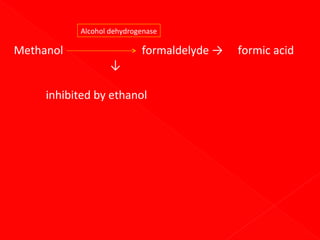
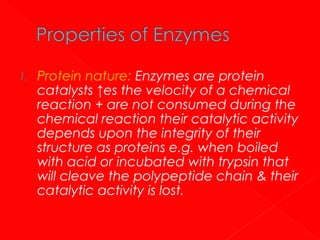
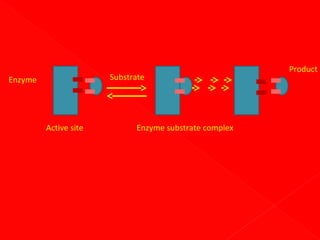
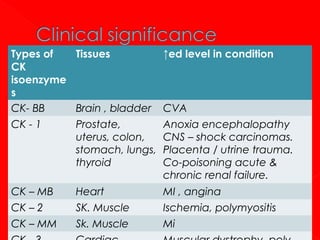
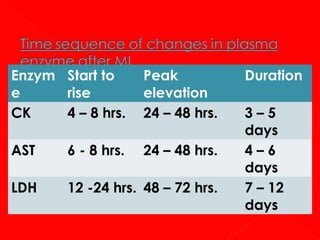
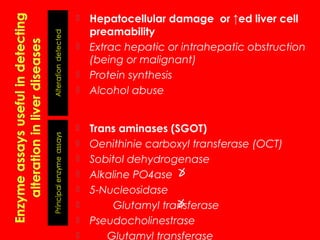
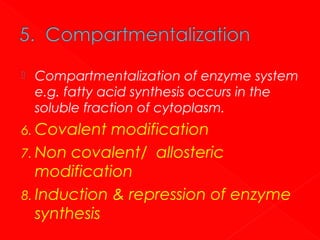
1. Enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed themselves. They direct all metabolic events in living organisms.
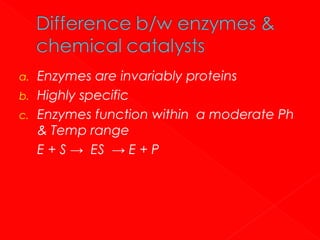
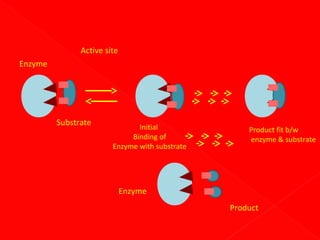
2. Enzymes have specific three-dimensional structures that form active sites which substrates bind to, forming enzyme-substrate complexes. Interactions at the active site facilitate the conversion of substrates to products.
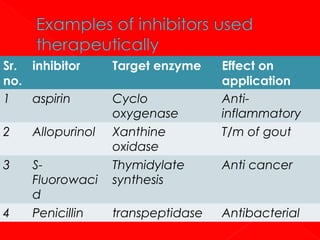
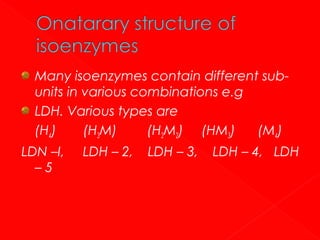
3. Enzymes can be classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze, such as oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. Each enzyme has a unique four-digit number identifying its catalytic reaction.











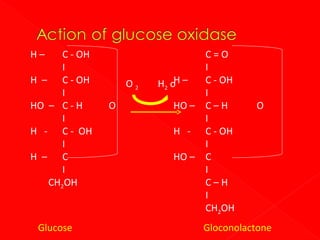













































































![Catalyes the reaction
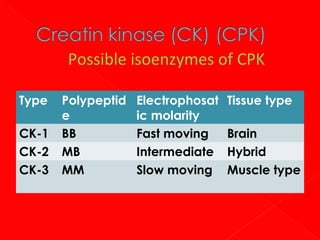
Creatinine – P + ADP → creatine + ATP
It is present in high [] in SK , muscle,
myocardia+ brain. In small[] it is present
in lung thyroid + kidneys. It is absent in
liver.
Normal value: 4- 60 iμ/L at 37 ⁰C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-108-320.jpg)

















![Michaerlis describes how reaction velocity varies
with substrate concentration
Vi = V max [ ]
Km + [s]
Where
Vi
=
initial reaction velocity
Vmax =
maximal velocity
Km
=
Michaerlis constant = ( K-1+K2)
K1
[s]
=
substrate concentration
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-131-320.jpg)

