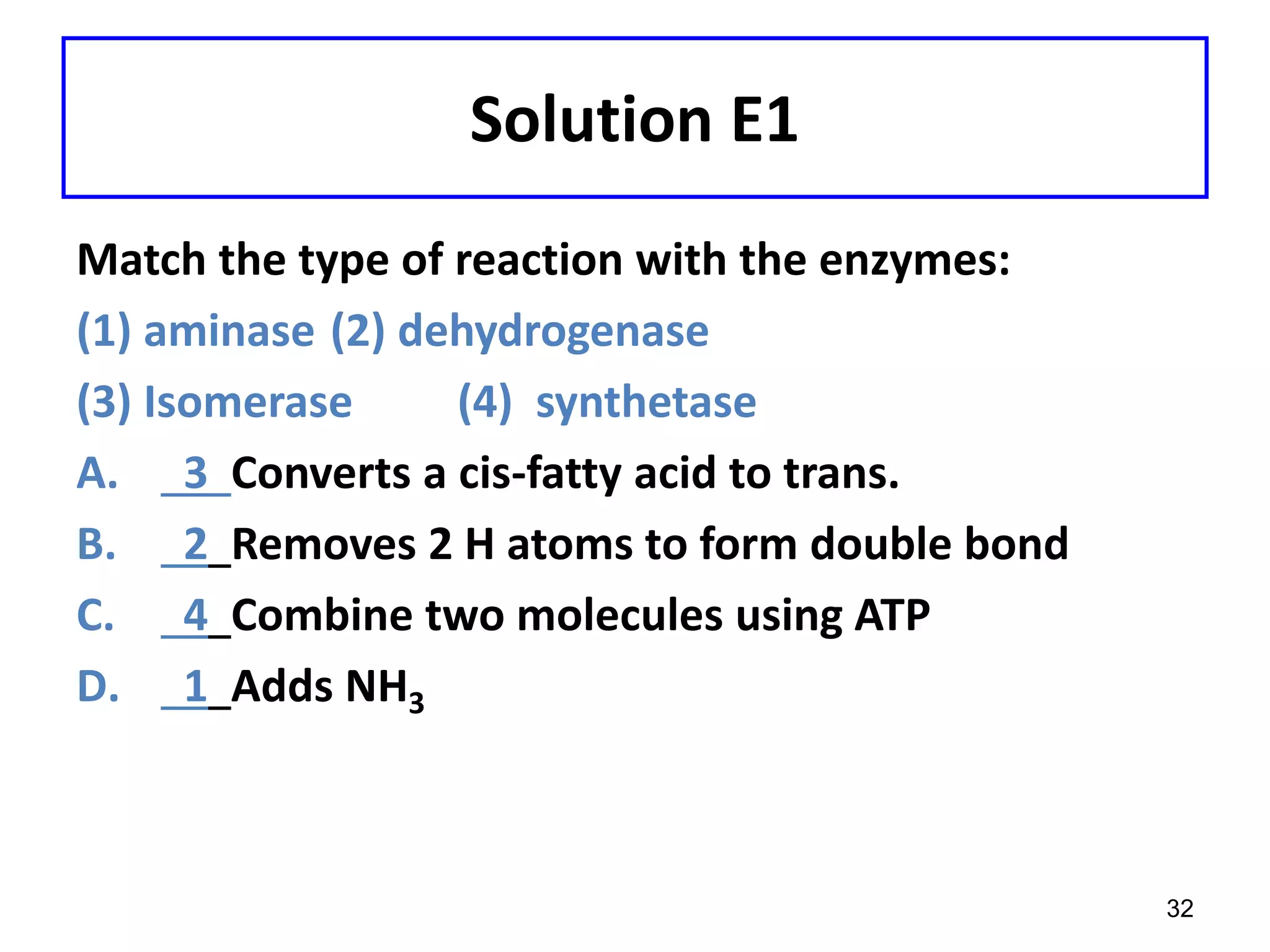
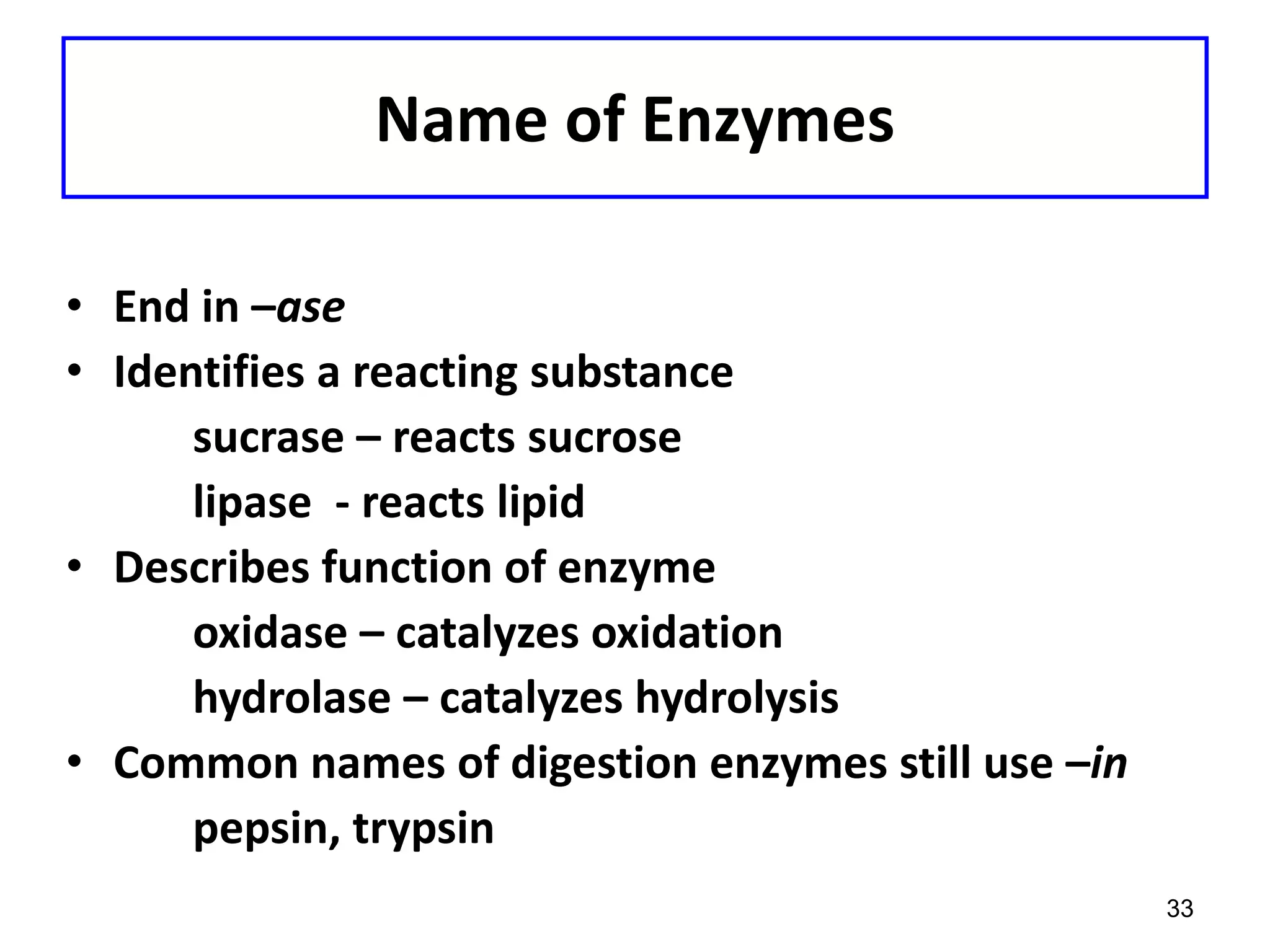
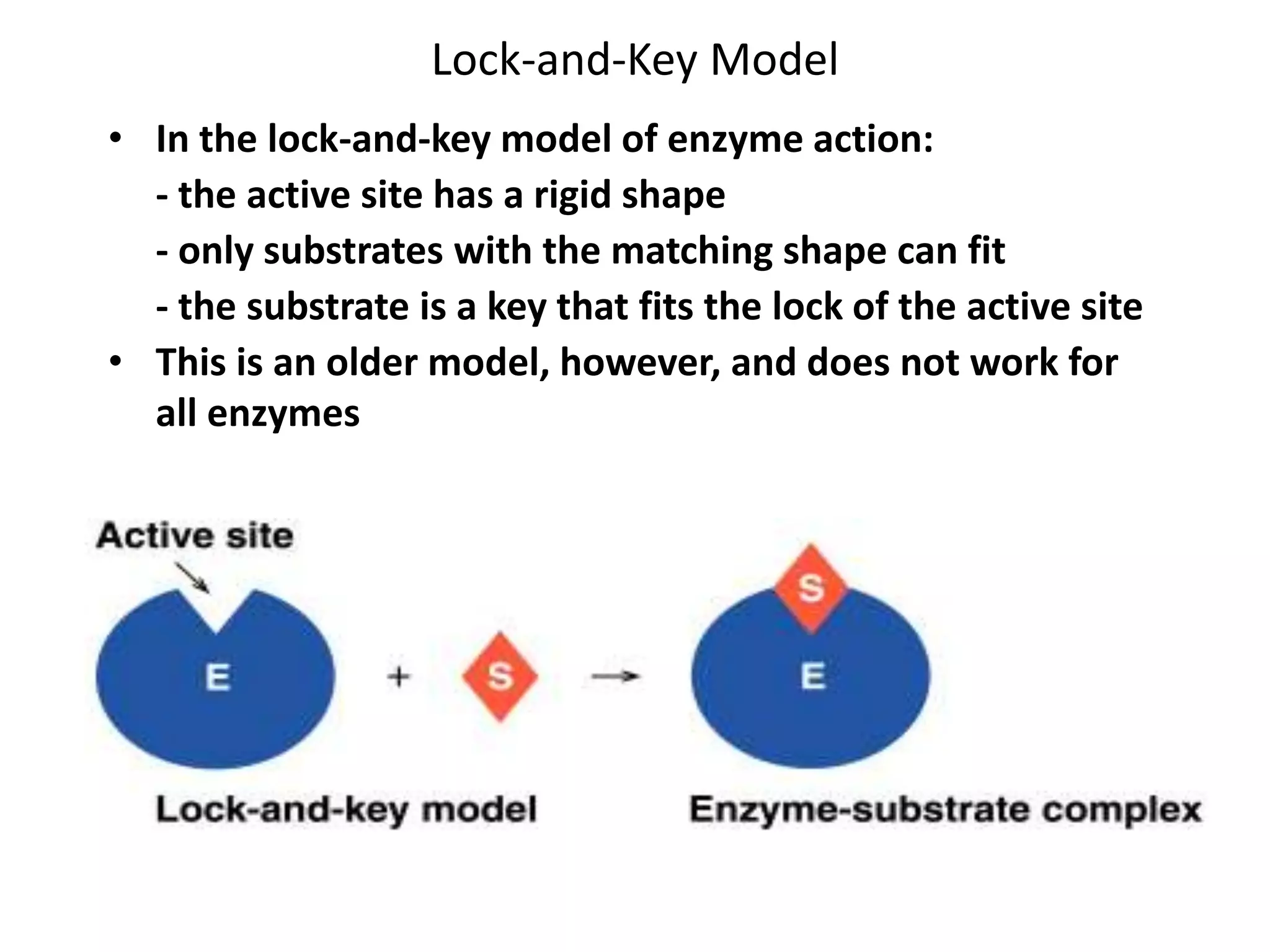
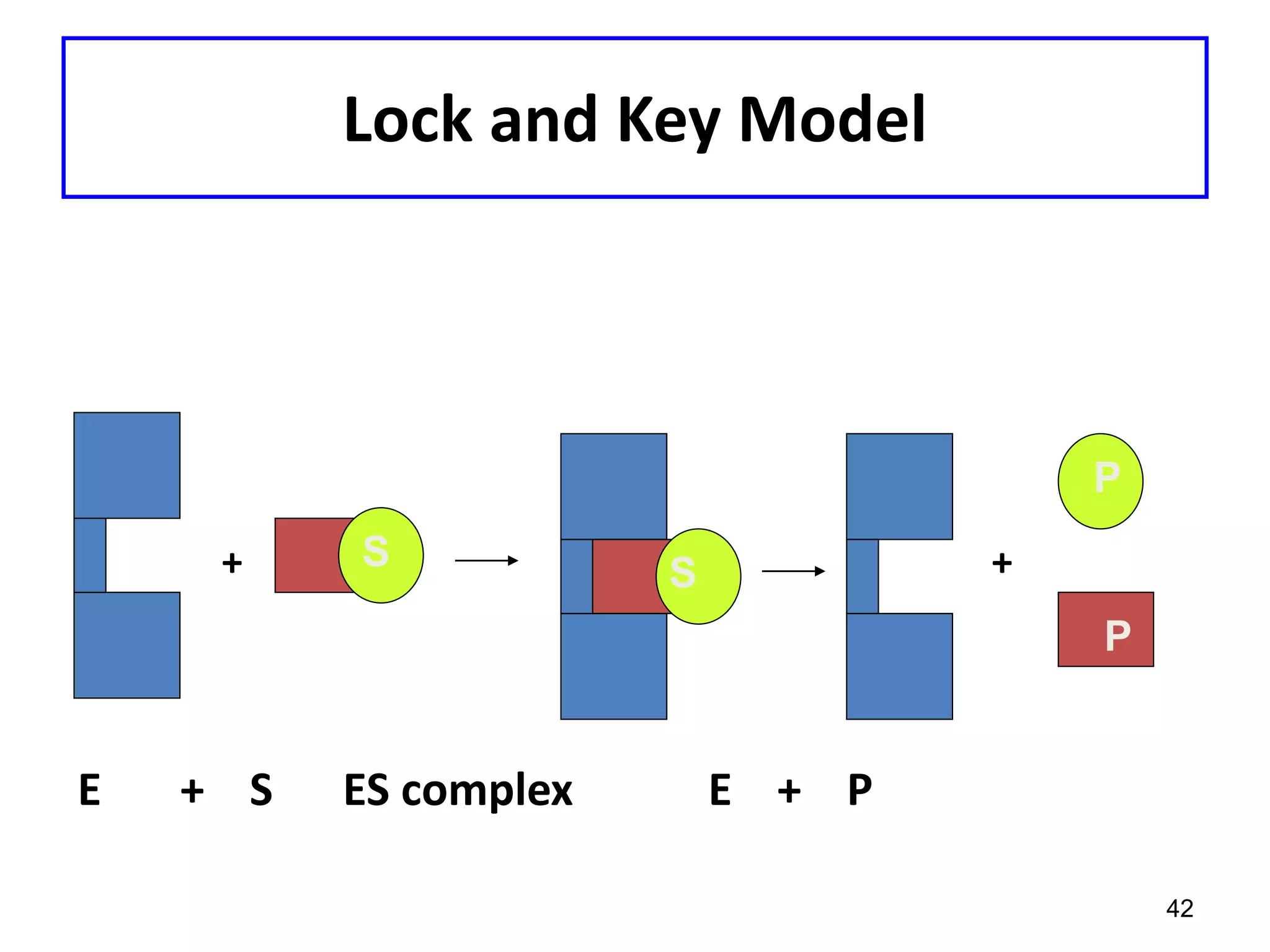
