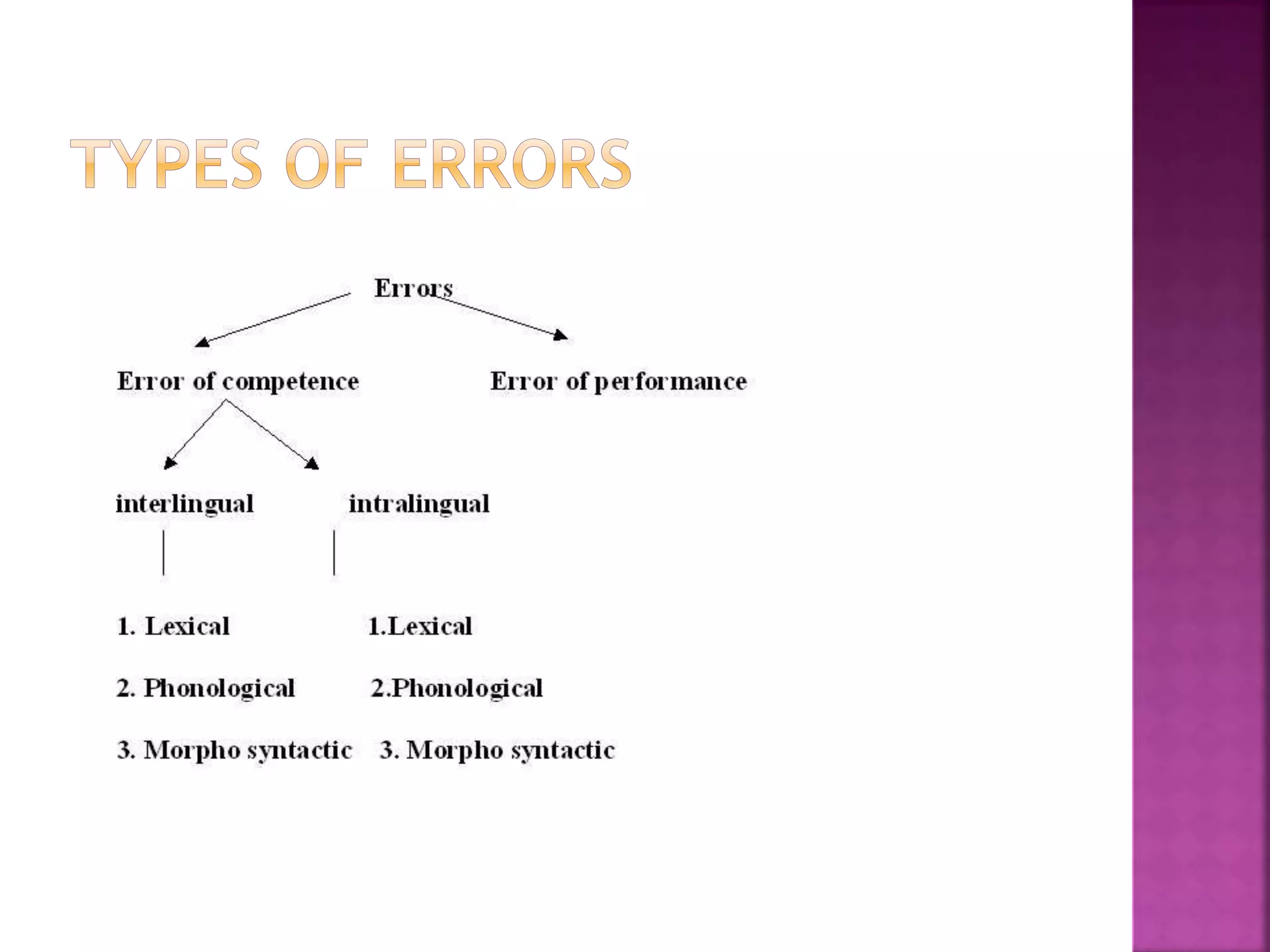
Error analysis is a technique used to identify, classify, and explain errors made by language learners. It emerged in the 1960s as proposed by Pit Corder and provides insights into the second language acquisition process. Error analysis involves collecting language samples from learners, identifying errors, describing and explaining them, and evaluating or correcting them. It is useful for both learners and teachers as it reveals the problem areas and current status of a learner's language development.