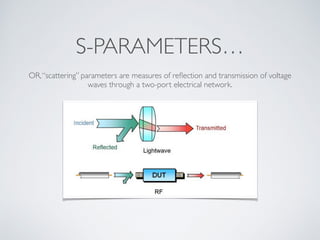
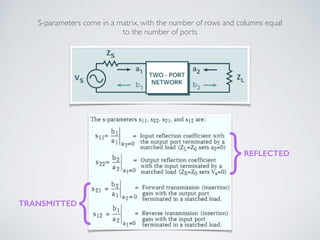
1. The document introduces microwave engineering concepts over 4 weeks, covering Maxwell's equations, plane wave solutions, propagation in lossy media, and S-parameters.
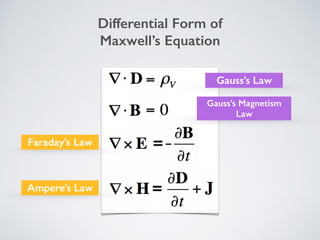
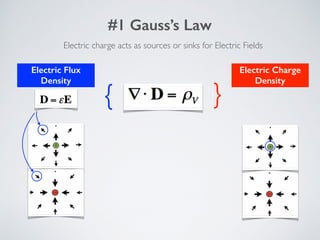
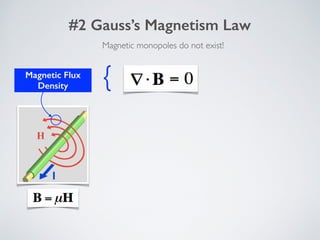
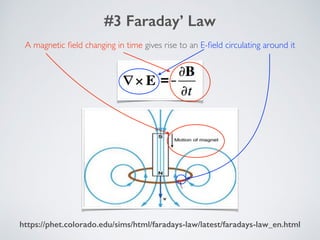
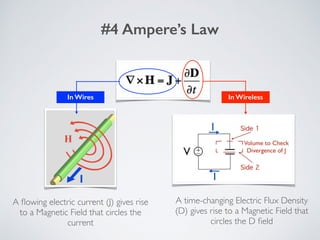
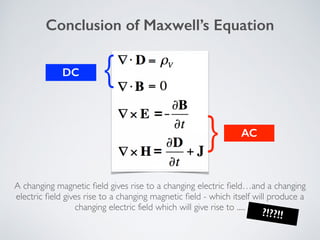
2. It describes applications of microwave engineering like wireless devices, 5G networks, satellite links, and direct broadcast. Maxwell's equations describe macroscopic electric and magnetic phenomena.
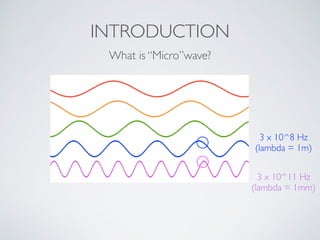
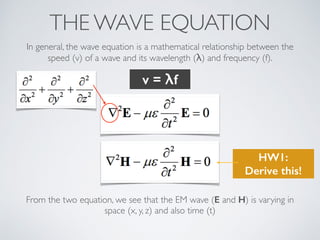
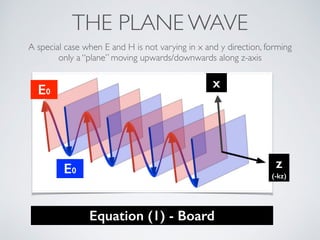
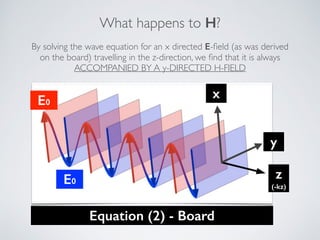
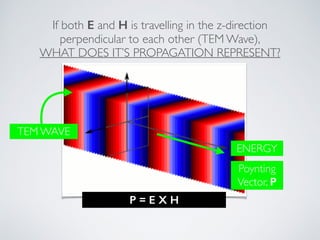
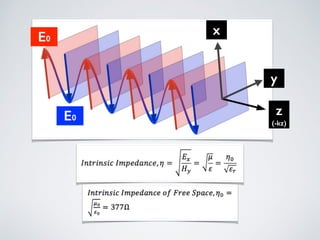
3. Plane waves have electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to the direction of propagation. The wave equation relates wavelength, frequency, and speed of waves. Plane waves in lossy media have complex propagation constants that cause amplitude changes over distance.