- Quantum theory proposes that atoms and molecules emit and absorb energy in discrete quantities called quanta, challenging the classical view that they behave like balls.
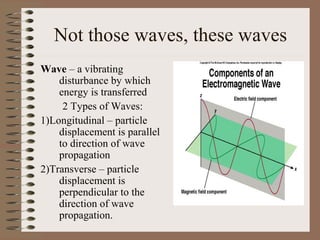
- There are two types of waves: longitudinal waves where particle displacement is parallel to propagation, and transverse waves where displacement is perpendicular.
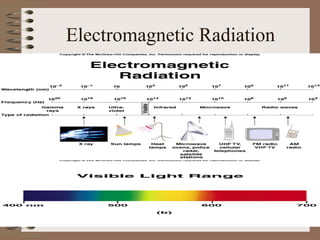
- The electromagnetic spectrum shows the difference in wavelength and frequency for different types of electromagnetic radiation, from radio waves to gamma rays. Microwaves use electromagnetic radiation at a frequency of 2.5 GHz to heat food by being readily absorbed by water.