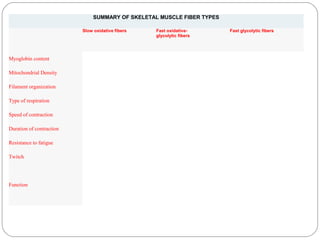
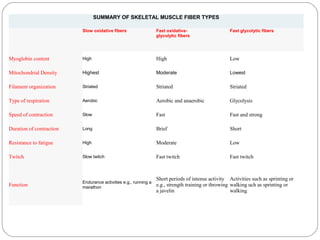
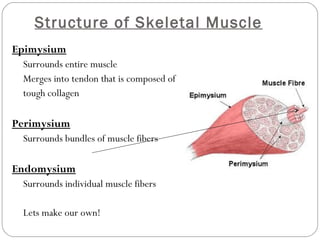
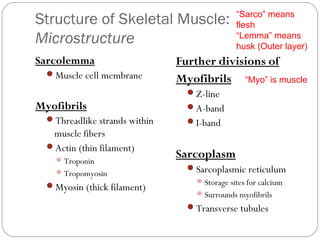
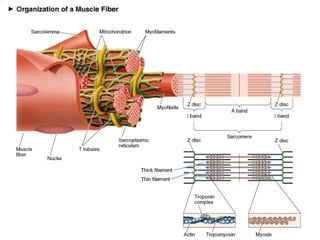
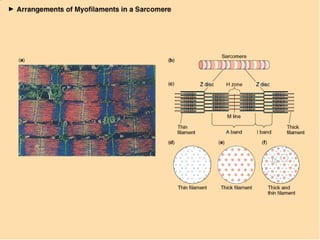
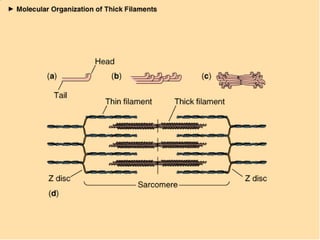
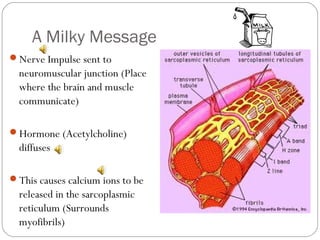
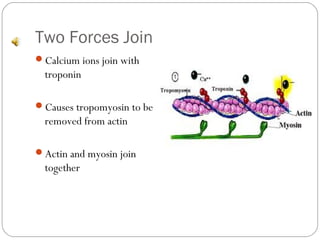
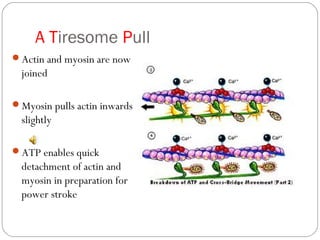
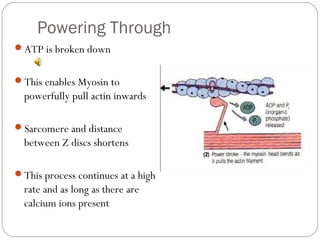
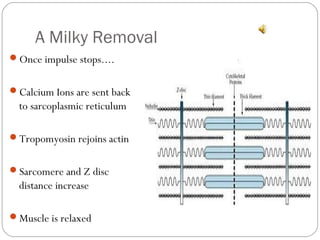
The document describes the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction. It explains that muscle shortening occurs when the actin filament slides over the myosin filament, reducing the distance between Z-lines in the sarcomere. It further describes the roles of calcium ions, tropomyosin, troponin, actin, myosin and ATP in the cross-bridge cycling that enables the sliding filament movement and generates force. It also mentions the all-or-none law, where a muscle fiber will contract fully or not at all in response to an impulse.