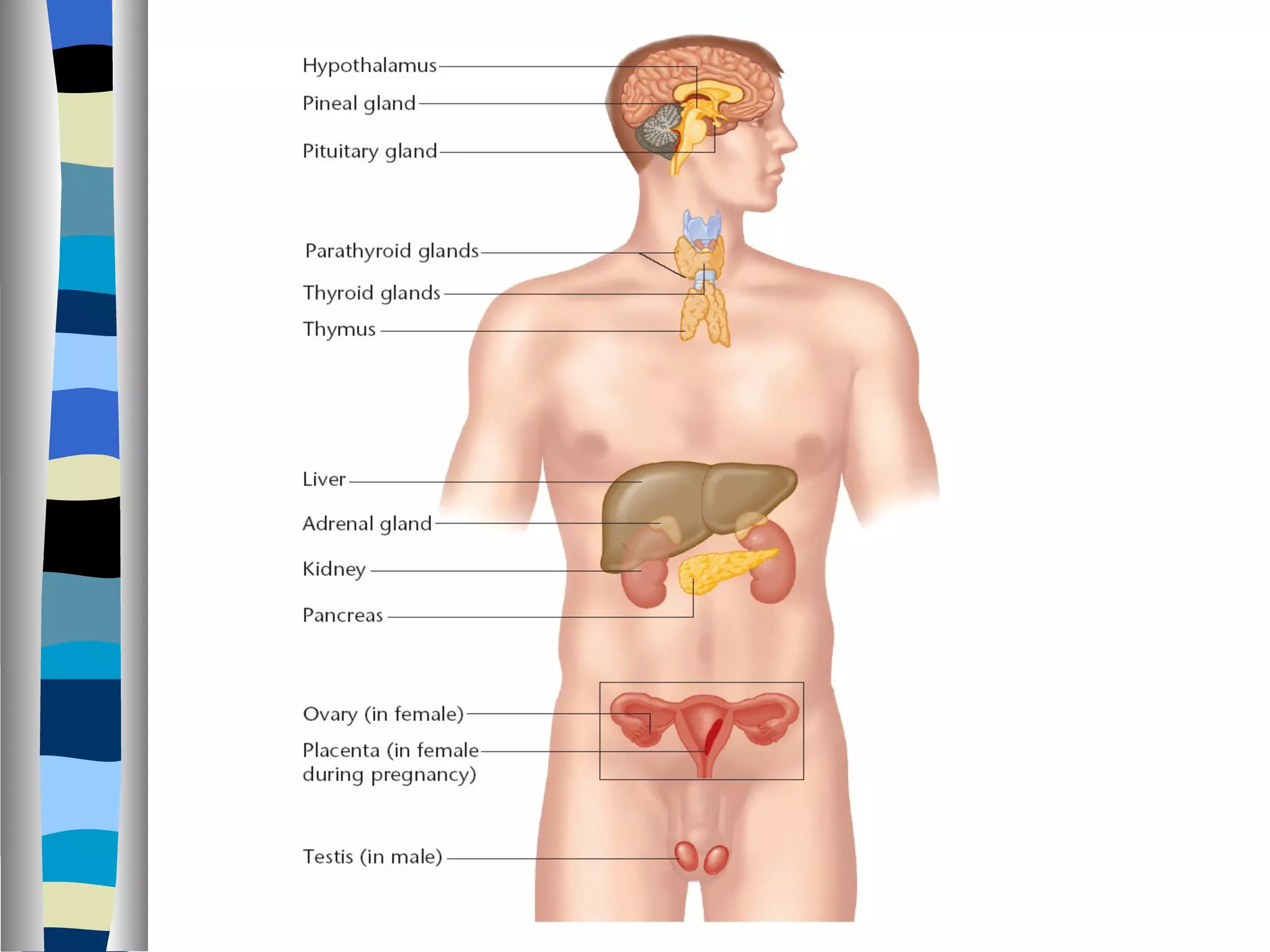
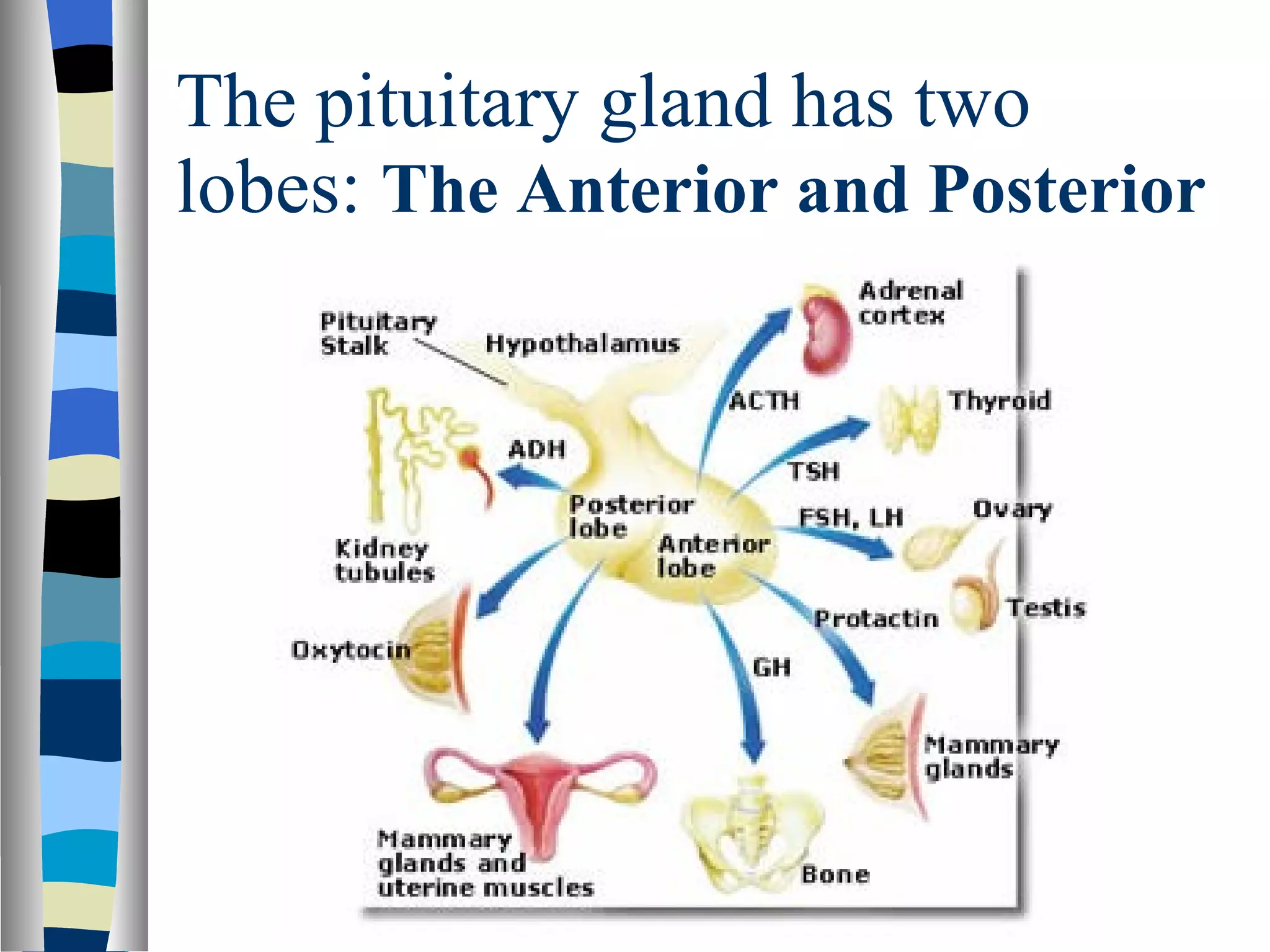
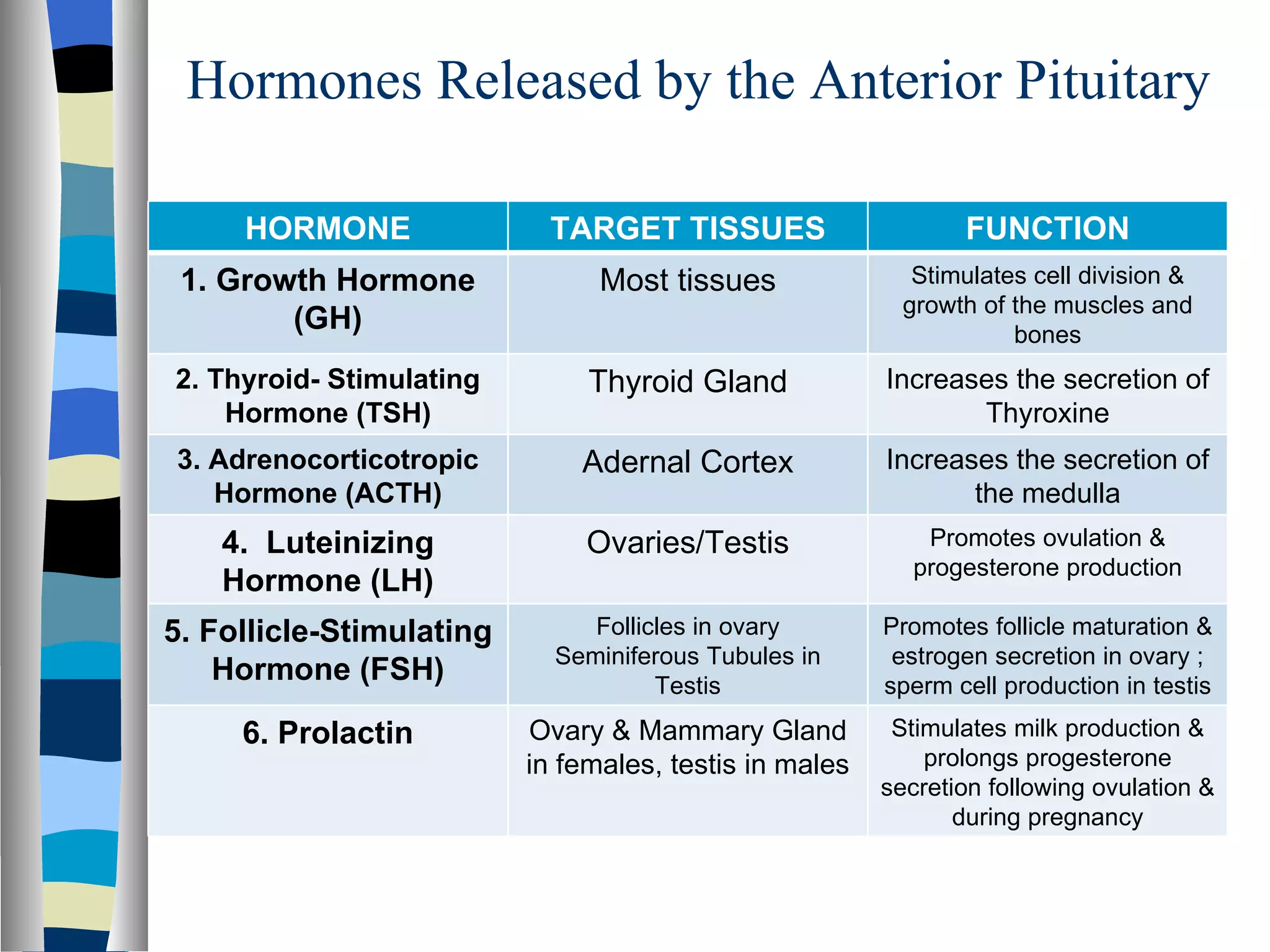