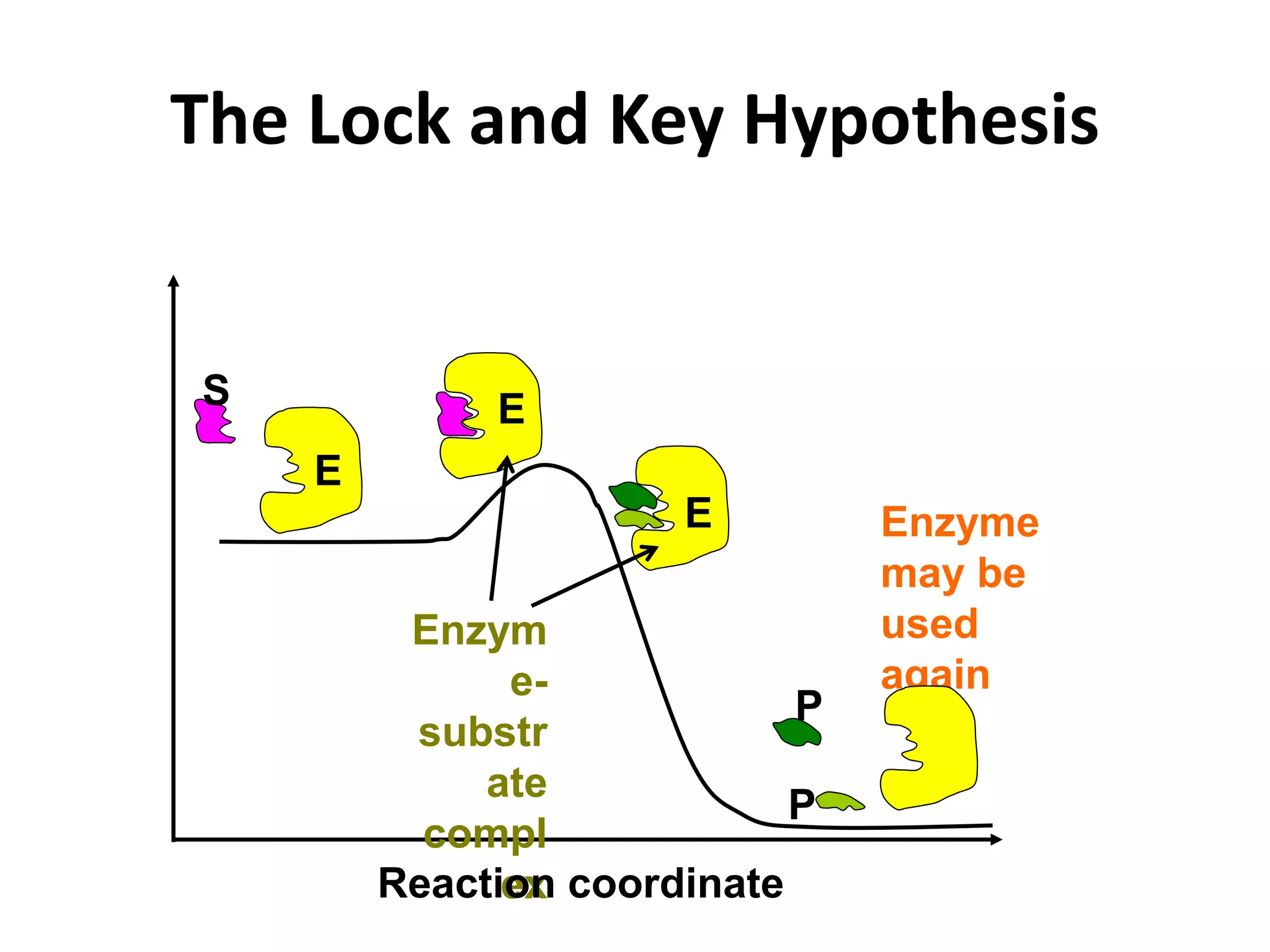
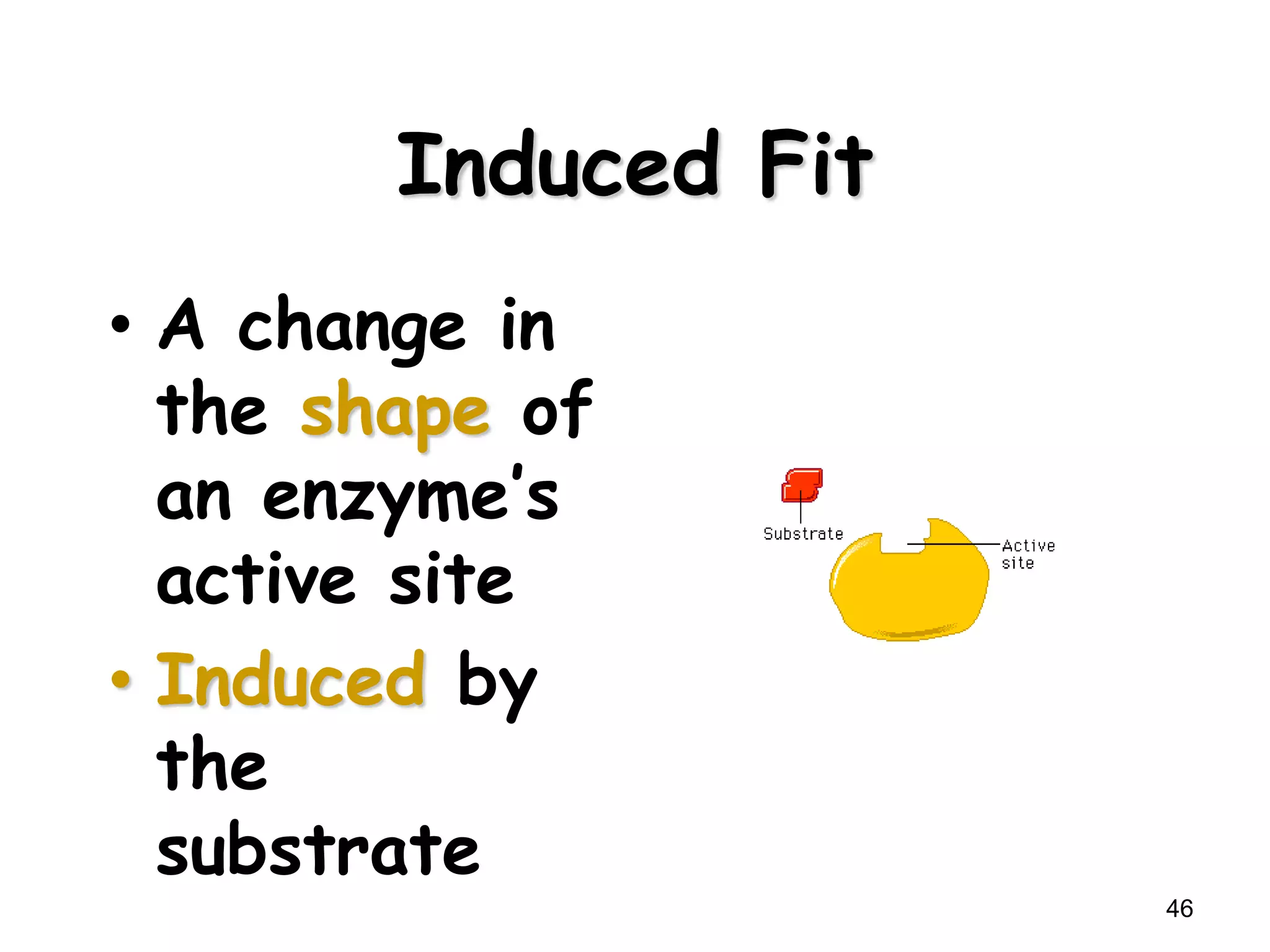
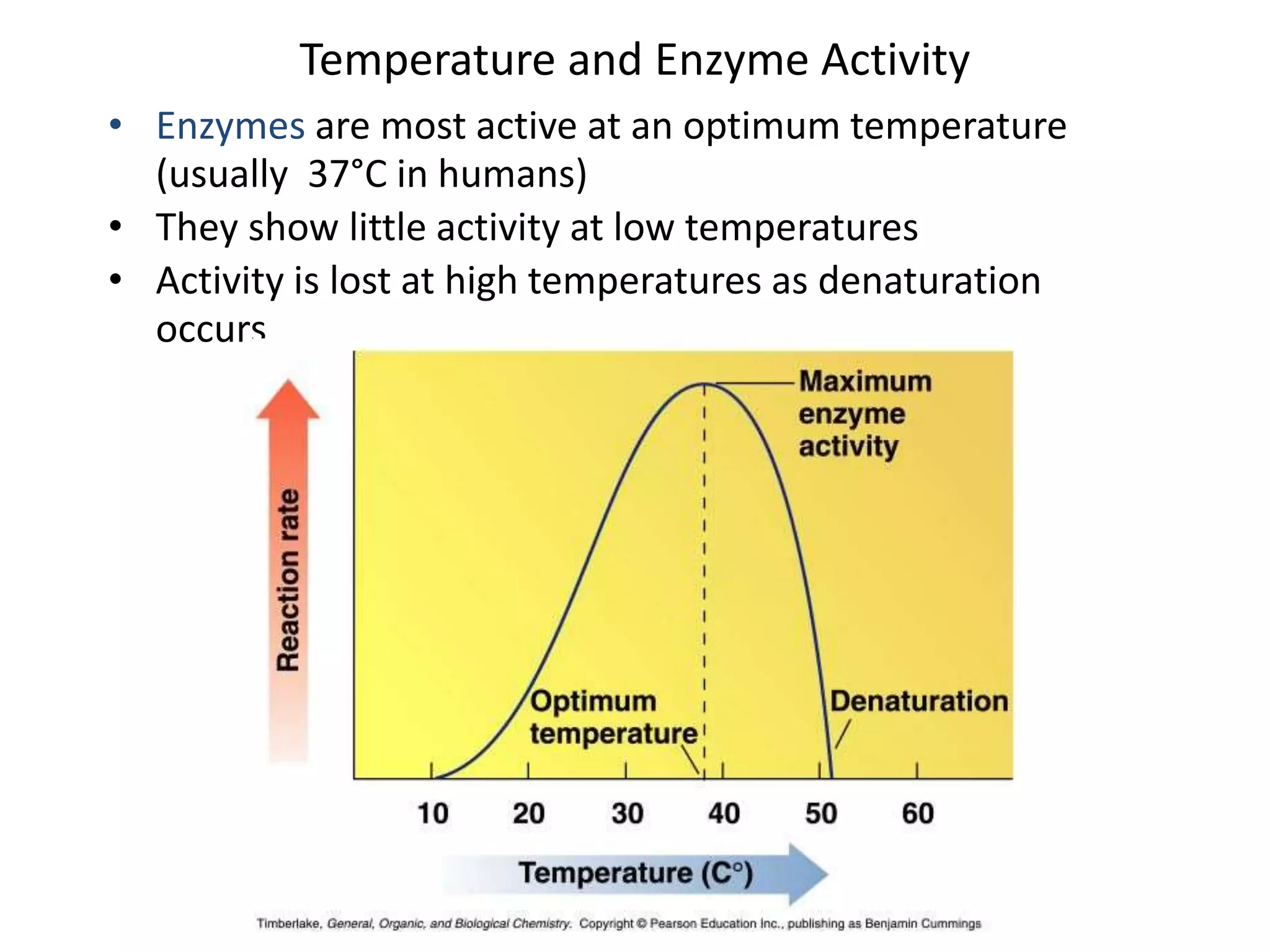
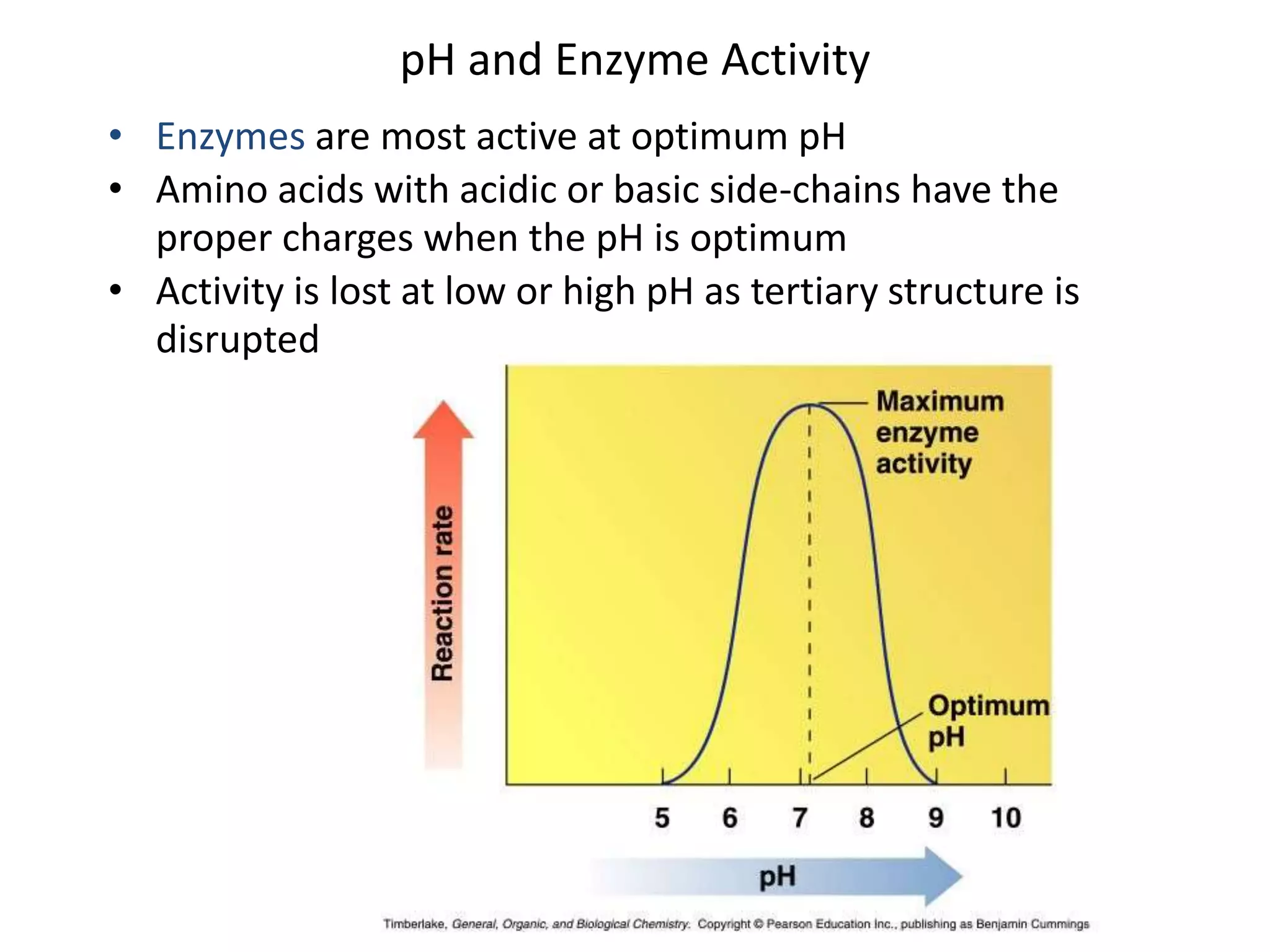
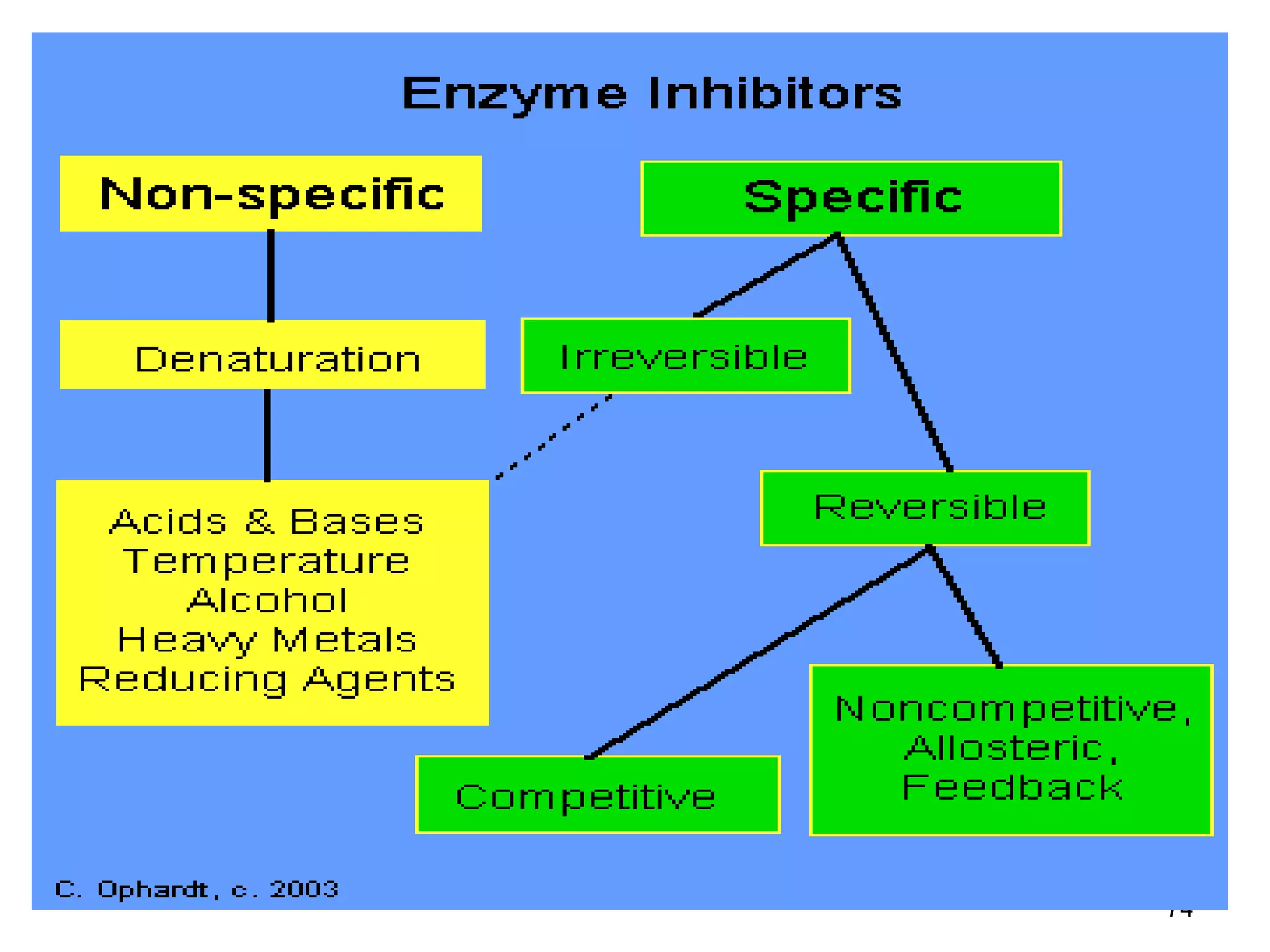
