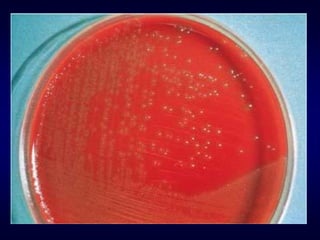
The document discusses Enterococci, including its natural habitats, morphology, general properties, medically important species, culture characteristics, virulence factors, pathogenicity, laboratory diagnosis, biochemical tests, Lancefield grouping, antibiotic resistance, and treatment options. Key points include that Enterococci normally inhabit the intestinal tract, oral cavity, and vaginal canal of humans and animals. The most common medically important species that cause nosocomial infections are Enterococcus faecalis and E. faecium. Laboratory identification involves culture, biochemical tests like catalase and sugar fermentation reactions, and determining Lancefield grouping. Antibiotic resistance is a concern, especially for vancomycin and penicillin.