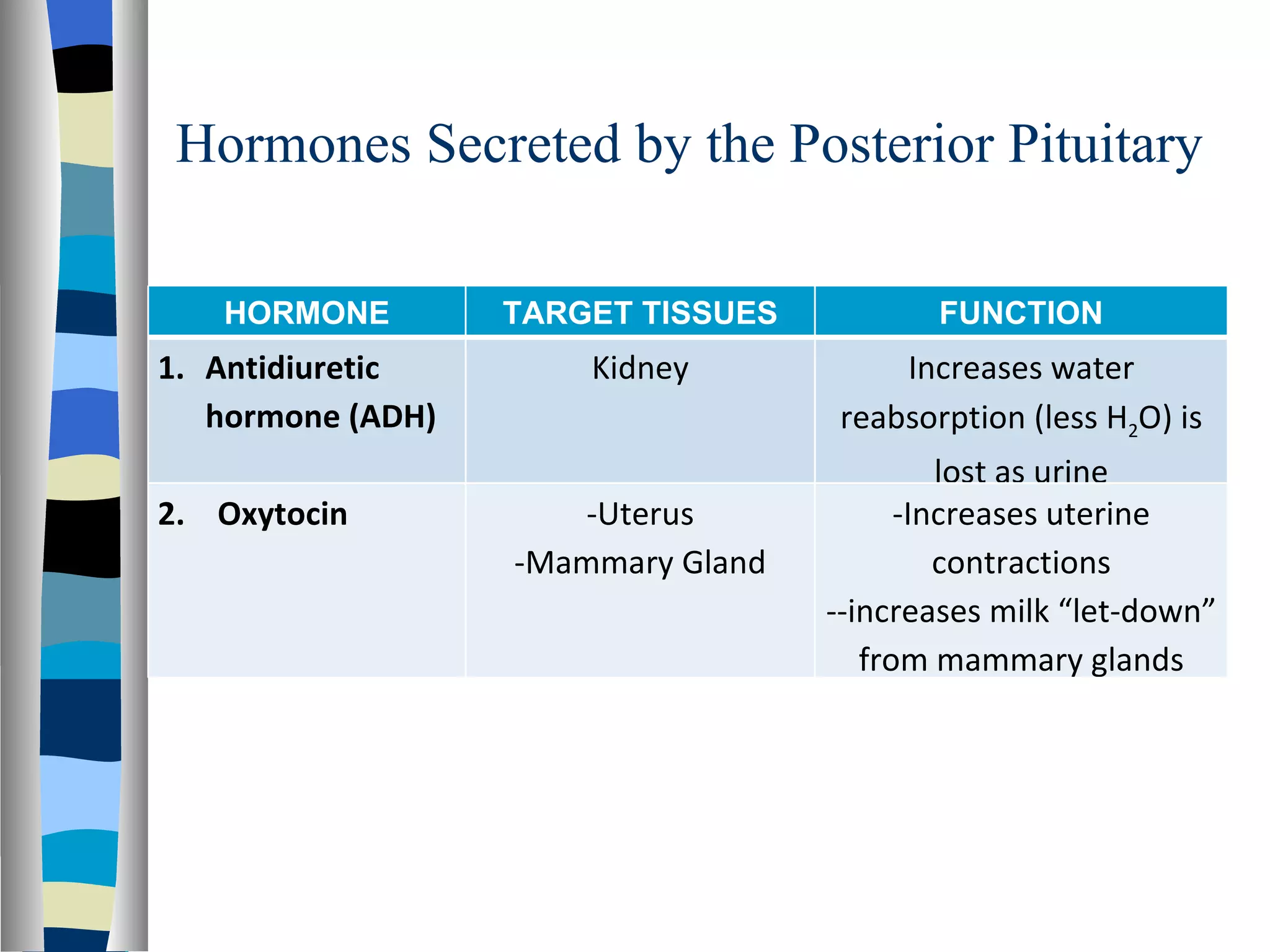
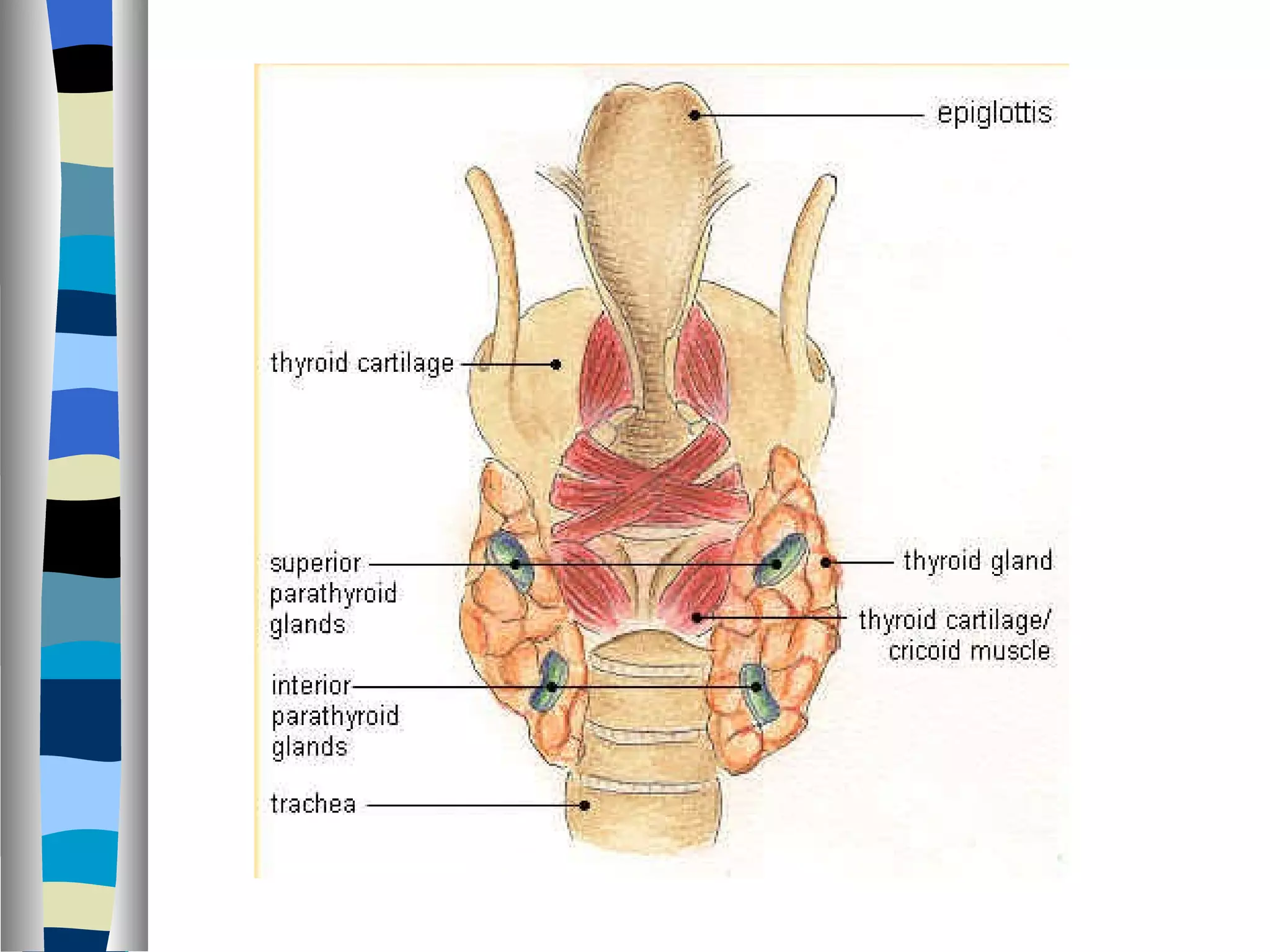
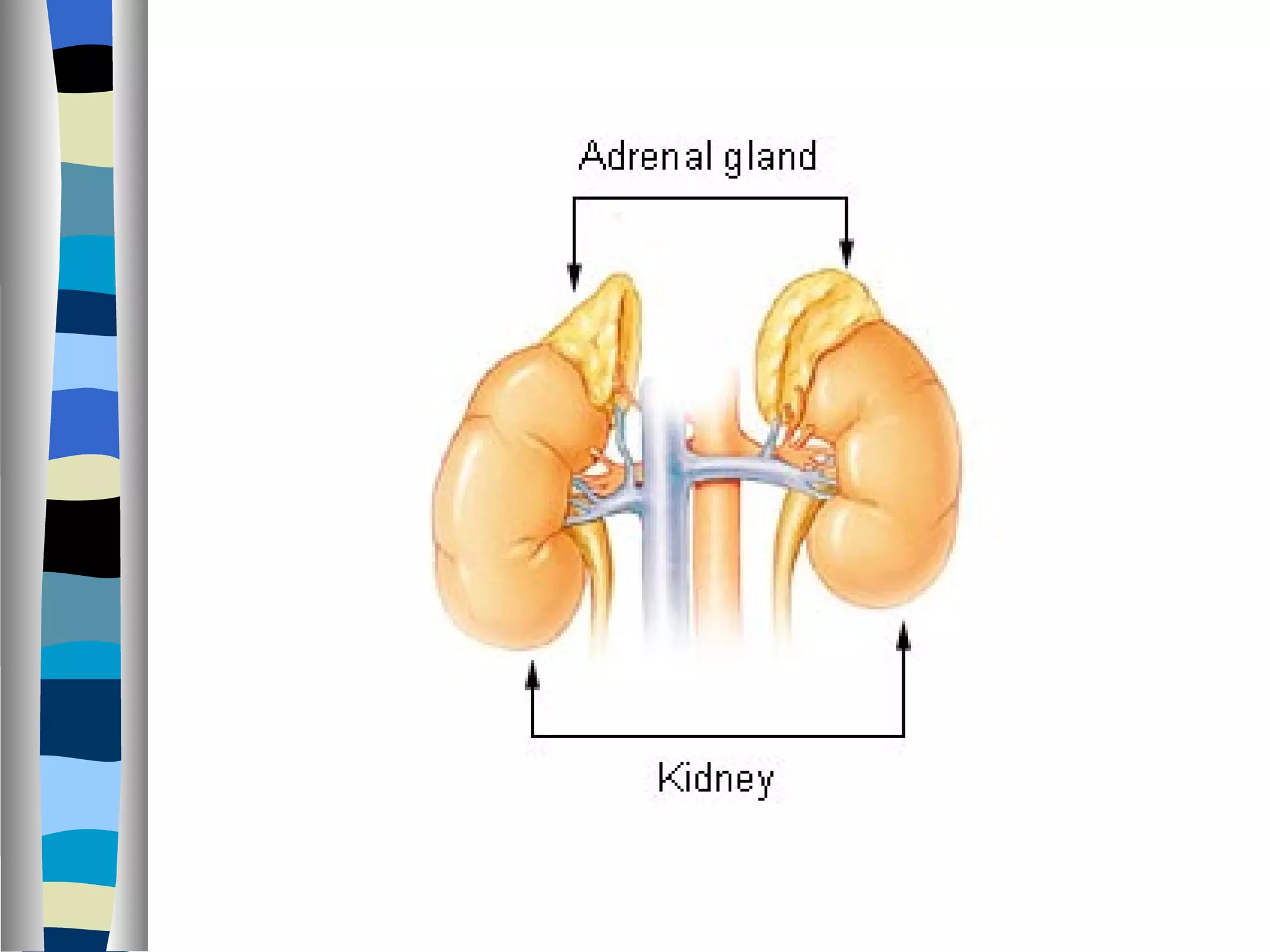
