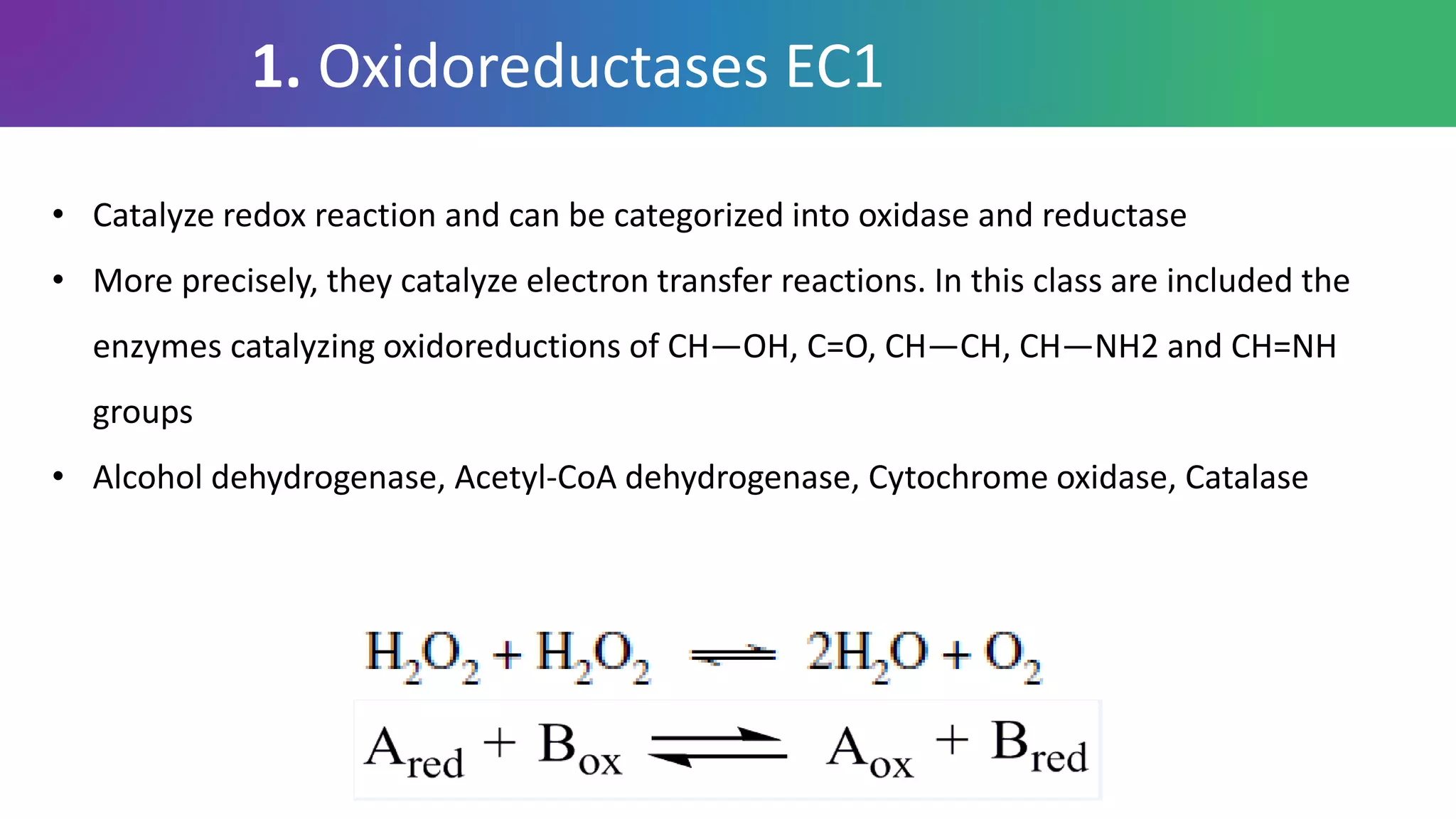
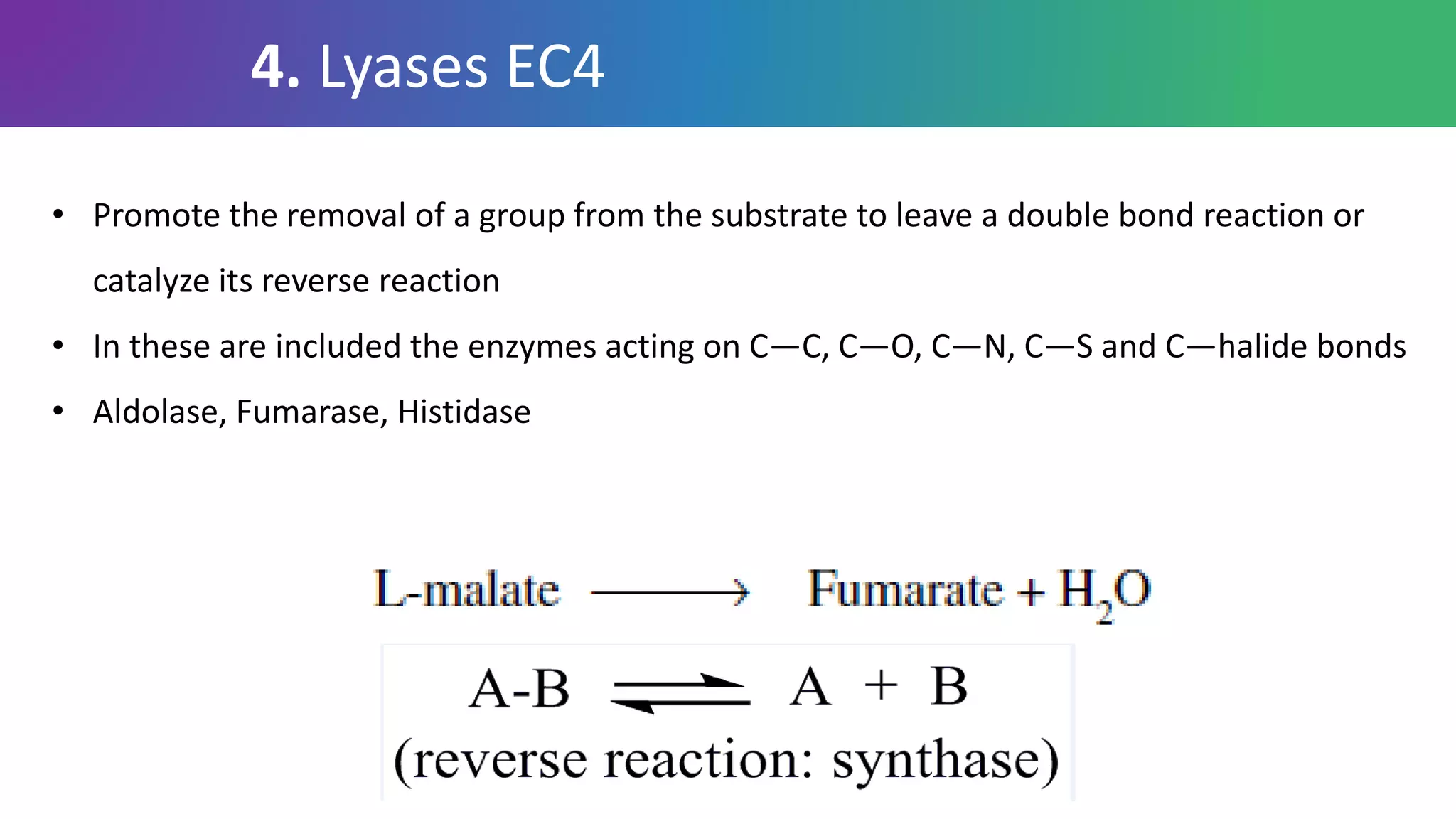
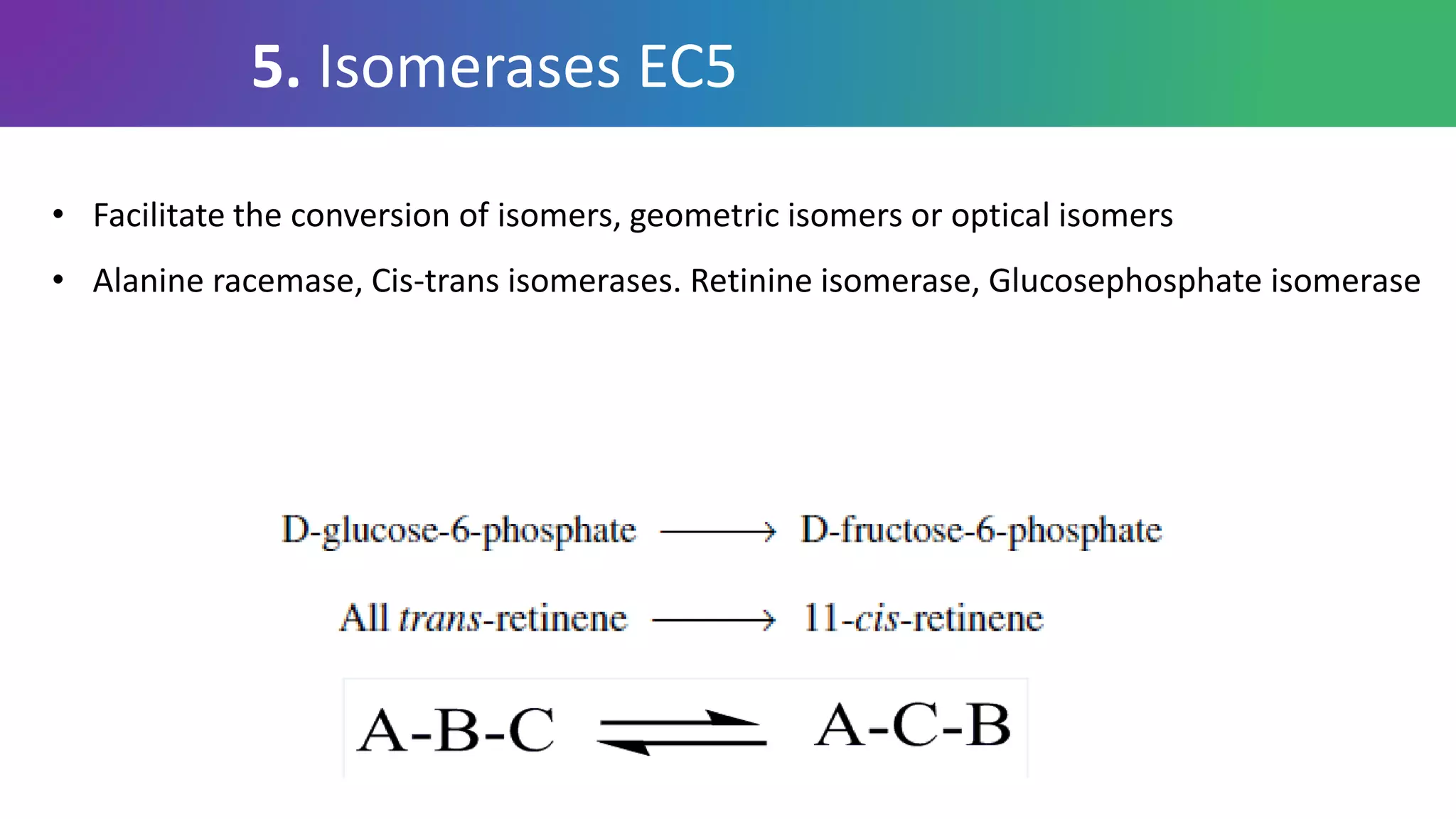
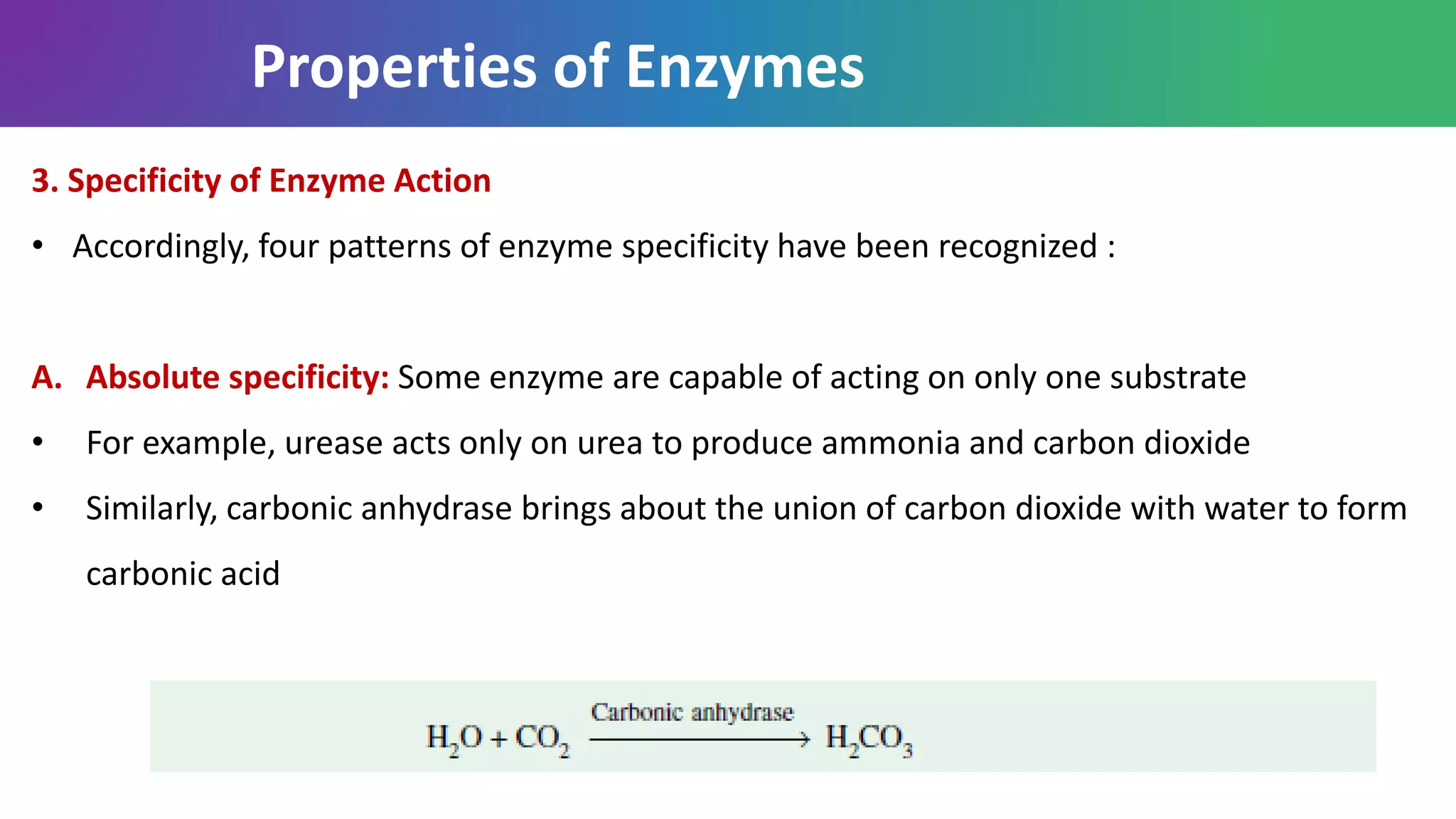
