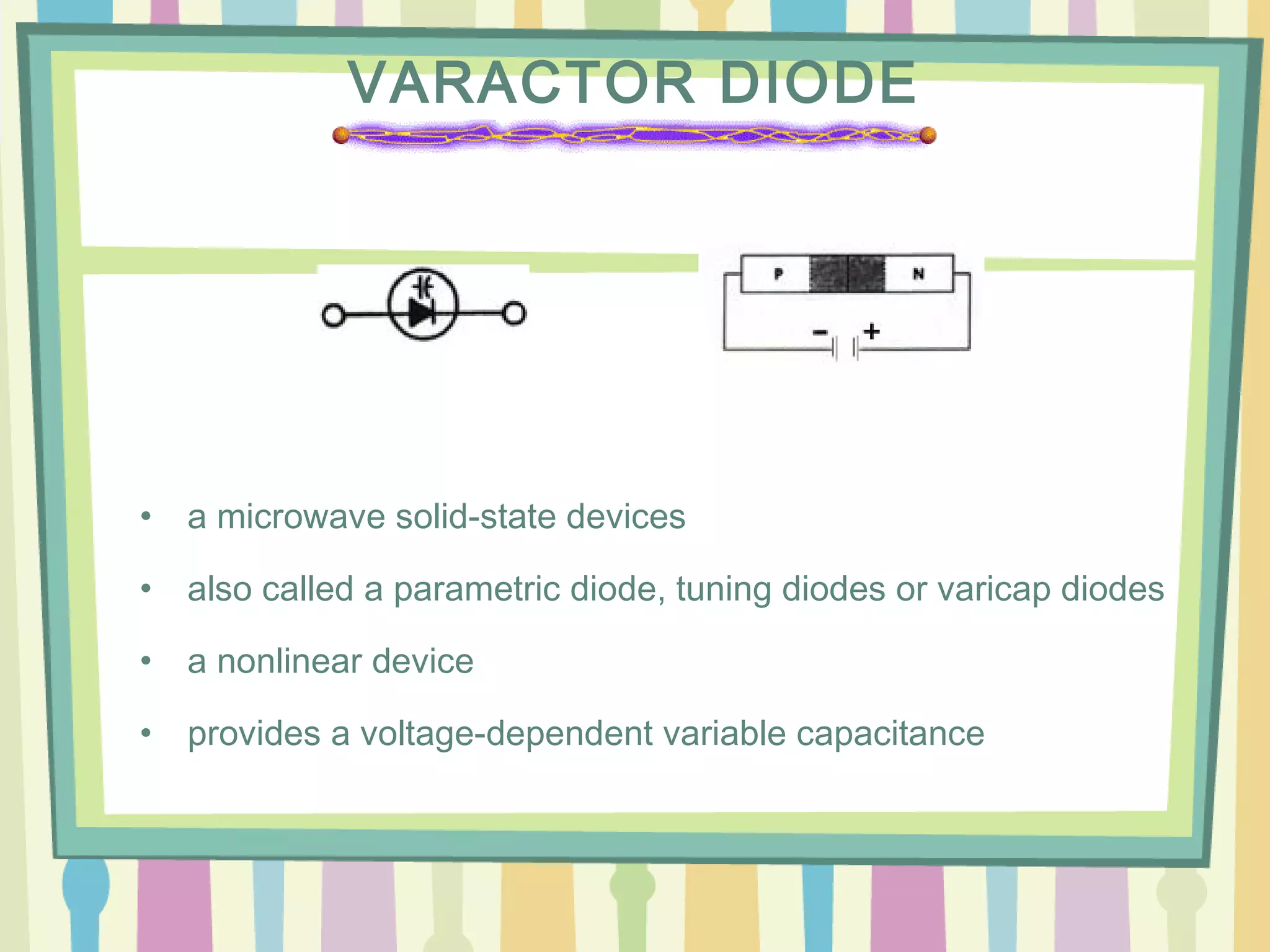
Varactor diodes are nonlinear semiconductor devices with a voltage-dependent variable capacitance. They come in abrupt and hyper abrupt types, and gallium arsenide varieties. Important criteria include capacitance, capacitance range, voltage range, and bias current. Varactor diodes have applications in frequency multipliers, parametric amplifiers, and electronic tuning due to their ability to vary capacitance based on reverse bias voltage. This affects the depletion width and allows the diode to be used for functions like signal multiplication and amplification.