This document discusses various techniques for measuring blood flow, including electromagnetic methods, thermal methods using thermistors or hot wires, ultrasound using implantable CMUT arrays, and tracer dyes. It also describes designs for photoplethysmograph probes and analyzing blood flow using thermal modeling and heat transfer analysis. Finally, it mentions a biotelemetry system that was implanted in sturgeon to measure blood flow and temperature using an implantable Doppler flow meter and wireless data transmission to an external base station.

![Electromagnetic methodsBlood being a conductive fluid adheres to the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic inductionFlow in a magnetic field results in a generation of electromagnetic force perpendicular to the magnetic field and flowAnother technique used is that of Nuclear magnetic resonance[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-5-320.jpg)
![Thermal methodsA thermistor or a hot wire anemometer can be implanted inside the body.Blood acts as a coolant for a thermistor .By different designs and calculations based on fluid mechanics and heat transfer flow of blood can be estimated[5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-6-320.jpg)
![Tracer dyes for measurementThe injection of some tracers helps in imaging and analyzing the blood flowIndocyanine Green is a dye which causes fluorescence and images the blood flow [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-7-320.jpg)
![Ultrasound measurementBlood flow measurement using implantable CMUT Array (Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer)CMUT consists of a SOC cmos electronics and transducer with cross section 40µm and shaft length 4-10mm[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-8-320.jpg)
![Experimental operationUltrasonic pulse transmitted at frequency 1/T Echo is received at time t1 from position 1, t2 from positions 2The velocity is calculated as c(t2-t1)/2T cosѳ[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-9-320.jpg)
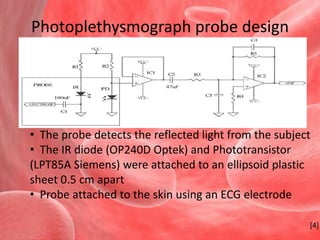

![Probe attached to the skin using an ECG electrode[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-12-320.jpg)
![Blood flow using thermal analysisArteriola and Venula connected by blood capillaries and AVABlood flow to capillaries controlled by AVATemperature regulation is based on blood flow in capillariesHeat transfer model analysis [7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-13-320.jpg)
![Blood flow in fingertip using heat transfer analysisNon Contact sensor placed below consists of an IR detector (Thermopile and resistance temperature sensor)Sensitivity enhanced by a Ge lensContact sensor consists of thermistor (0.25mm) to transmit the heat [7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-14-320.jpg)
![Blood flow in fingertip using heat transfer analysisFirst step ambient temperature measured (25s)Second step finger placed on the sensor initial temperature of skin surface measured (35s)Third step measure the thermal release characteristics for correction in second step (15s)Blood flow coefficient is calculated by using the temperature gradient in step 2[7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-15-320.jpg)
![Biotelemetry systemThe implant module (B) consists of a doppler flow meter µcontroller and a RF link communicatorThe base station (A) consists of RF link µcontroller and D-A Converter[8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perspectivesinbloodflowmeasurement-100514163614-phpapp02/85/Perspectives-in-blood-flow-measurement-16-320.jpg)