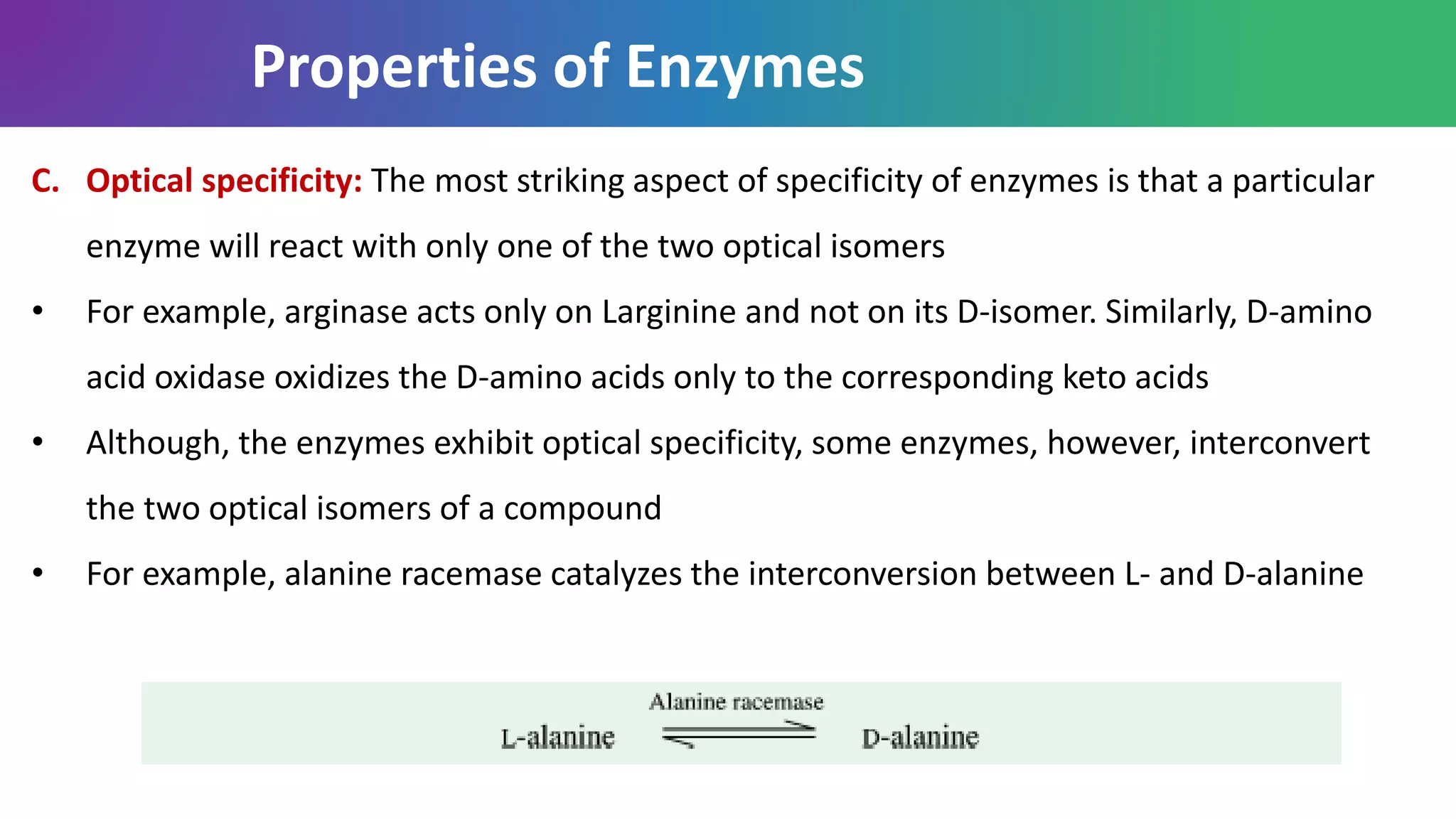
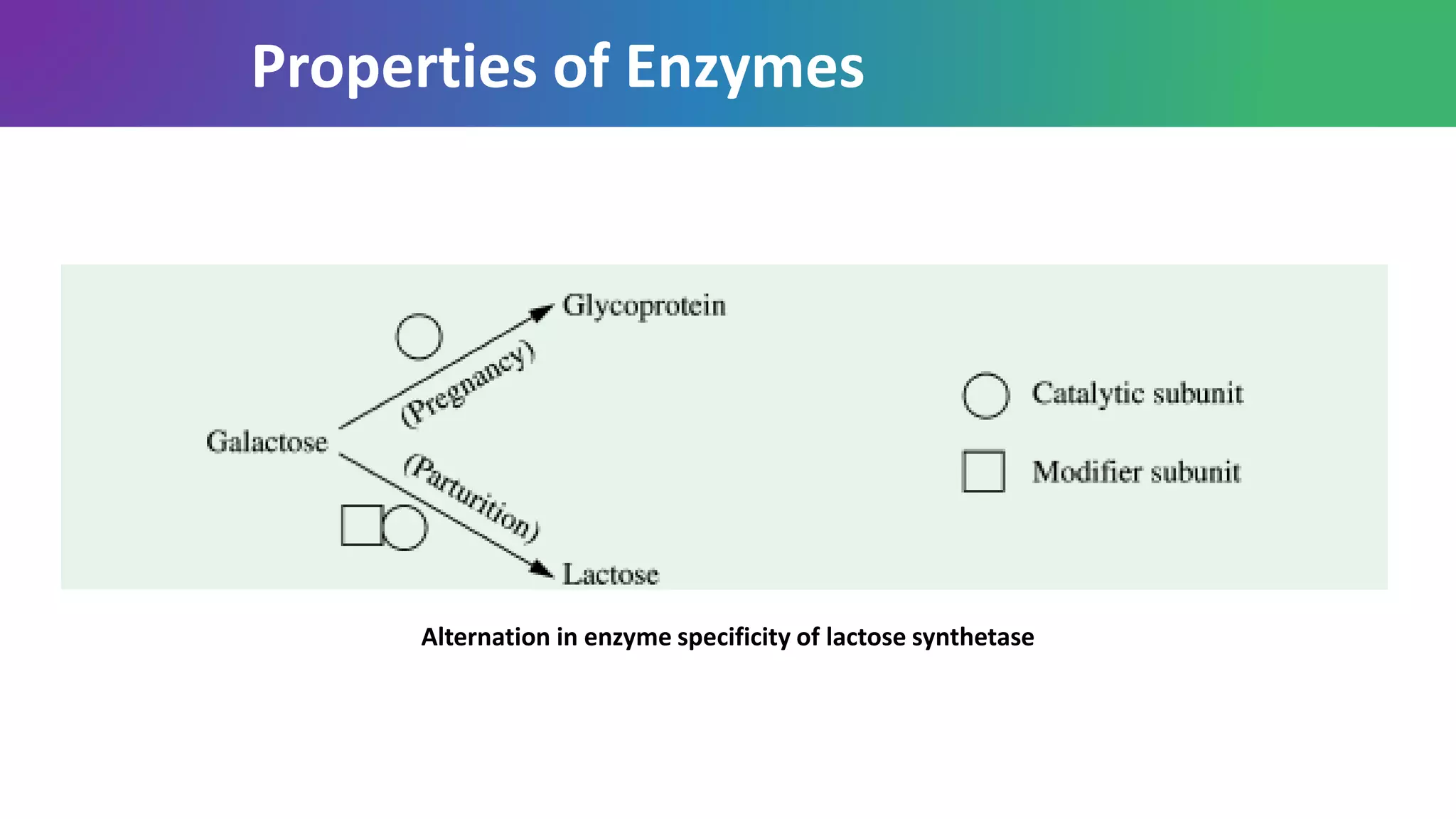
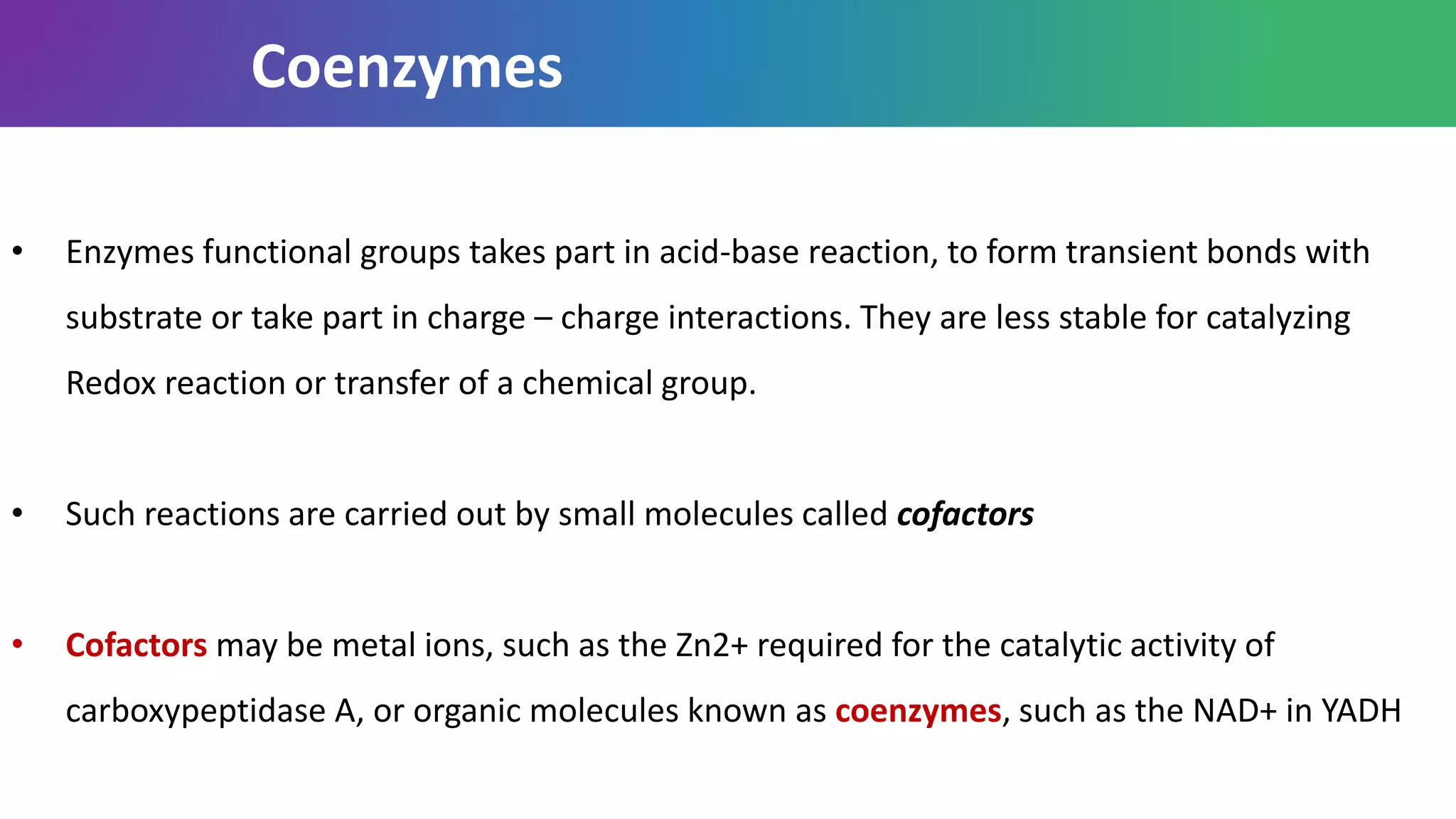