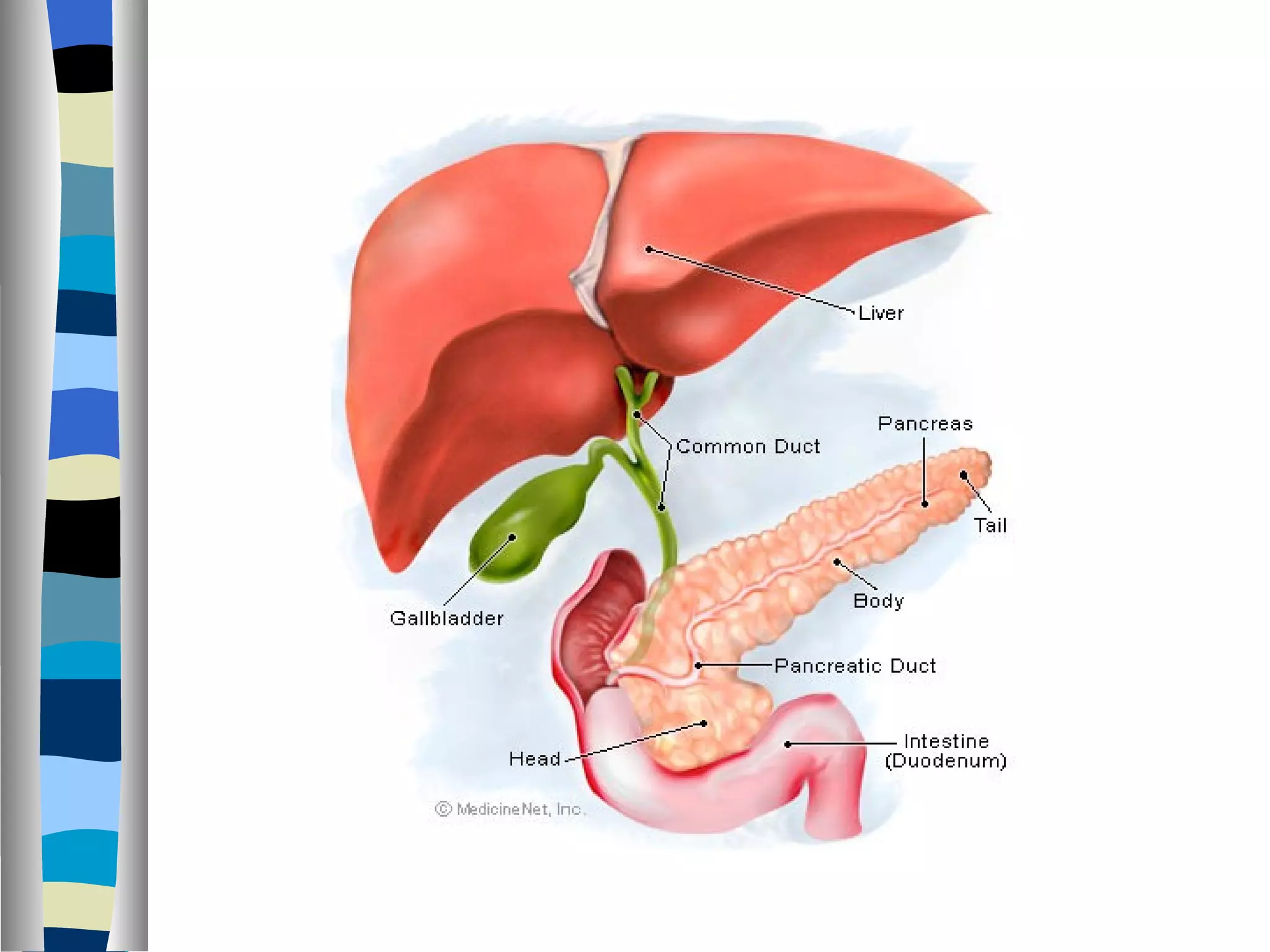
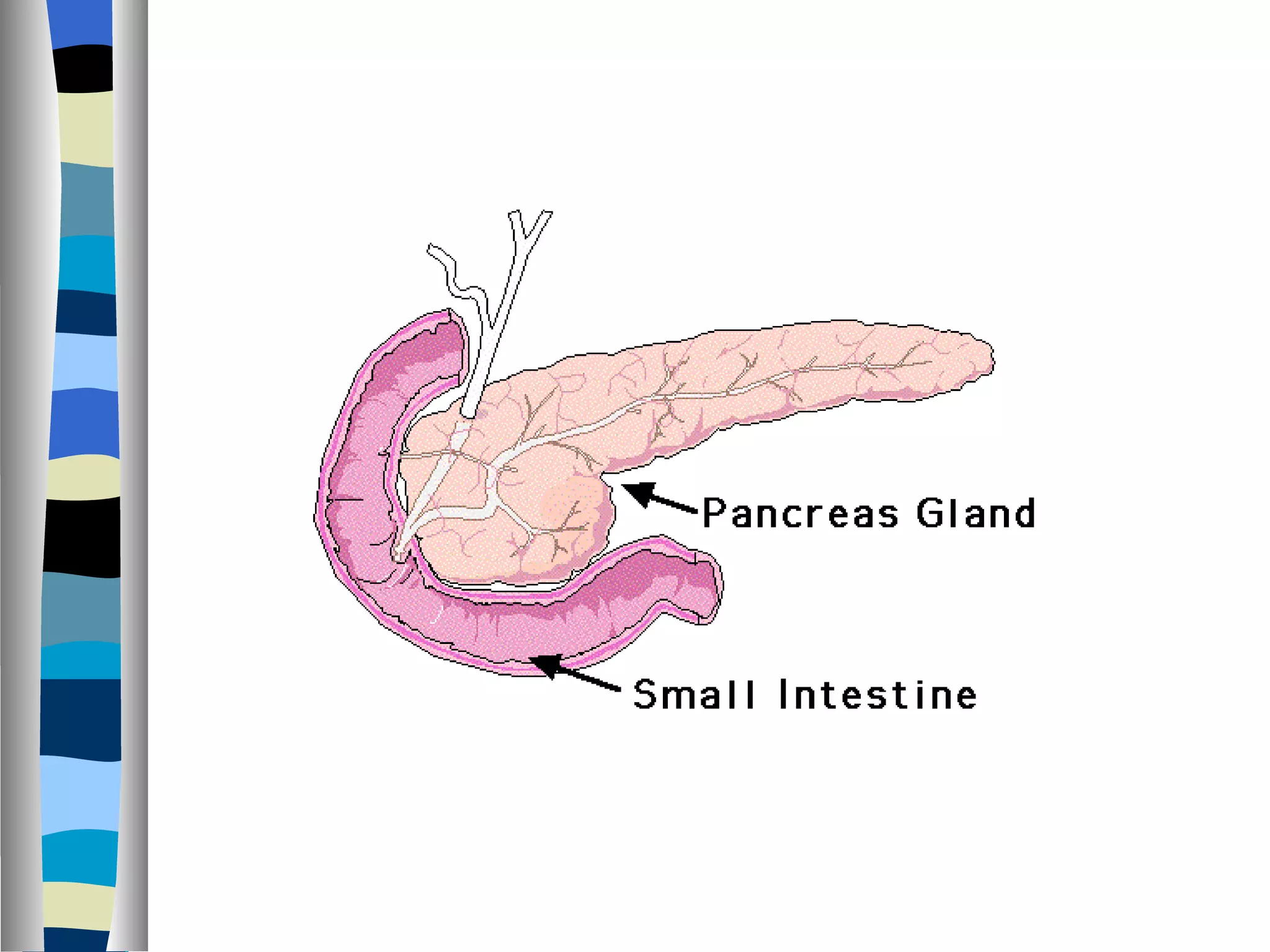
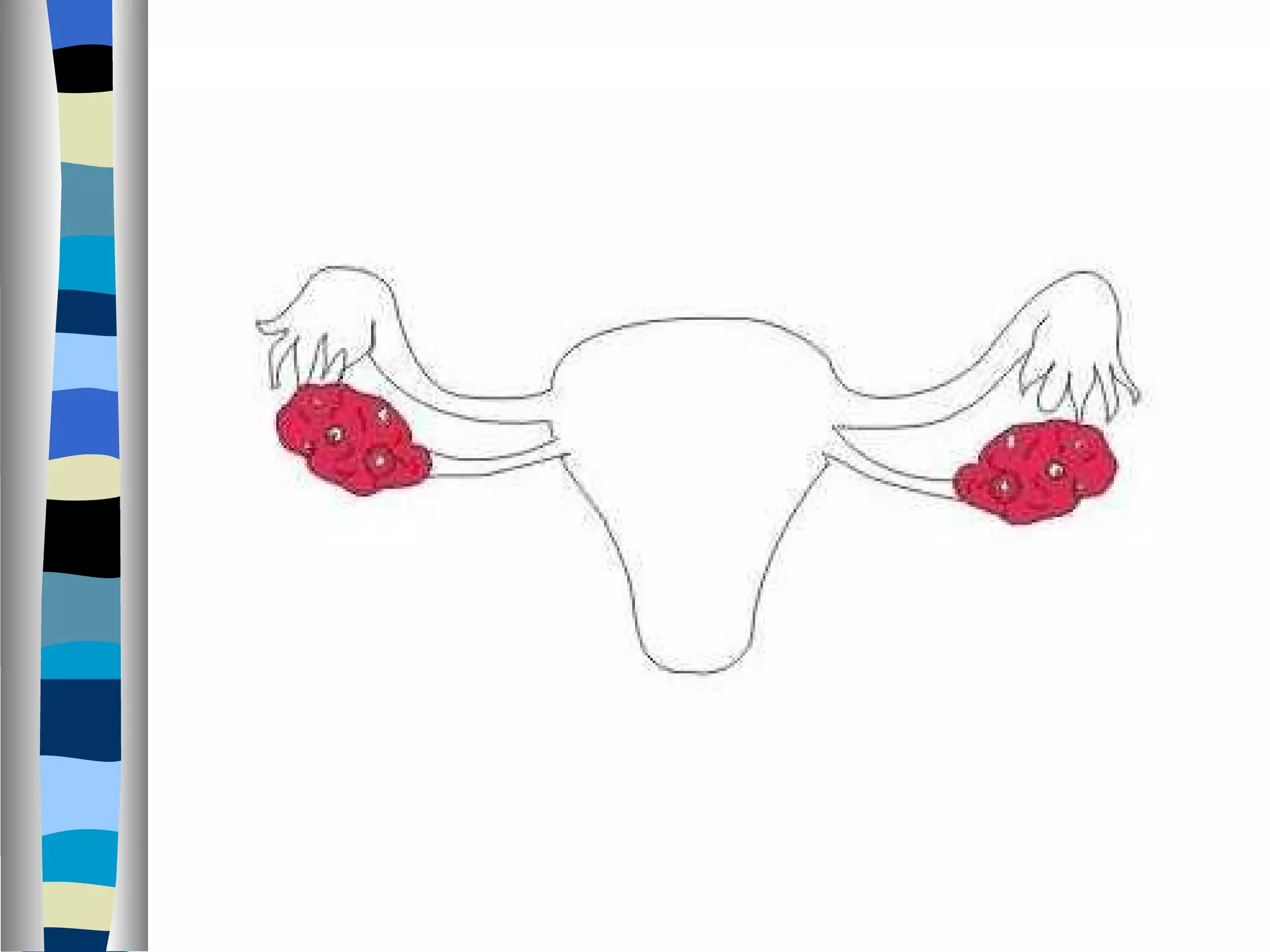
