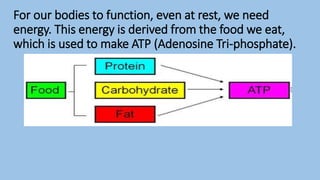
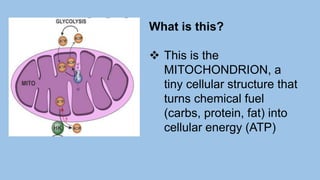
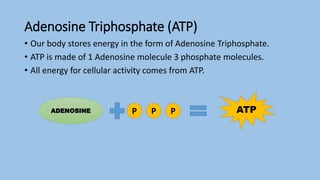
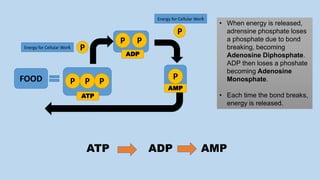
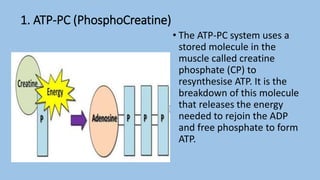
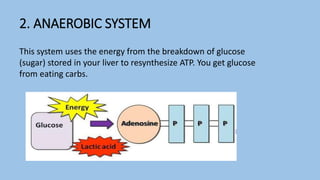
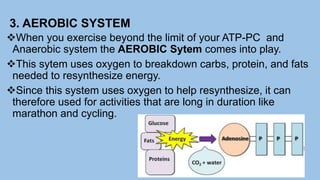
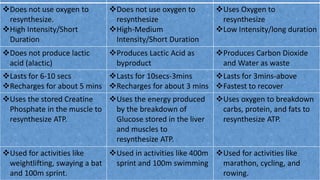
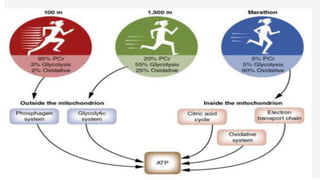
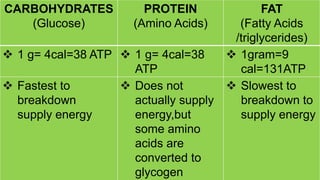
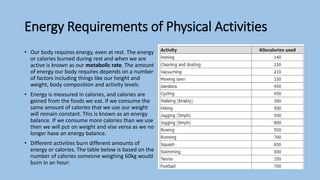
This document discusses human energy systems and how the body converts food into energy for movement and activity. It covers the three main energy systems - ATP-PC, anaerobic, and aerobic. The ATP-PC system provides immediate energy through phosphocreatine stores but lasts only 10 seconds. The anaerobic system breaks down glucose without oxygen and fuels activity for 10 seconds to 3 minutes. The aerobic system uses oxygen to break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, fueling longer duration lower intensity activities. Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are all sources of stored energy and calories that can be broken down to synthesize ATP through cellular respiration.