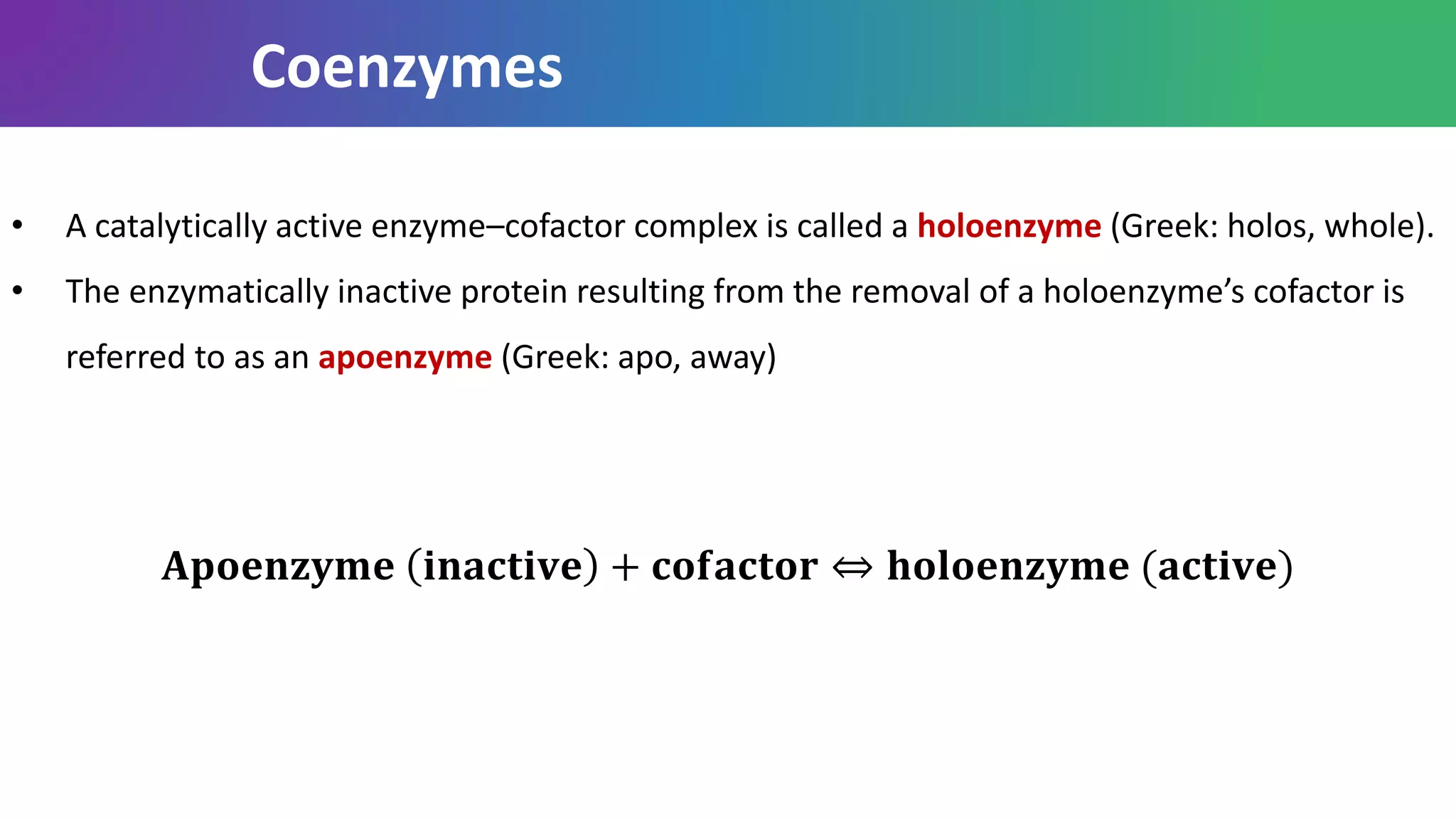
Enzymes are biological catalysts that are highly specific and efficient in facilitating chemical reactions in living cells without altering equilibrium points, differing from simple catalysts by being protein-based and contextually active. They are categorized into various classes, like oxidoreductases and transferases, with a nomenclature system to classify their functions, involving a unique EC number for each enzyme. Enzymatic efficiency is influenced by their active sites, which facilitate binding and catalysis, and their specificity can be altered by physiological conditions.



































