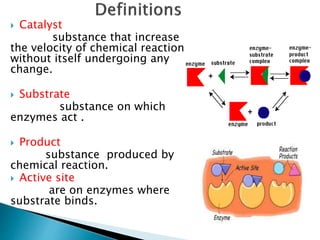
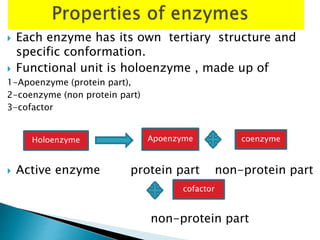
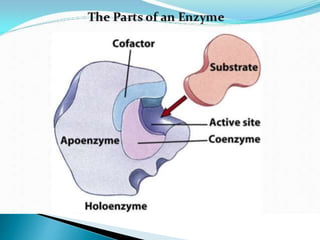
Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They achieve catalysis through four main mechanisms: proximity of substrates, acid-base catalysis, catalysis by strain, and covalent catalysis. Enzymes are highly specific and contain an active site that binds substrates in a way that lowers their activation energy and facilitates the formation of products.