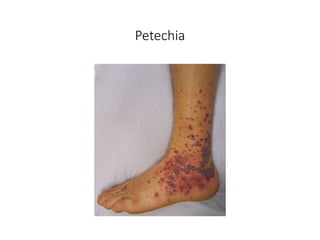
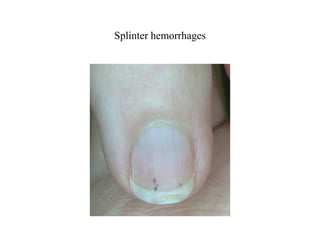
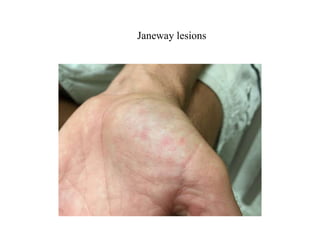
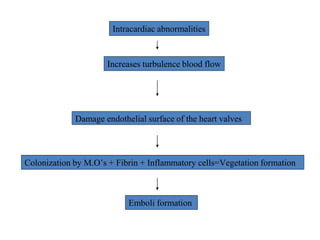
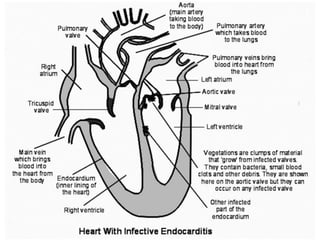
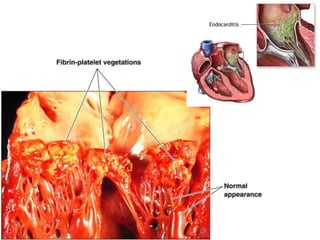
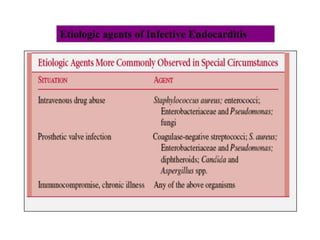
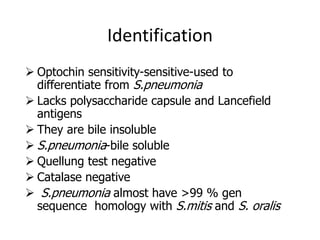
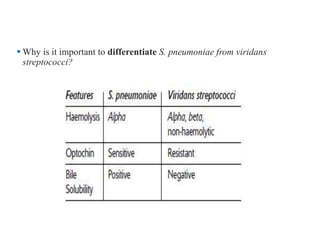
Viridans streptococci are a group of commensal bacteria that normally inhabit the mouth and gastrointestinal tract. They are a common cause of subacute bacterial endocarditis, in which the bacteria enter the bloodstream through small mucosal lesions and colonize on damaged heart valves, forming vegetations. While usually harmless commensals, certain species like S. gordonii and S. sanguis are pathogenic and known to cause subacute bacterial endocarditis. It is important to differentiate viridans streptococci from other streptococcal species like S. pneumoniae because they require different treatment approaches. Enterococci are another group of bacteria including E. faecalis and E. faecium