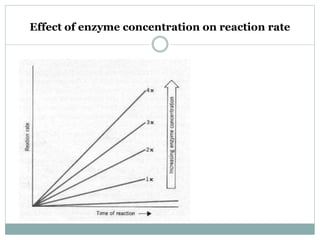
1) Chemical kinetics describes relationships between reaction rates and concentrations of reactants and products. Enzyme kinetics follows Michaelis-Menten kinetics which describes reaction rates at varying substrate concentrations.
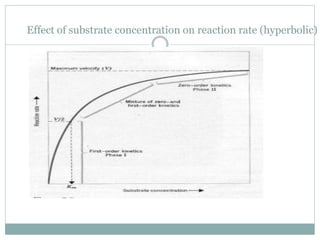
2) The Michaelis-Menten equation models reaction rates as substrate concentration increases, with an initial linear increase until reaching the maximum reaction rate (Vmax) at substrate saturation.
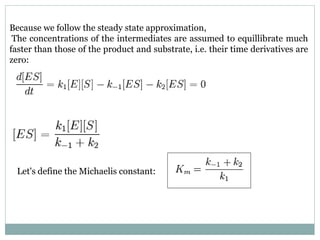
3) The Michaelis constant KM represents the substrate concentration at half Vmax and indicates an enzyme's affinity for its substrate. Lower KM means higher affinity.
![Chemical kinetics
Relationships between product (P) formed in a unit of time (ΔP/ Δt)
Velocity (v) of the reaction
Rate of equation
ΔP
Δt
= V = k[S]
S P
k1
k-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekinetics-170218051049/85/Enzyme-kinetics-1-320.jpg)
![Progress curve for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Initial slope = v0 =
Δt
Δ[P]
Δ[P]
Δ[P]
Δt ΔtProgress curve at two different
enzyme concentration in the
presence of the high initial
concentrations of substrate:
[S] >> [E]
In this case = the rate product
formation depends on enzyme
concentration and not on the
substrate concentration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekinetics-170218051049/85/Enzyme-kinetics-3-320.jpg)

![ To determine the maximum rate of an enzyme mediated
reaction, the substrate concentration ([S]) is increased until
a constant rate of product formation is achieved.
This is the maximum velocity (Vmax) of the enzyme.
In this state enzyme active sites are saturated with
substrate.
Note that at the maximum velocity, the other factors that
affect the rate of reaction (ie. pH, temperature, etc) are at
optimal values.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekinetics-170218051049/85/Enzyme-kinetics-6-320.jpg)
![Reaction rate/velocity V
The speed V means the number of
reactions per second that are catalyzed by
an enzyme.
With increasing substrate concentration
[S], the enzyme is asymptotically
approaching its maximum speed Vmax,
but never actually reaching it.
Because of that, no [S] for Vmax can be
given.
Instead, the characteristic value for the
enzyme is defined by the substrate
concentration at its half-maximum speed
(Vmax/2).
This KM value is also called
the
Michaelis-Menten constant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekinetics-170218051049/85/Enzyme-kinetics-7-320.jpg)
![Michaelis-Menten constant 'KM'
Since Vmax cannot be reached at any substrate concentration
(because of its asymptotic behaviour, V keeps growing at any [S],
albeit ever more slowly), enzymes are usually characterized by the
substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is half its
maximum.
This substrate concentration is called the Michaelis-Menten constant
(KM).
This represents (for enzyme reactions exhibiting simple Michaelis-
Menten kinetics) the dissociation constant (affinity for substrate) of
the enzyme-substrate (ES) complex.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekinetics-170218051049/85/Enzyme-kinetics-9-320.jpg)


![This simplifies the form of the equation:
The total (added) concentration of enzyme is a sum of that which is free in
the solution and that which is bound to the substrate, and the free enzyme
concentration is derived from this:
[E0] = [E] + [ES]
[E] = [E0] − [ES] (2)
Using this concentration (2), the bound enzyme concentration (1) can now
be written:
(1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekinetics-170218051049/85/Enzyme-kinetics-13-320.jpg)

![Substituting (3) in (4) and multiplying numerator and denominator by [S]:
This equation may be analyzed experimentally with a Lineweaver-Burk
diagram or a Hanes-Woolf Plot.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekinetics-170218051049/85/Enzyme-kinetics-15-320.jpg)
![This equation may be analyzed experimentally with a Lineweaver-Burk
diagram or a Hanes-Woolf Plot.
The plot provides a useful graphical
method for analysis of the Michaelis-
Menten equation:
Taking the reciprocal gives:
V = reaction velocity (the reaction rate),
Km = Michaelis-Menten constant,
Vmax = maximum reaction velocity
[S] is the substrate concentration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymekinetics-170218051049/85/Enzyme-kinetics-16-320.jpg)