![The conc. Of substrate is much greater
than the concentration of enzyme [E] so
that the amount of substrate bond by
the enzyme at any one time is small.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-133-320.jpg)
![
[ES] does not change with time – that is
the rate of formation of ES is equal to
that of the breakdown of ES ( E+ S + to
E+P)
In general, intermediate in a series of
reaction is said to be in steady state
when the rate of synthesis is equal to its
rate of degradation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-134-320.jpg)

![Characteristic of Km:
The michaelis constant is characteristic of
an enzyme & a particular substrate &
reflect the affinity of the enzyme for that
substrate.
Km is numerically equal to substrate [ ] at
with the reaction velocity is equal to ½ V
max.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-136-320.jpg)

![The rate of reaction is directly
proportioned to the enzyme [ ] at all
substrate [ ] e.g. if the enzyme [ ] is halved.
The initial rate of reaction (V) is related to
one half that of original.
Km + Vmax may be influenced by pH,
temp. & other factors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-138-320.jpg)

![When K >> K2
[ES] + [S]
ES dissociating more after to yield E+S than
to yield product
When K2 >> K-1
The rate of dissociation of ES to E+S is small,
so that products are usually formed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-140-320.jpg)
![When [S] >>Km
The characteristic property of the turnover
number for an enzyme can be invoked. This
no. provides information regarding how
many times it forms the ES complex & is
regenerated by yielding P.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-141-320.jpg)
![Order of reaction:
At high [ ] of substrates the velocity of
reaction is zero order. i.e constant &
independent of substrate concentration. At
low [ ] of substrate, the velocity of reaction is
1st order i.e proportional to substrate
concentration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-142-320.jpg)
![Equation
I =
Vo
Km
Vmax
I
Vmax
I
V
Km
V max
-I
Km
I
V max
O
I
[S]
+
[S]
I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-143-320.jpg)
![When the reaction velocity Vi is plotted
against substrate concentration, [S}, it is
not always possible to determine when V
max has been achieved, because of the
curve at high substrate [ ]. However of
I/Vo plotted Vs I/[S ] a straight line is
obtained. This plot is called line weaver
burke plot & can be used to calculate Km
& Vmax as well as determine mechanism
of action of enzyme inhibitions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-144-320.jpg)



![If the concentration of a substrate [s] is
↑ed while all other conclusions are kept
constant the measured initial velocity Vi
↑ed to a maximum value Vmax. The
velocity ↑ed as the substrate [] is ↑ed up
to a point where the enzyme is said to
be saturated with substrate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-149-320.jpg)
![Velocity
V max
V max
2
B
A
Km [S]
C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-150-320.jpg)
![At point A+B only a portion of enzyme
present to combined with substrate.
At point A or b ↑ing or ↓ing [S] with
therefore ↑ or ↓ the amount of E
associated with S as ES of Vi will depend
on [s] at C all enzyme is combined with
substrate so that further ↑se in [S],
although it ↑es the frequency of
collision b/w enzyme & substrate, cannot
result in ↑ rate of reaction since no free
enzyme is available to react.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-151-320.jpg)

















![The effect of a competitive inhibitor is
reversed by ↑ing [S] . At a sufficiently high
[S] the reaction velocity reaches the
Vmax observed in the absence of
inhibitor.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-170-320.jpg)

![Reaction Velocity
V max
V max
2
Km
Km
[S]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-172-320.jpg)
![I
Vo
Comp. inhibition
No inhibition
I
V max
-I
Km
-I
Km
I
[ -S]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-173-320.jpg)



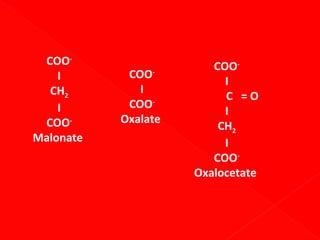




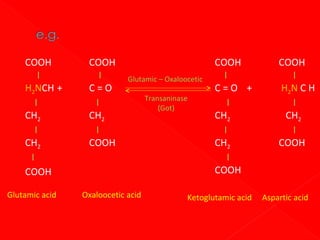
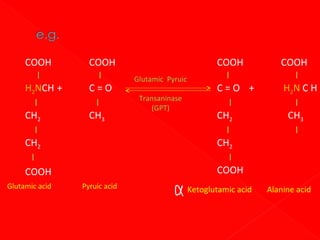
![In two substrate enzyme-catalysed
reactions, high [] of 2nd substrate may
complete with the first substrate for
binding e.g. reaction catalysed by
aspartate aminotransferase. L-aspartate
& ketoglutarate Lglutamate +
oxaloacetate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymebiochemistry-140204233141-phpapp01/85/Enzyme-biochemistry-184-320.jpg)