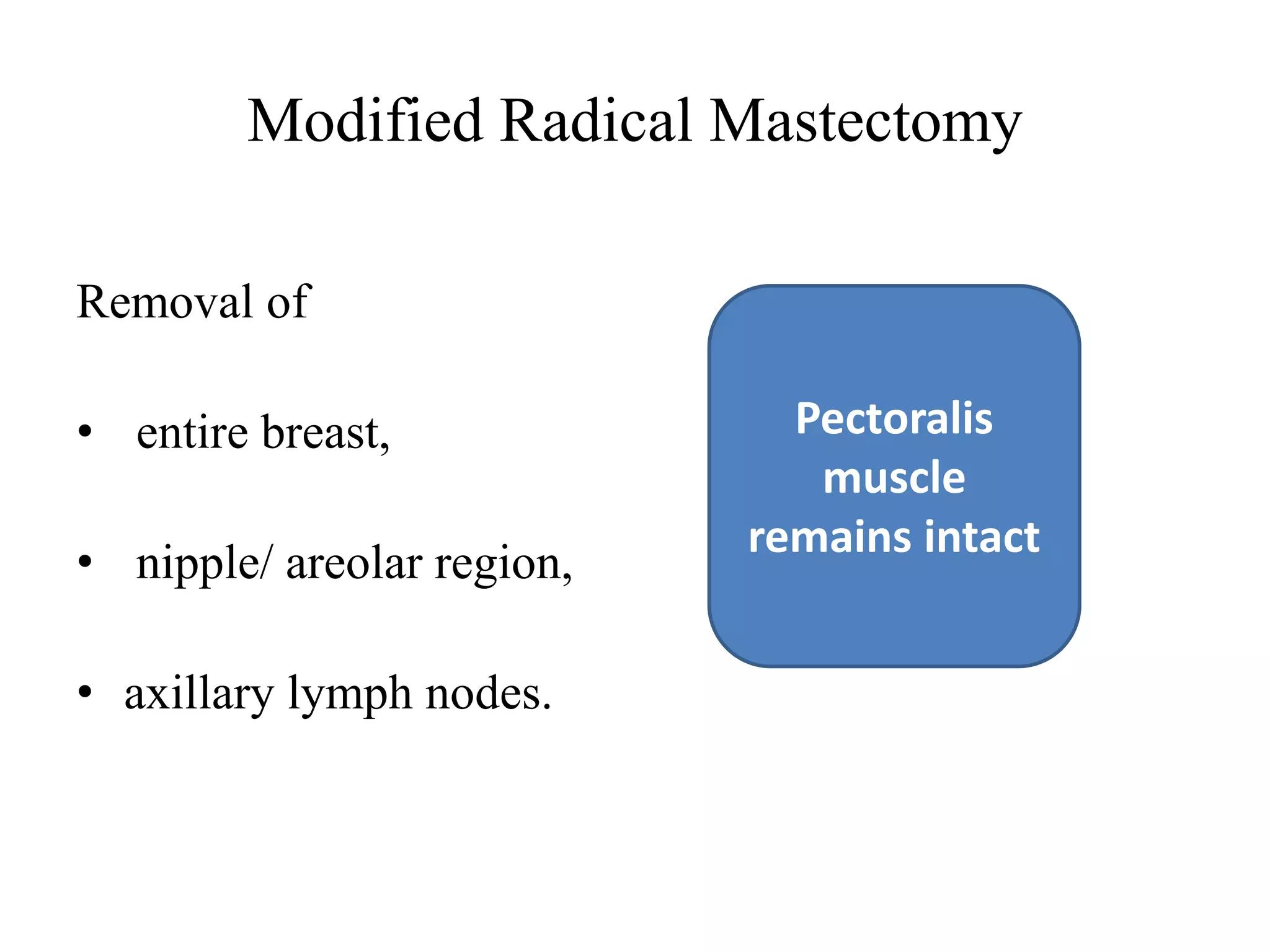
The document is a comprehensive presentation on physiotherapeutic management following radical mastectomy, aimed at final year bachelor of physiotherapy students. It covers various aspects of post-operative care, including assessment methods, therapeutic management techniques, and patient education regarding do’s and don’ts. Key topics include types of mastectomy, common postoperative issues, and management strategies to promote recovery and prevent complications.