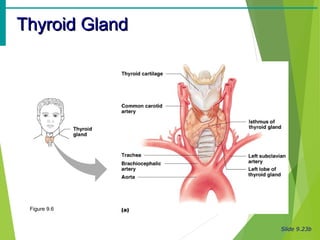
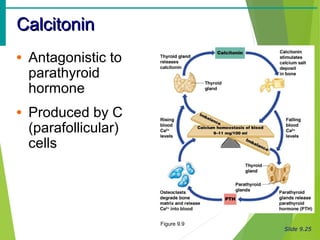
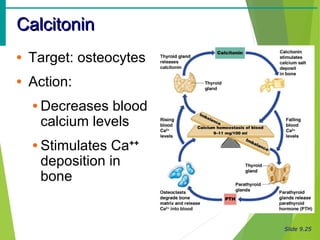
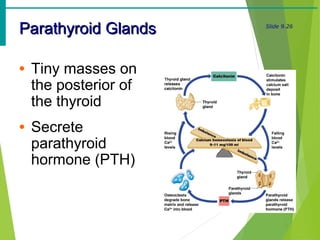
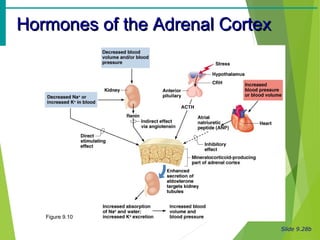
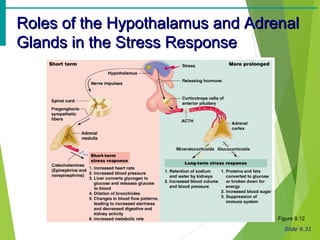
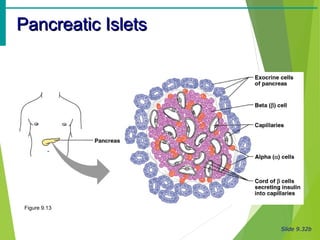
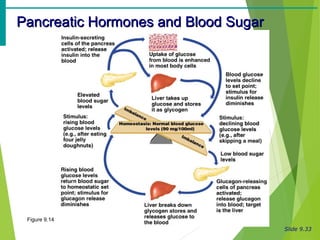
The document summarizes the major endocrine glands and hormones in the human body. It describes the location and functions of the thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, pineal gland, ovaries, testes, placenta and other minor hormone producing tissues. The key hormones produced by each gland are identified along with their targets and actions in regulating metabolism, growth, development, and other physiological processes throughout the body.