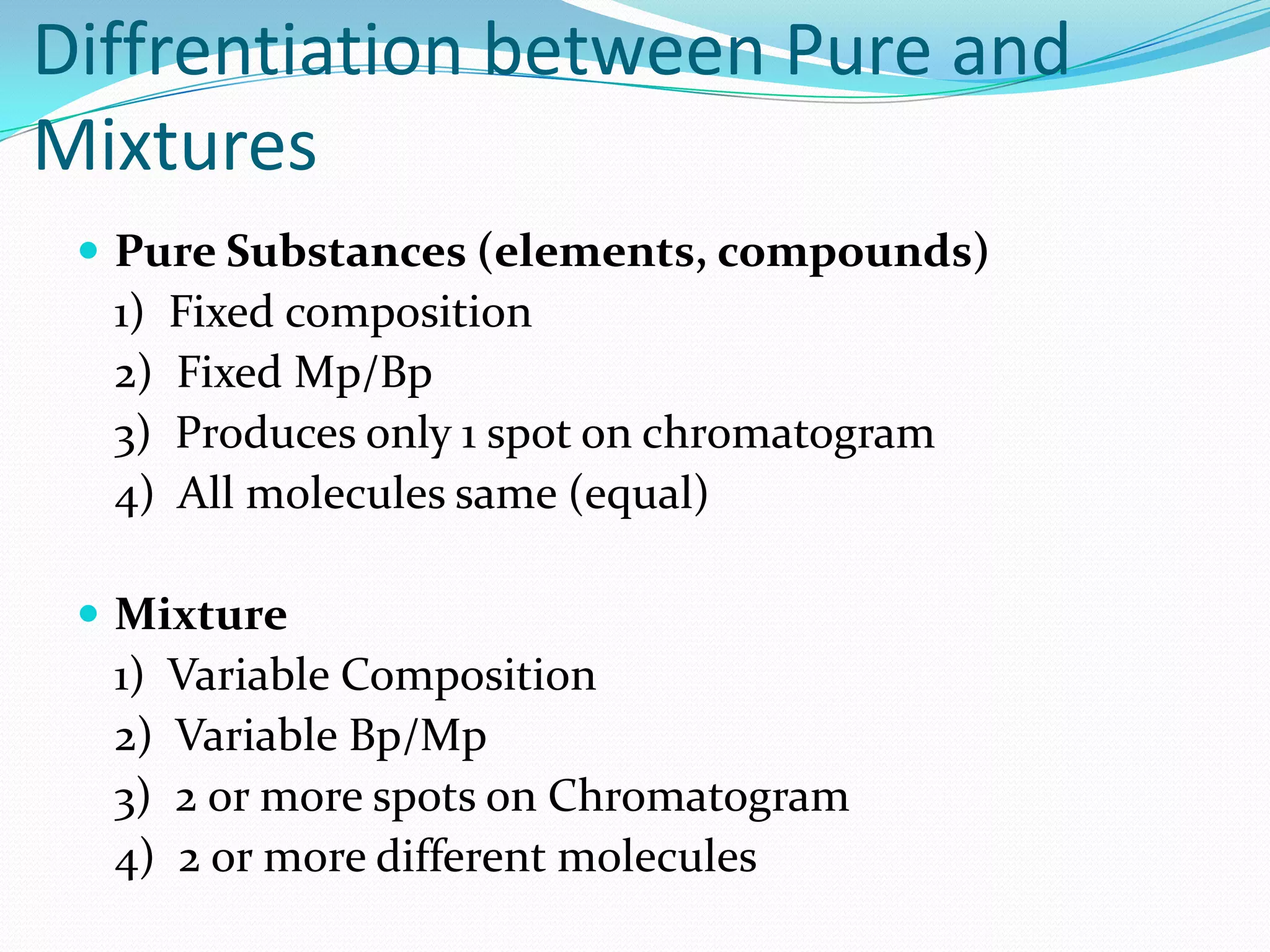
This document defines key chemistry concepts and differentiates between them. It explains that elements are substances that cannot be broken down further, and atoms are the smallest particles of elements. Compounds are formed by chemical combination of two or more elements. Mixtures contain two or more substances that are not chemically combined. The document outlines the differences between compounds and mixtures, noting that mixtures can be separated physically while compounds require chemical means to separate constituent elements. It also differentiates between pure substances and mixtures based on their composition and properties.