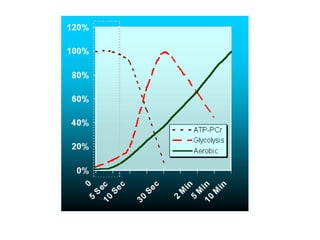
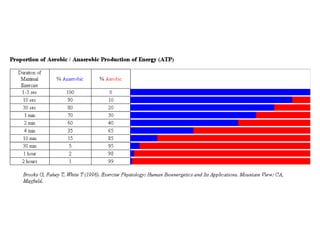
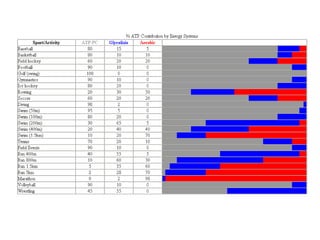
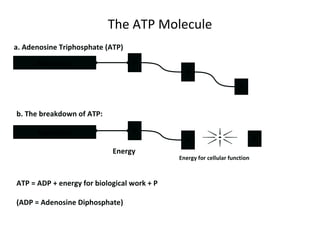
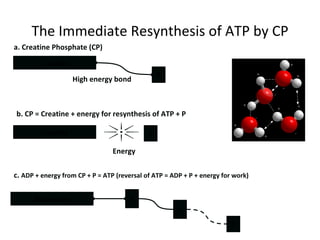
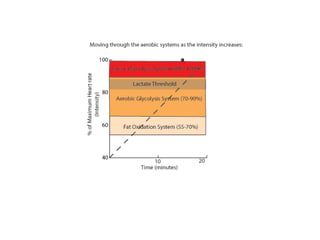
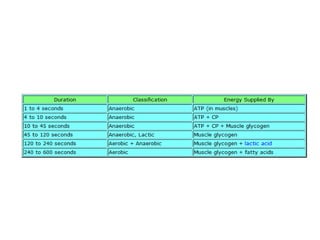
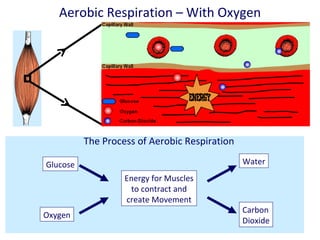
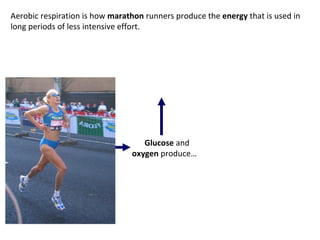
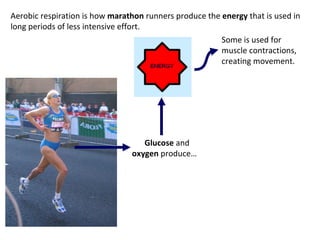
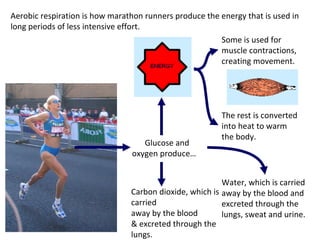
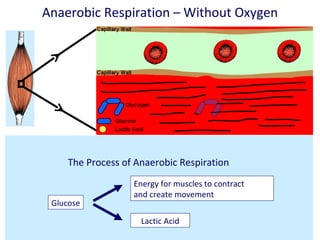
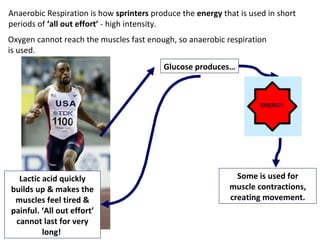
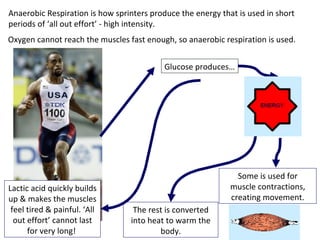
The human body uses three main energy systems - the ATP-PCr system, anaerobic glycolysis, and oxidative phosphorylation - to produce energy for muscle contraction. The ATP-PCr system provides energy for intense bursts of activity lasting up to 10 seconds. Anaerobic glycolysis is used for activities lasting 20 seconds to 2 minutes and produces lactic acid as a byproduct. Oxidative phosphorylation provides virtually unlimited energy through aerobic metabolism for endurance activities lasting several minutes or more.