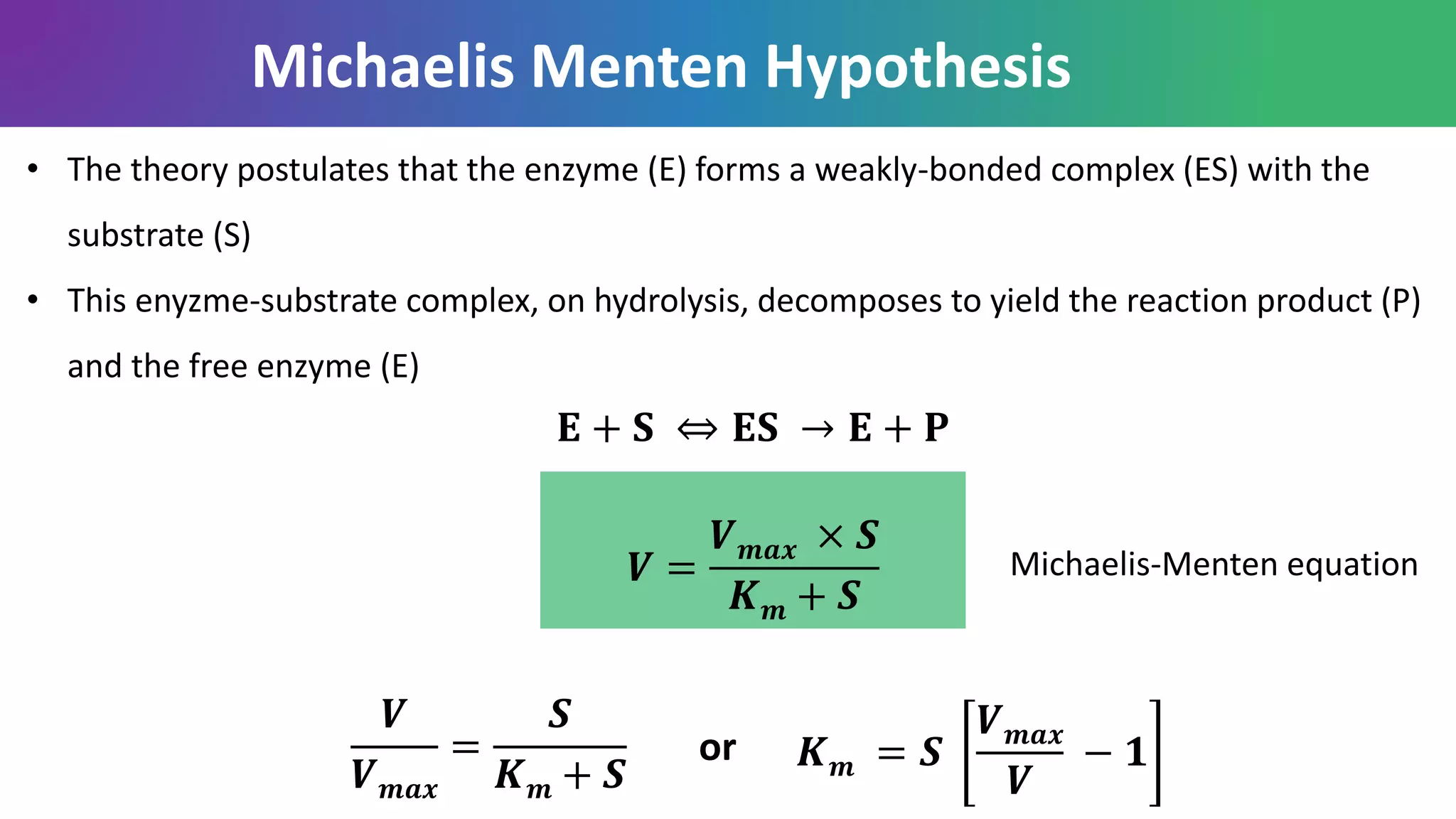



![• Km value is used as a measure of an enzyme’s affinity for its substrate. The lower the Km
value the higher the enzyme’s affinity for the substrate and vice versa
• Km value also provides an idea of the strength of binding of the substrate to the enzyme
molecule. The lower the Km value the more tightly bound the substrate is to the enzyme
for the reaction to be catalyzed and vice versa.
