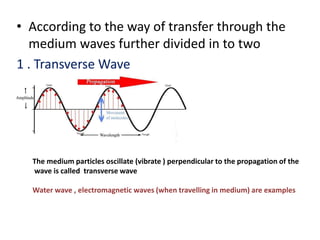
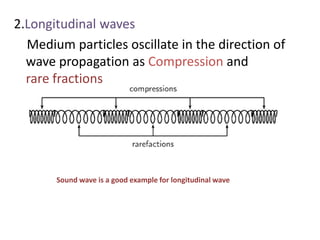
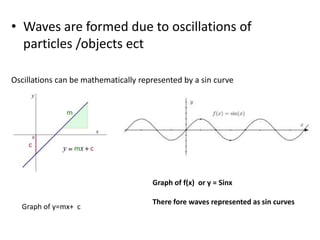
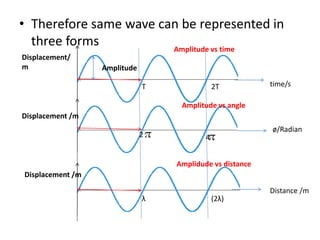
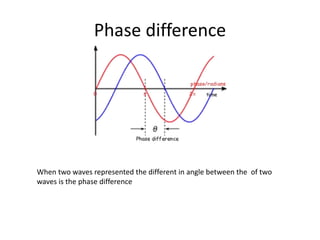
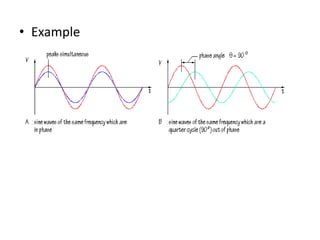
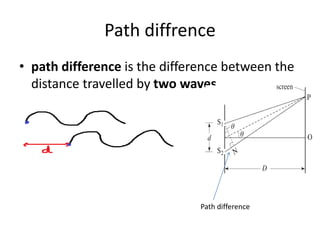
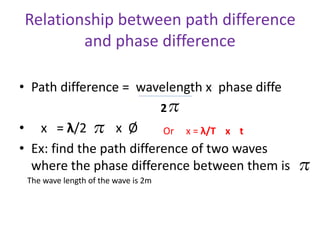
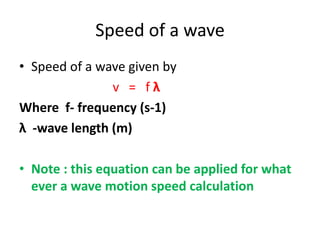
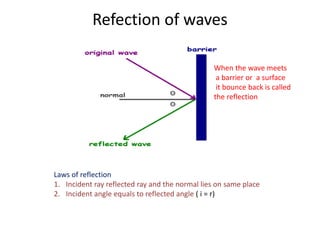
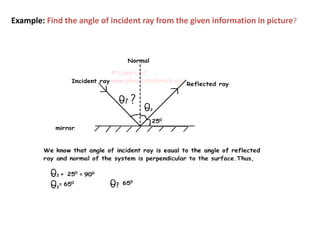
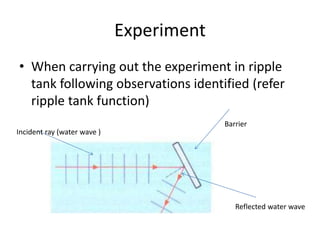
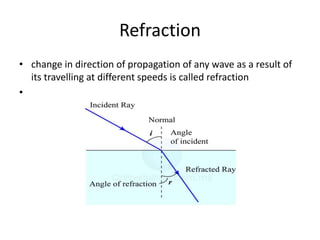
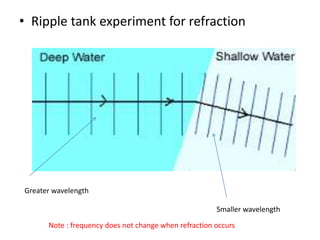
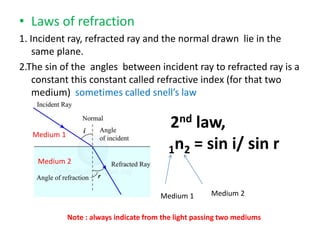
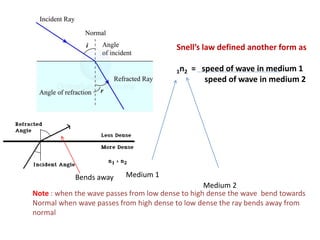
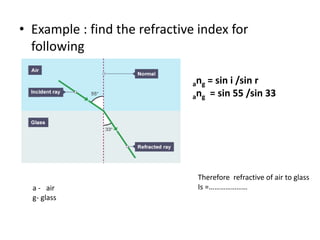
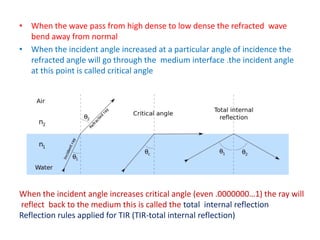
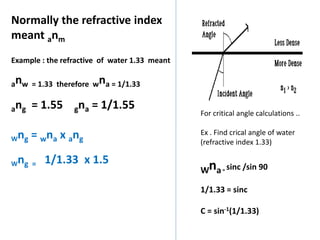
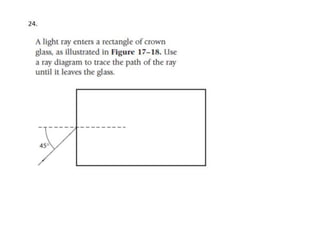
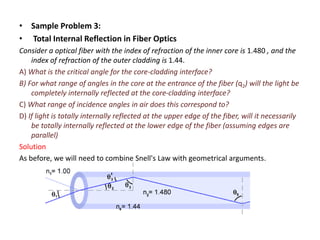
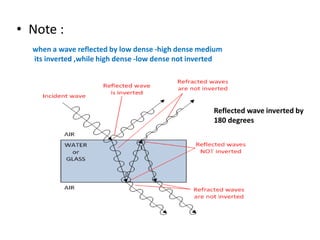
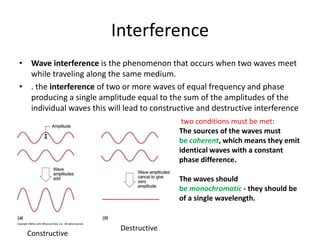
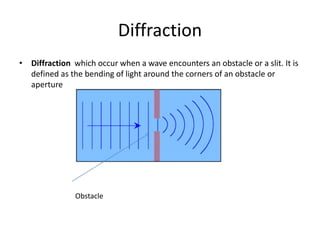
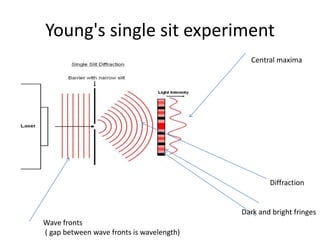
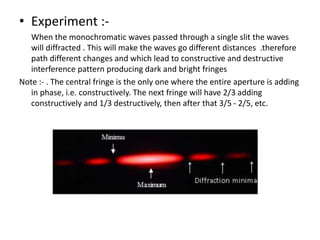
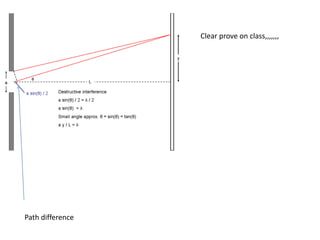
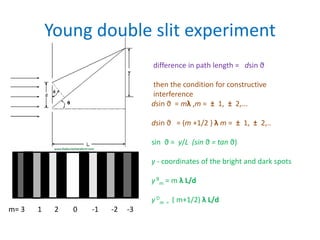
