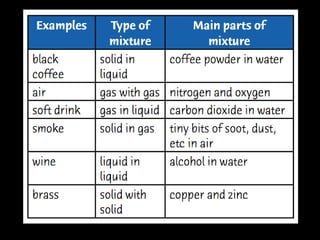
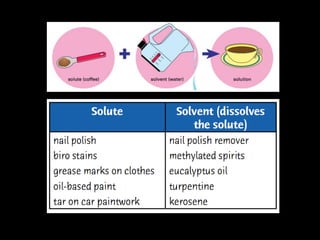
This document discusses various methods for separating mixtures, including:
- Crystallization to separate sugar from a soft drink by heating and evaporating water.
- Filtration to separate insoluble solids from liquids by passing the liquid through a filter.
- Distillation to separate liquids with different boiling points by evaporating and condensing them.
- Gravity separation to separate mixtures where components have different densities, like gold panning.
- Chromatography to separate colored substances in a mixture.