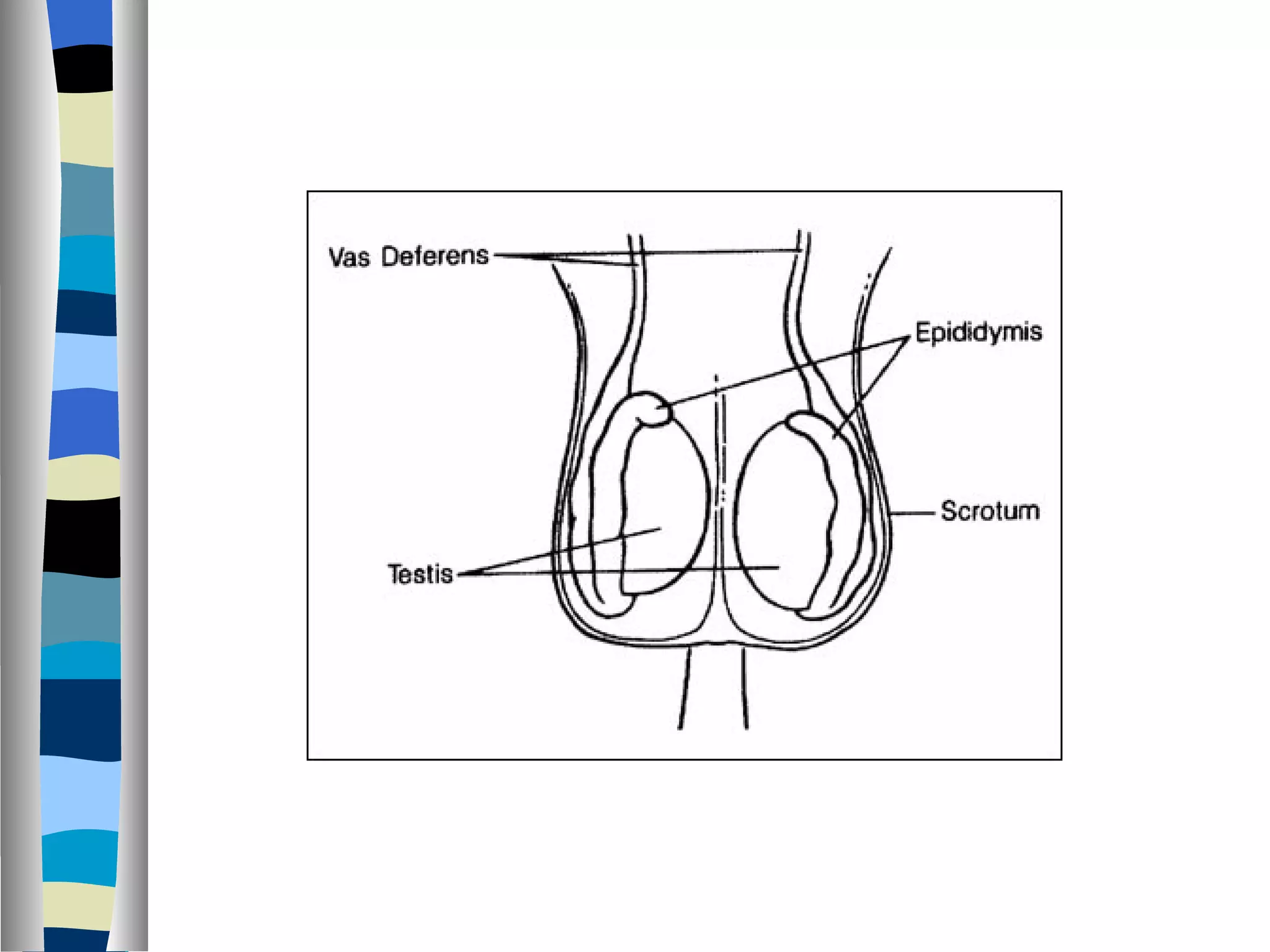
The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce hormones. The pituitary gland, called the "master gland," controls many of the other endocrine glands and produces several important hormones. Other major glands include the thyroid, which produces hormones that regulate metabolism, the adrenals, which produce hormones such as adrenaline, and the ovaries and testes, which produce sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone. Each endocrine gland releases different hormones that target various tissues and organs to regulate many essential body functions.