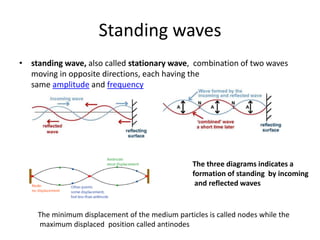
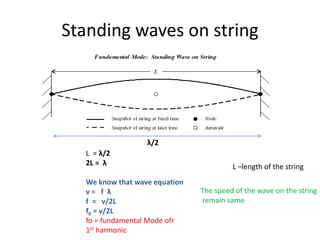
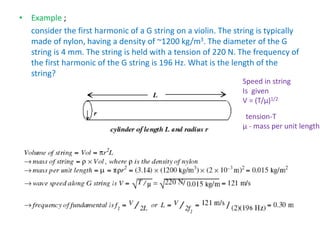
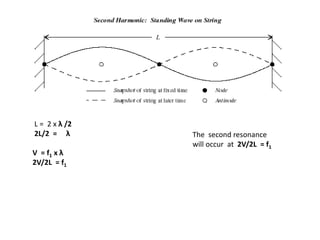
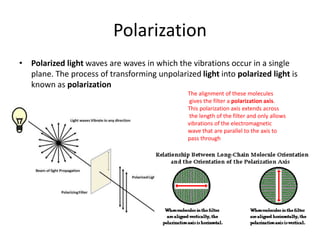
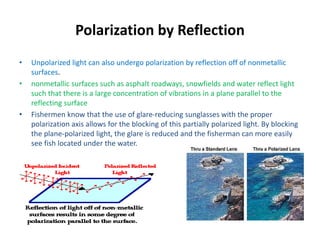
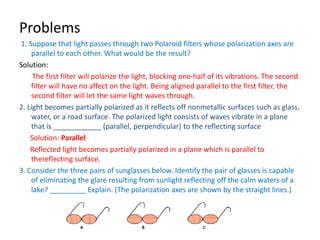
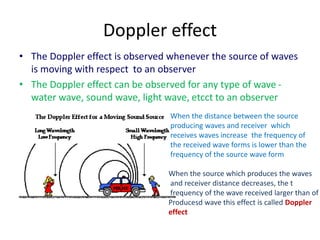
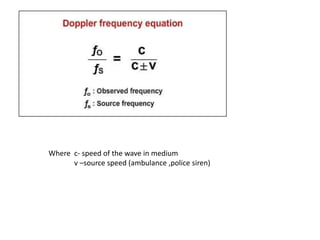
Waves can be categorized as mechanical or electromagnetic. Mechanical waves require a medium to travel through, while electromagnetic waves do not. Waves can also be transverse or longitudinal depending on the direction of particle oscillation relative to wave propagation. Important wave properties include amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. Reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, and polarization are key wave phenomena. Reflection follows the laws of reflection, while refraction follows Snell's law. Diffraction and interference result in constructive and destructive patterns. Polarization occurs when waves vibrate in a single plane. Waves have many applications including ultrasound imaging, fiber optics, and 3D displays.