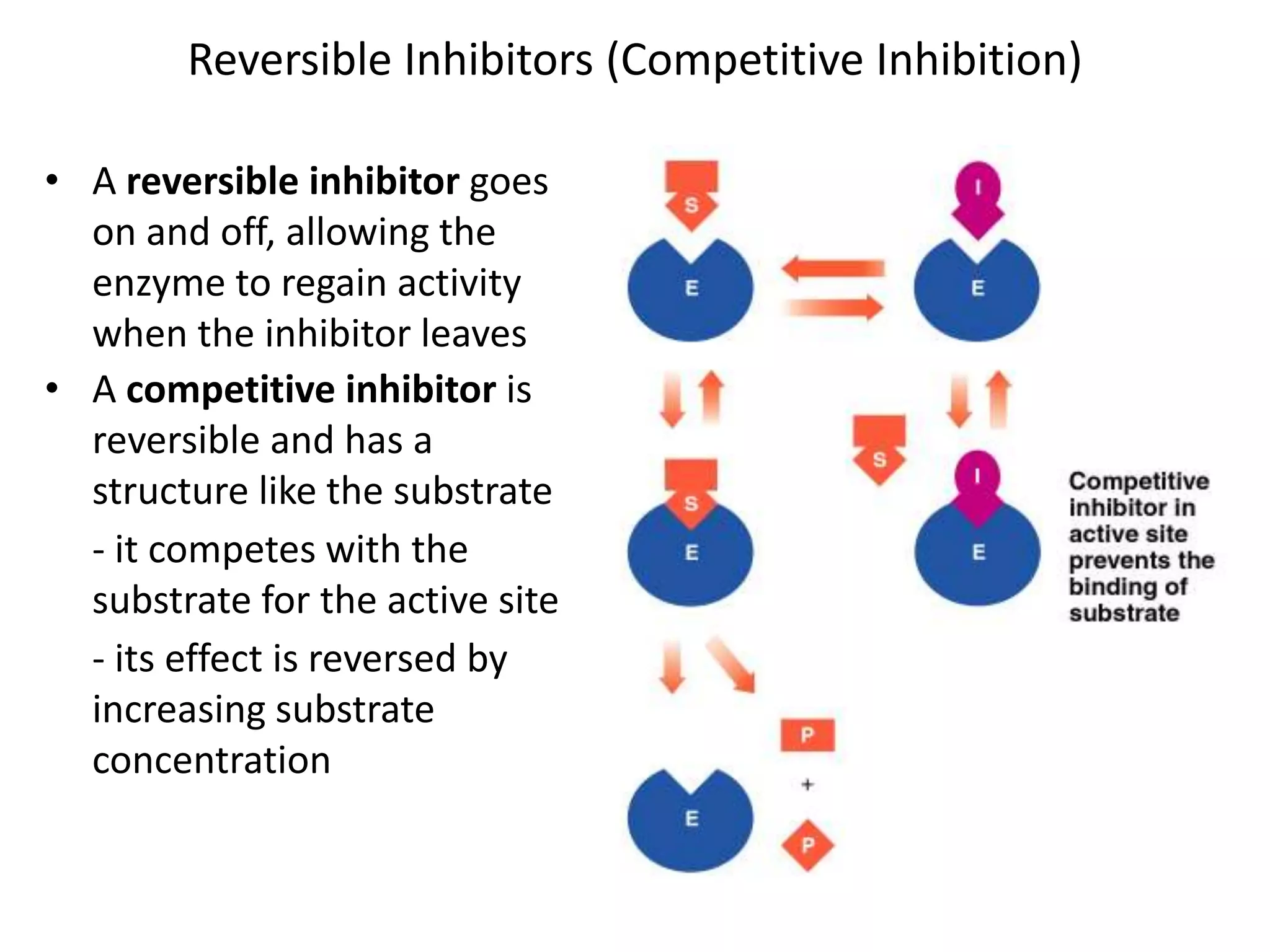
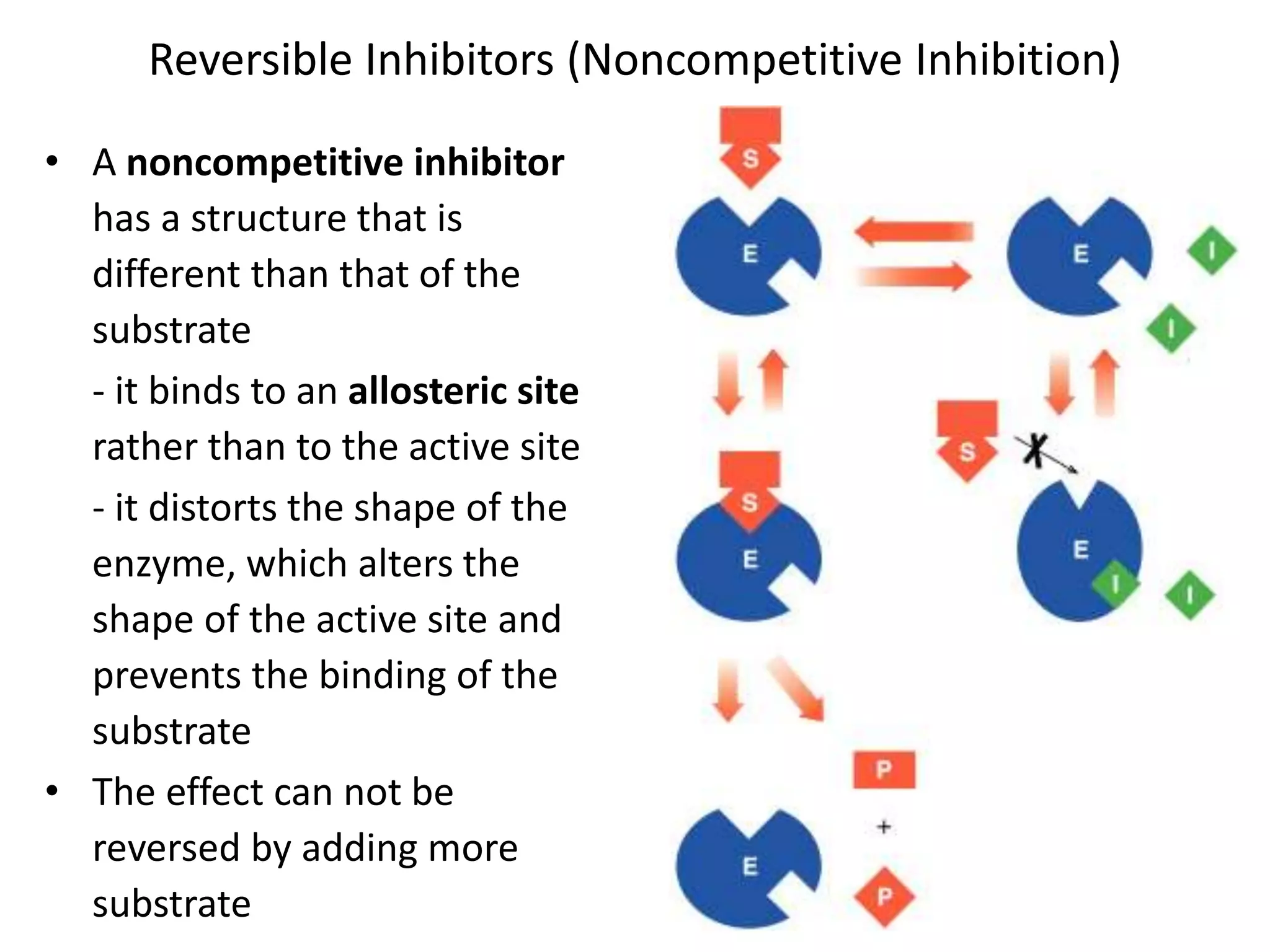
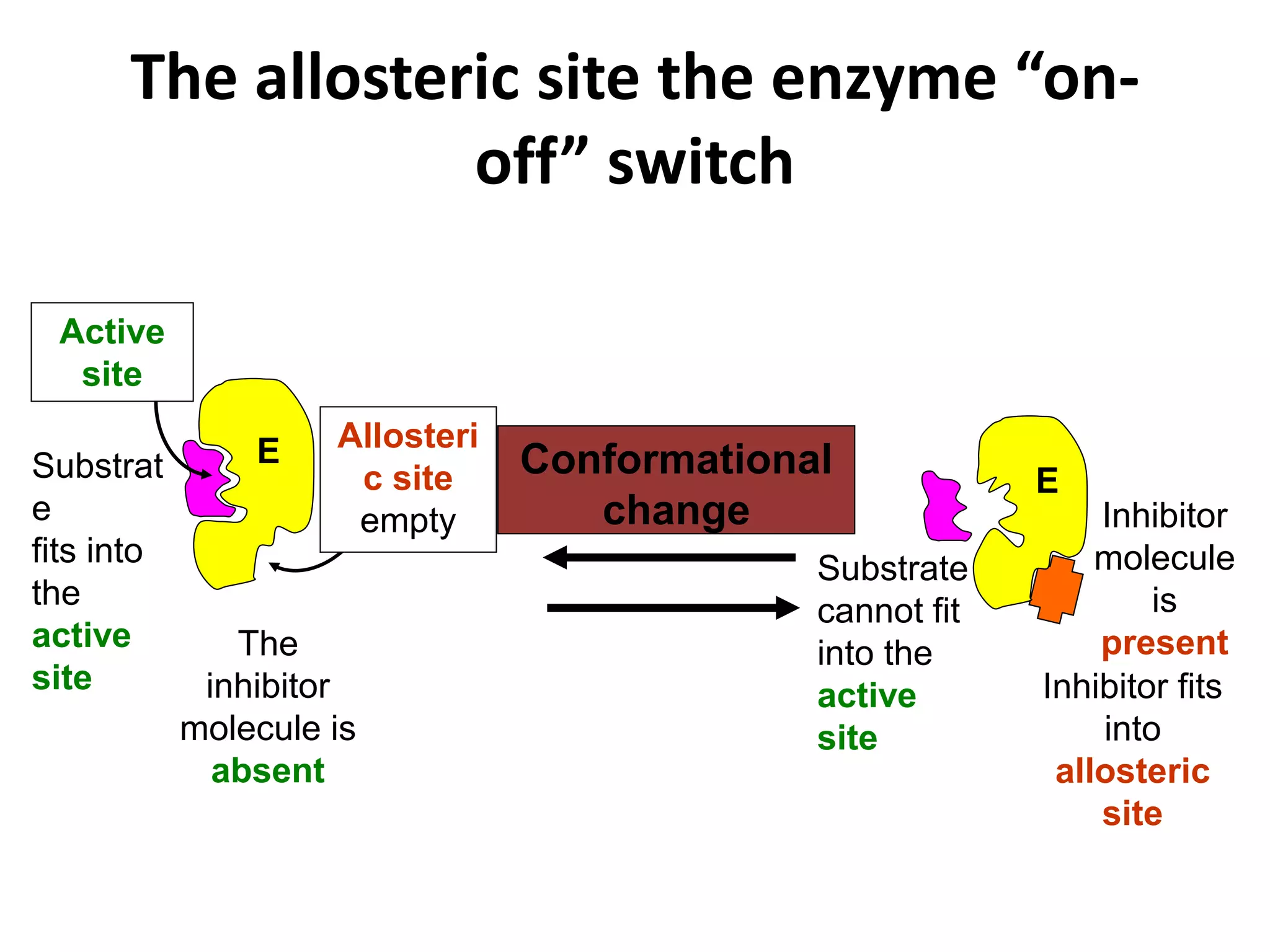
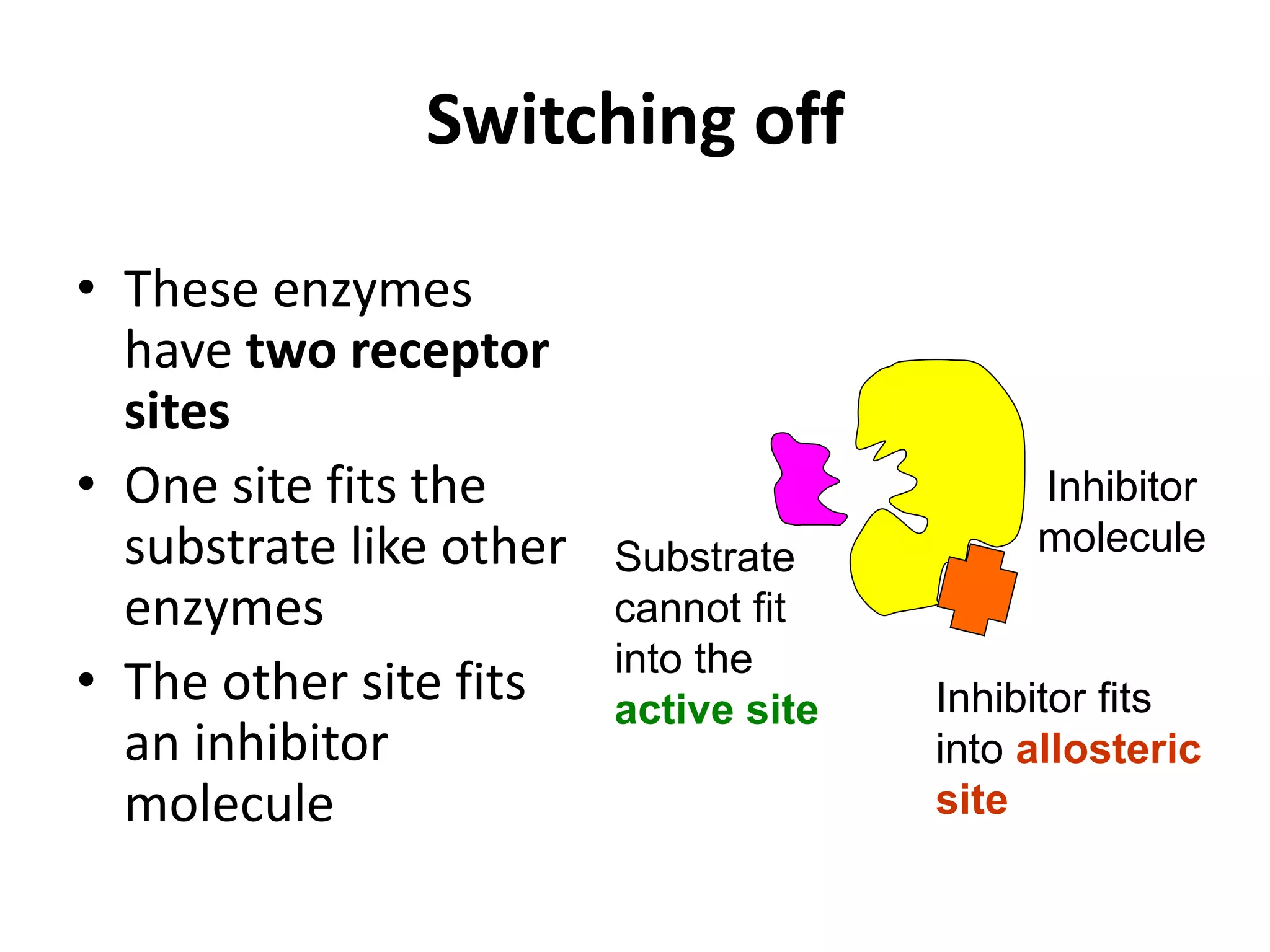
