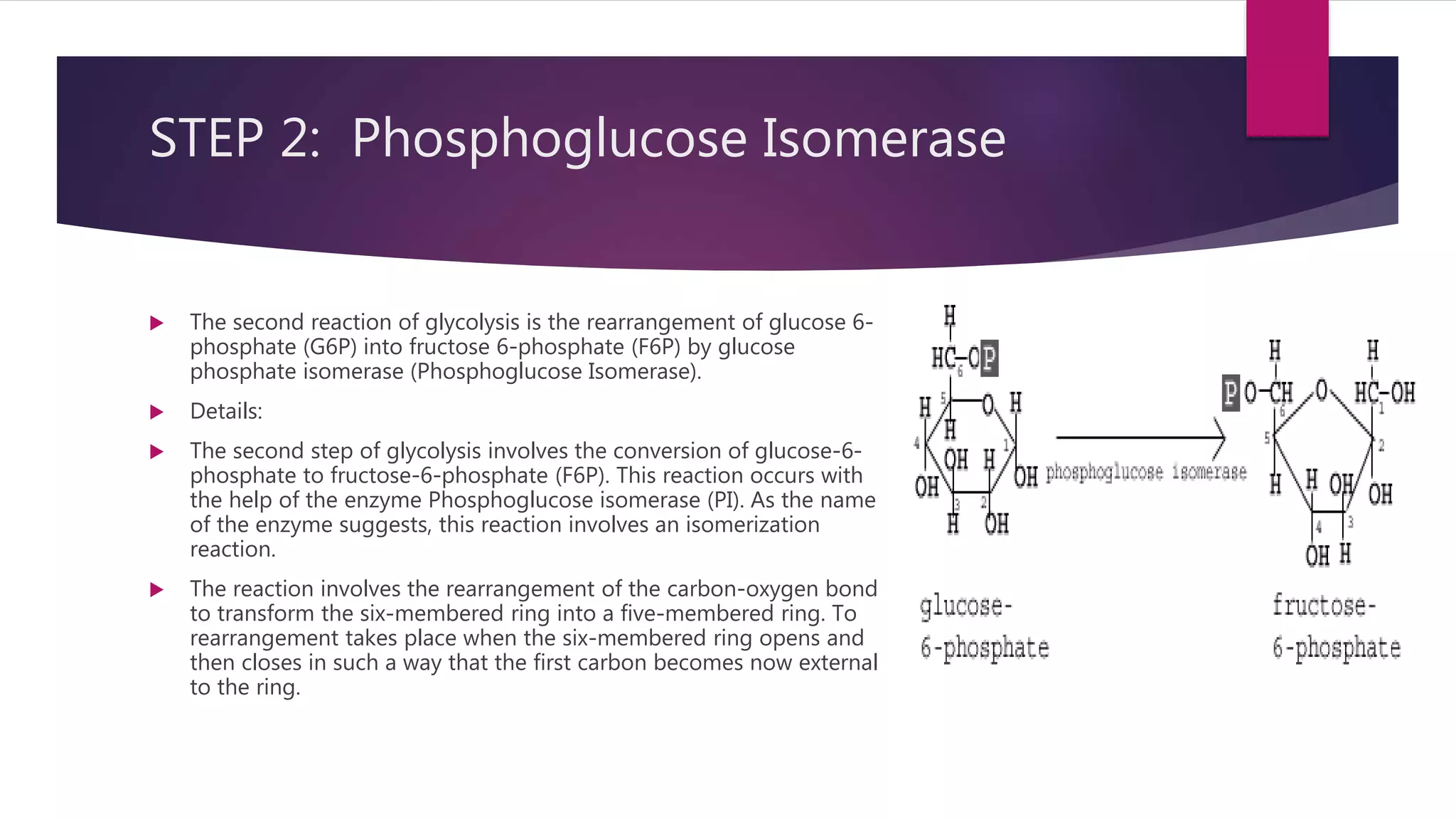
Glycolysis is a series of biochemical reactions that convert glucose into pyruvate, generating energy in the form of ATP, and can occur anaerobically or aerobically. The process involves multiple steps with specific enzymes converting glucose through various intermediates, resulting in different ATP yields based on the presence of oxygen. Aerobic glycolysis is more efficient, producing 36 to 38 ATP per glucose molecule, while anaerobic glycolysis yields only 2 ATP, producing lactate as a byproduct.