• Km value indicates the lowest concentration of the substrate [S] the enzyme can
recognize before reaction catalysis can occur.
Significance of Km and Vmax value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzyme-191130180618/75/Enzyme-57-2048.jpg)
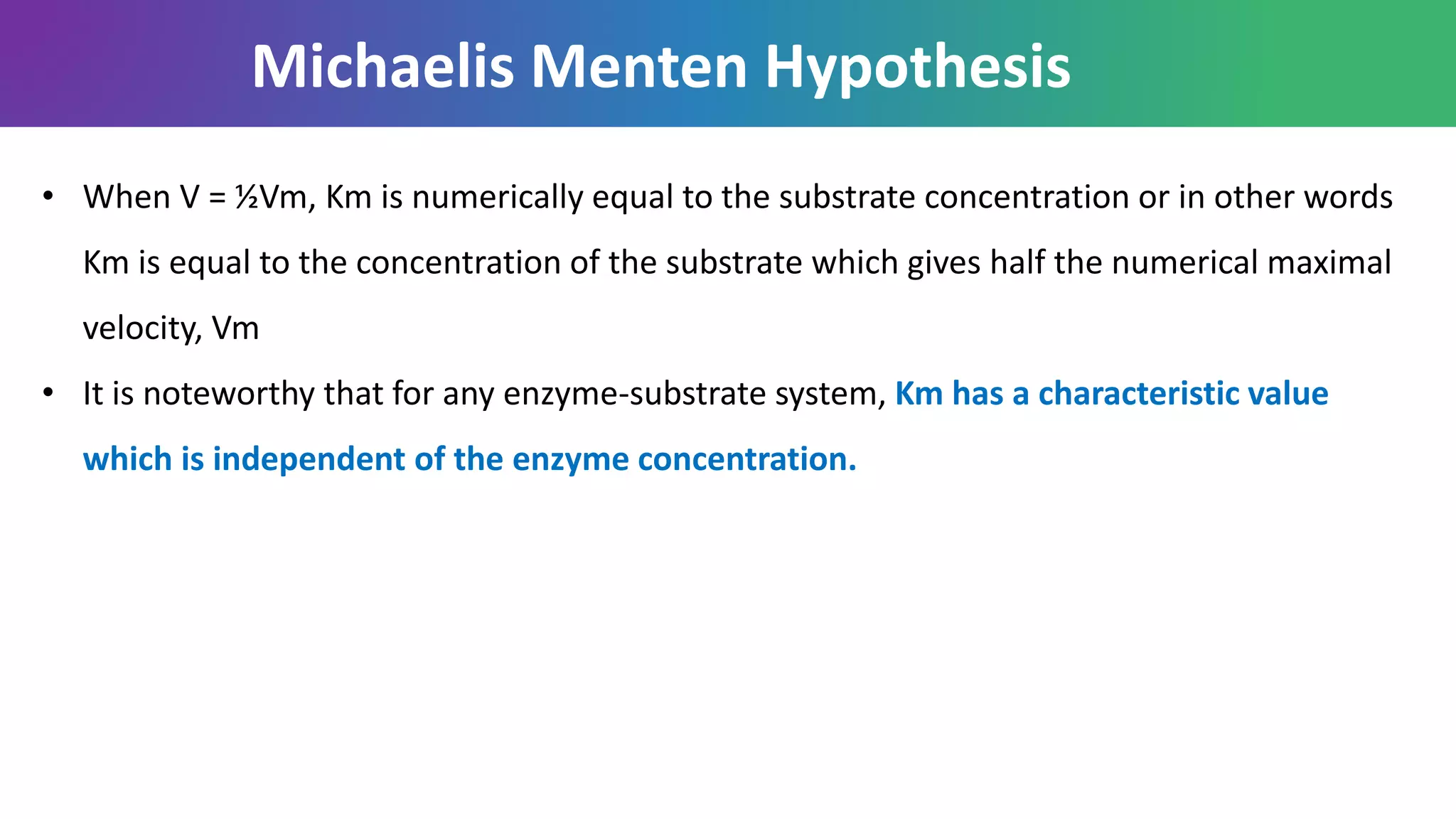
![• An enzyme's Km describes the substrate concentration at which half the enzyme's active
sites are occupied by substrate
• Km value is also used as a measure of the substrate concentration [S] when the reaction
rate half maximal velocity (50%). i.e Km = [S] at ½ Vmax.
• The maximal rate (Vmax) reveals the turnover number of an enzyme i.e. the number of
substrate molecules being catalysed per second. This varies considerably from 10 in the
case of lysozyme to 600,000 in the case of carbonic anhydrase.
Significance of Km and Vmax value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzyme-191130180618/75/Enzyme-58-2048.jpg)