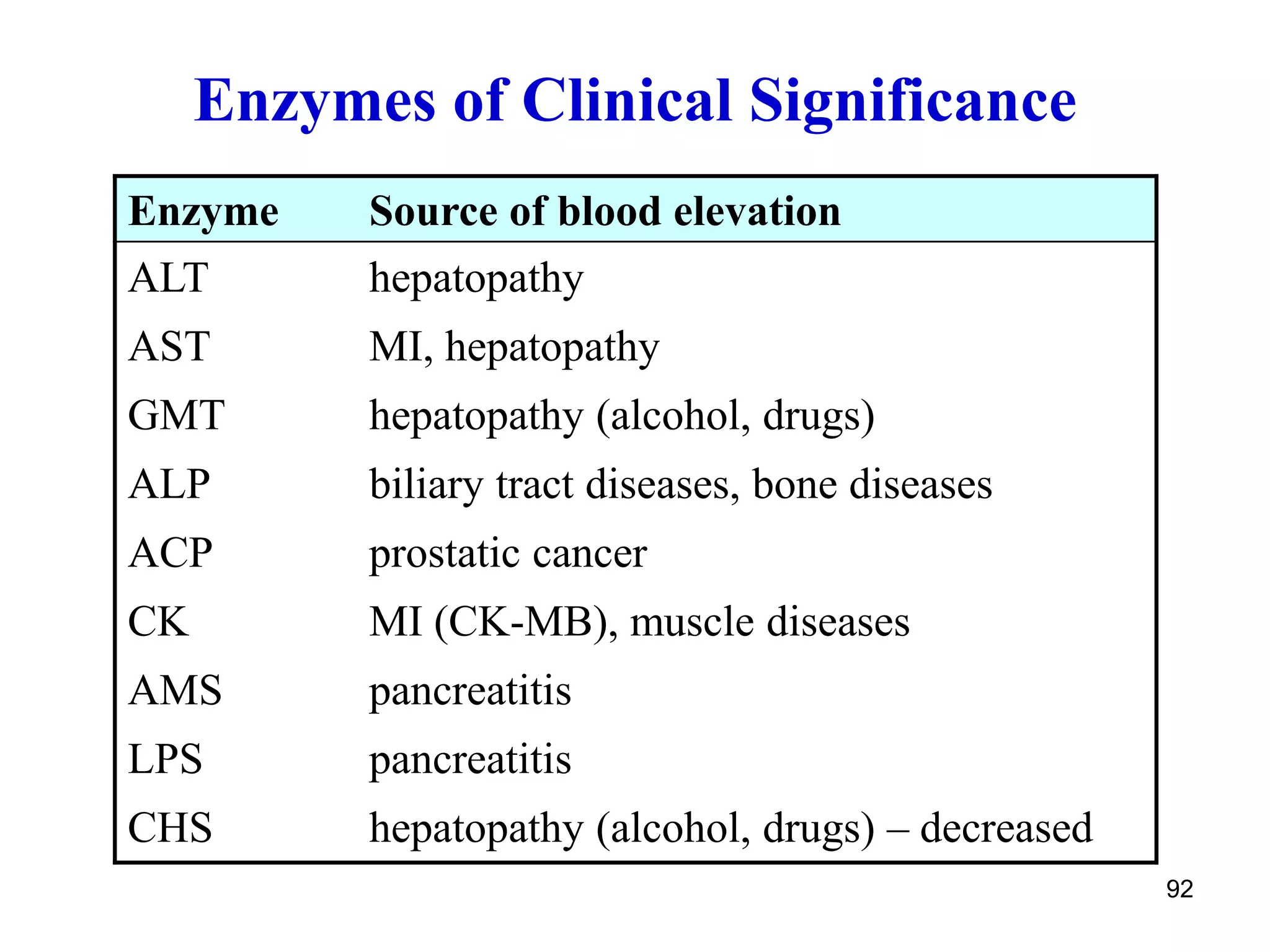
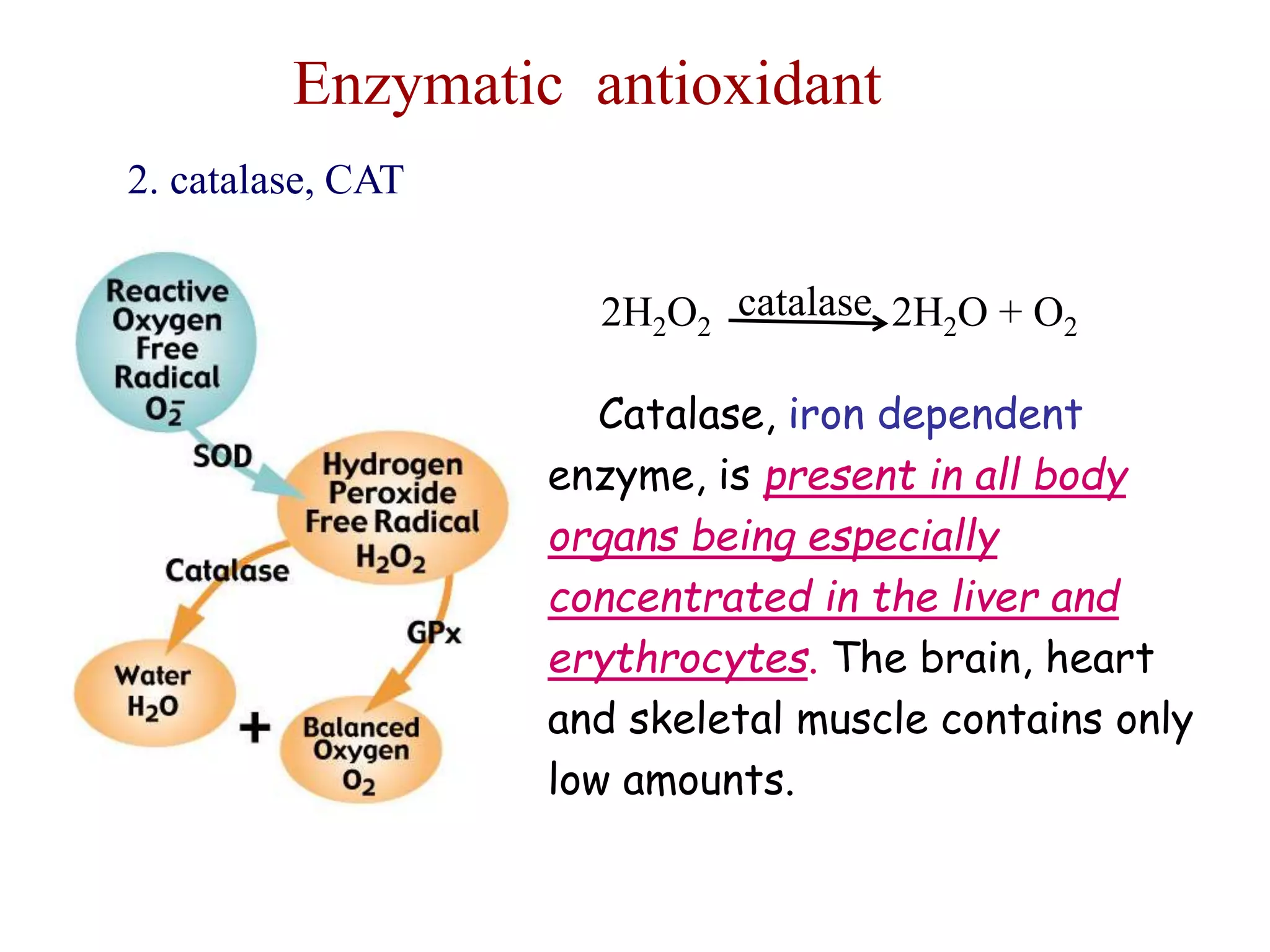
This document discusses enzymes and factors that affect their activity. It begins by defining enzymes as proteins that act as biological catalysts by lowering the activation energy of chemical reactions. It describes the structure of enzymes including their globular shape and complex 3D folds that form active sites where substrates bind. It discusses several factors that influence enzyme activity, including temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and the presence of cofactors. The optimal temperature is usually 37°C but activity decreases at higher temperatures due to denaturation. Reaction rates increase with higher substrate concentrations until all enzyme active sites are occupied. Most enzymes function best near a neutral pH of 6-8 as changes in pH can alter the charges on amino acids in the active site. Cof