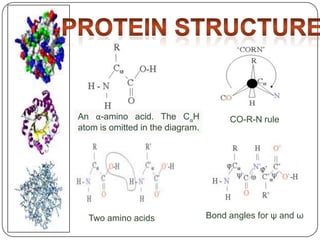
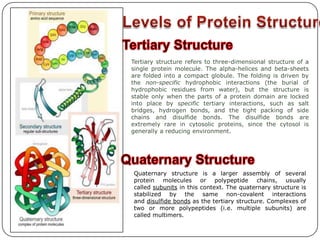
Proteins are composed of amino acids and play many essential roles in the body. They have four levels of structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The primary structure is the amino acid sequence, secondary involves hydrogen bonding into shapes like alpha helices and beta sheets, tertiary is the 3D folding of these structures, and quaternary involves the assembly of multiple protein subunits. Proteins serve as enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and structures. They undergo synthesis from amino acids and breakdown through catabolism. Disorders can occur if amino acid metabolism is disrupted.






![Protein catabolismis the process by which proteins are broken down to their amino acids. This is also called proteolysis.Proteins contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen , and sometimes other atoms. They form the cellular structural elements, are biochemical catalysts, and are important regulators of gene expression . Nitrogen is essential to the formation of twenty different amino acids, the building blocks of all body cells. Amino acids are characterized by the presence of a terminal carboxyl group and an amino group in the alpha position, and they are connected by peptide bonds.Digestion breaks protein down to amino acids. If amino acids are in excess of the body's biological requirements, they are metabolized to glycogen or fat and subsequently used for energy metabolism. If amino acids are to be used for energy their carbon skeletons are converted to acetyl CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle for oxidation, producing ATP. The final products of protein catabolism include carbon dioxide, water, ATP, urea, and ammonia.Vitamin B 6 is involved in the metabolism (especially catabolism) of amino acids, as a cofactor in transamination reactions that transfer the nitrogen from one keto acid (an acid containing a keto group [-CO-] in addition to the acid group) to another. This is the last step in the synthesis of nonessential amino acids and the first step in amino acid catabolism. Transamination converts amino acids to L-glutamate, which undergoes oxidative deamination to form ammonia, used for the synthesis of urea. Urea is transferred through the blood to the kidneys and excreted in the urine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biochempresentation-111005235741-phpapp02/85/Protein-10-320.jpg)







