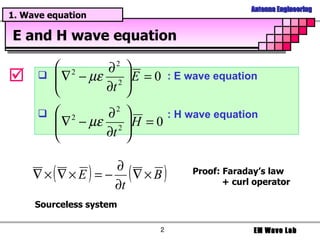
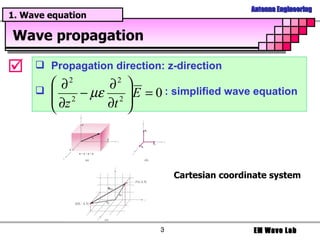
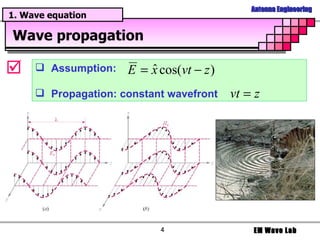
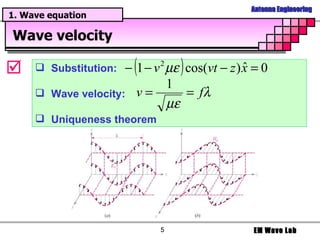
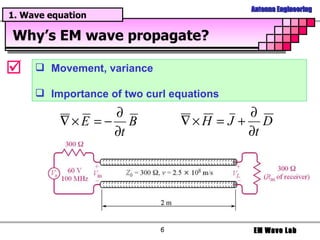
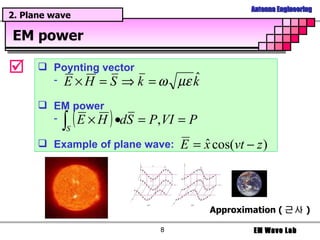
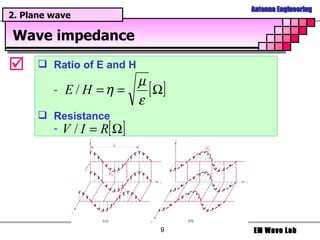
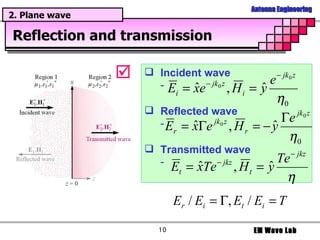
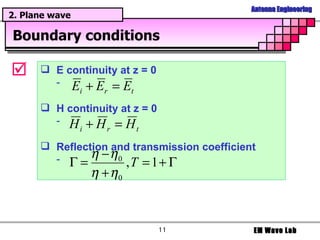
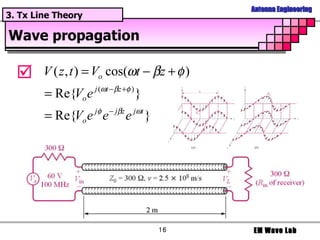
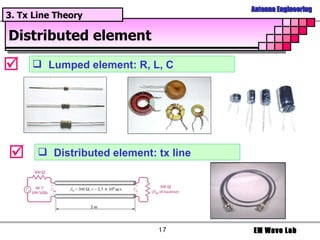
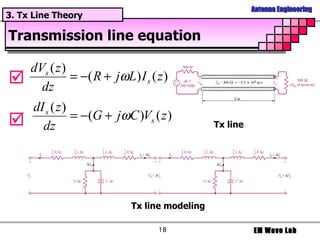
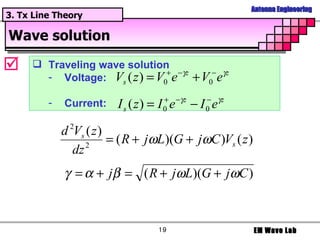
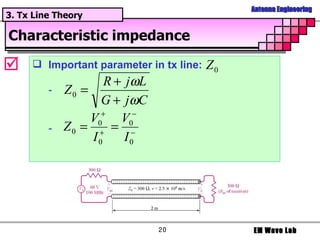
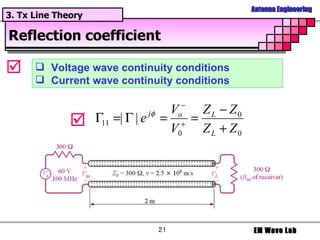
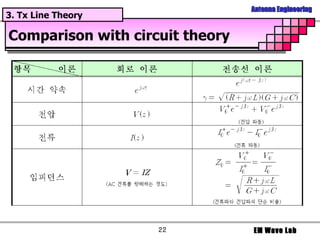
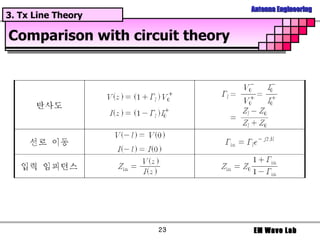
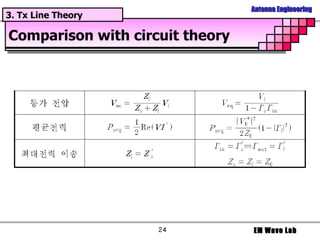
The document discusses antenna engineering and electromagnetic wave propagation, focusing on wave equations for electric and magnetic fields. It includes topics such as wavefront propagation, wave impedance, reflection and transmission coefficients, and various polarizations. Additionally, it explores transmission line theory and the comparison between distributed and lumped elements.