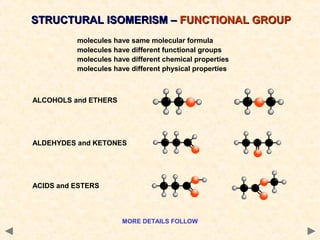
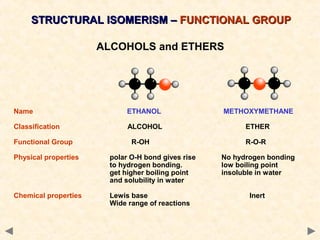
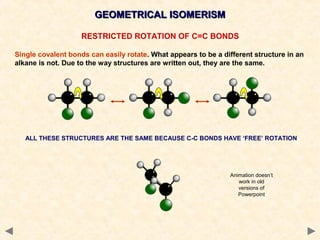
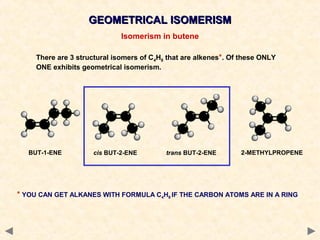
There are several types of isomerism that can occur when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas:
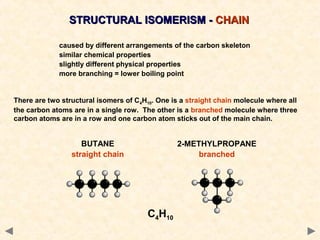
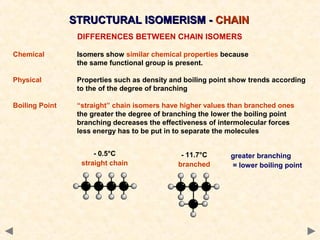
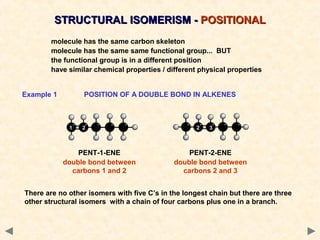
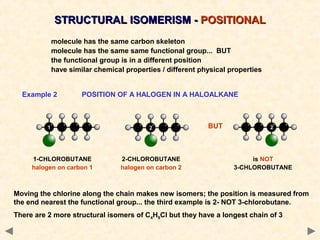
Structural isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms. This includes chain isomers which have different carbon skeleton arrangements and positional isomers which have functional groups in different positions.
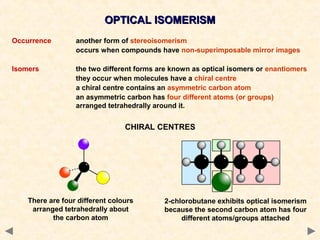
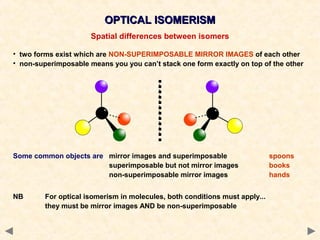
Stereoisomerism occurs when compounds have the same connectivity of atoms but different three-dimensional orientations. This includes geometric isomers, which can exist as cis or trans forms due to restricted bond rotation, and optical isomers which are non-superimposable mirror images known as enantiomers.
Different structural and stereoisomeric forms can have similar chemical properties