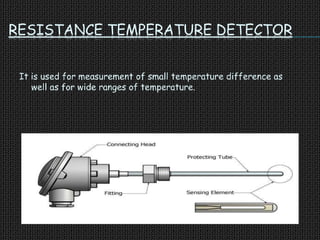
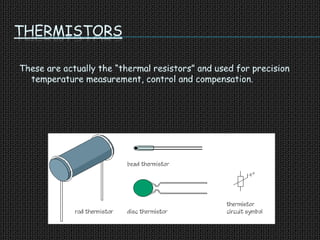
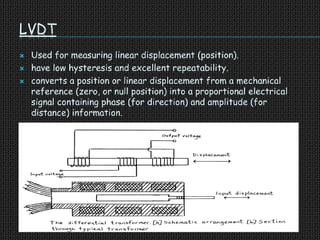
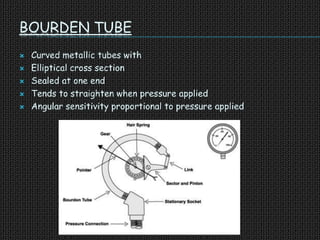
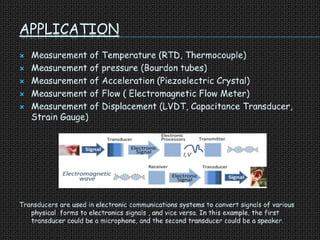
The document is a seminar presentation on transducers, defining them as devices that convert one form of energy into another, with subsections detailing types, classifications, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. Key examples discussed include resistance temperature detectors, thermistors, and strain gauges, each having distinct applications in measurement and control. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of transducers in various applications, including electronics and communications.