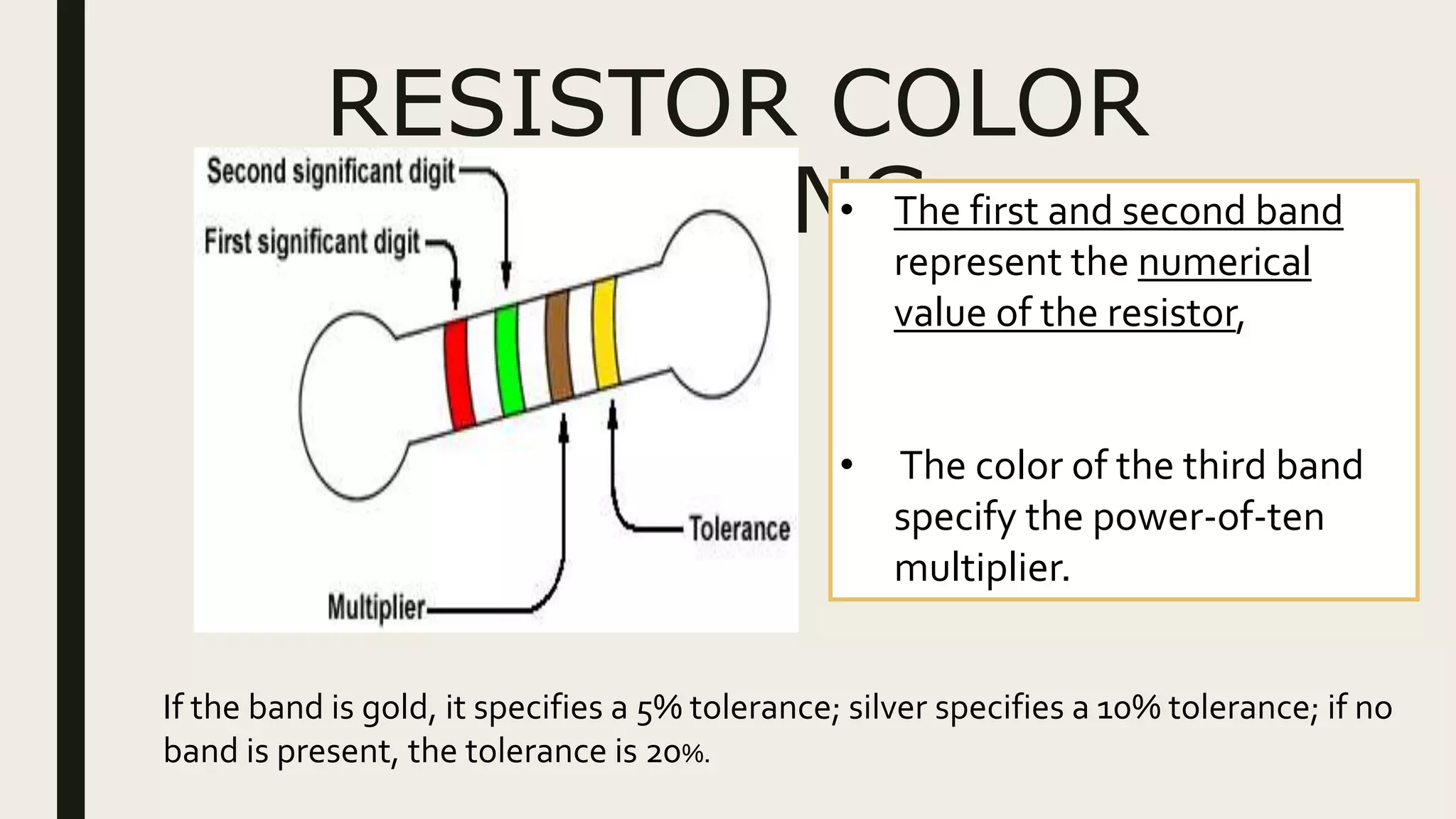
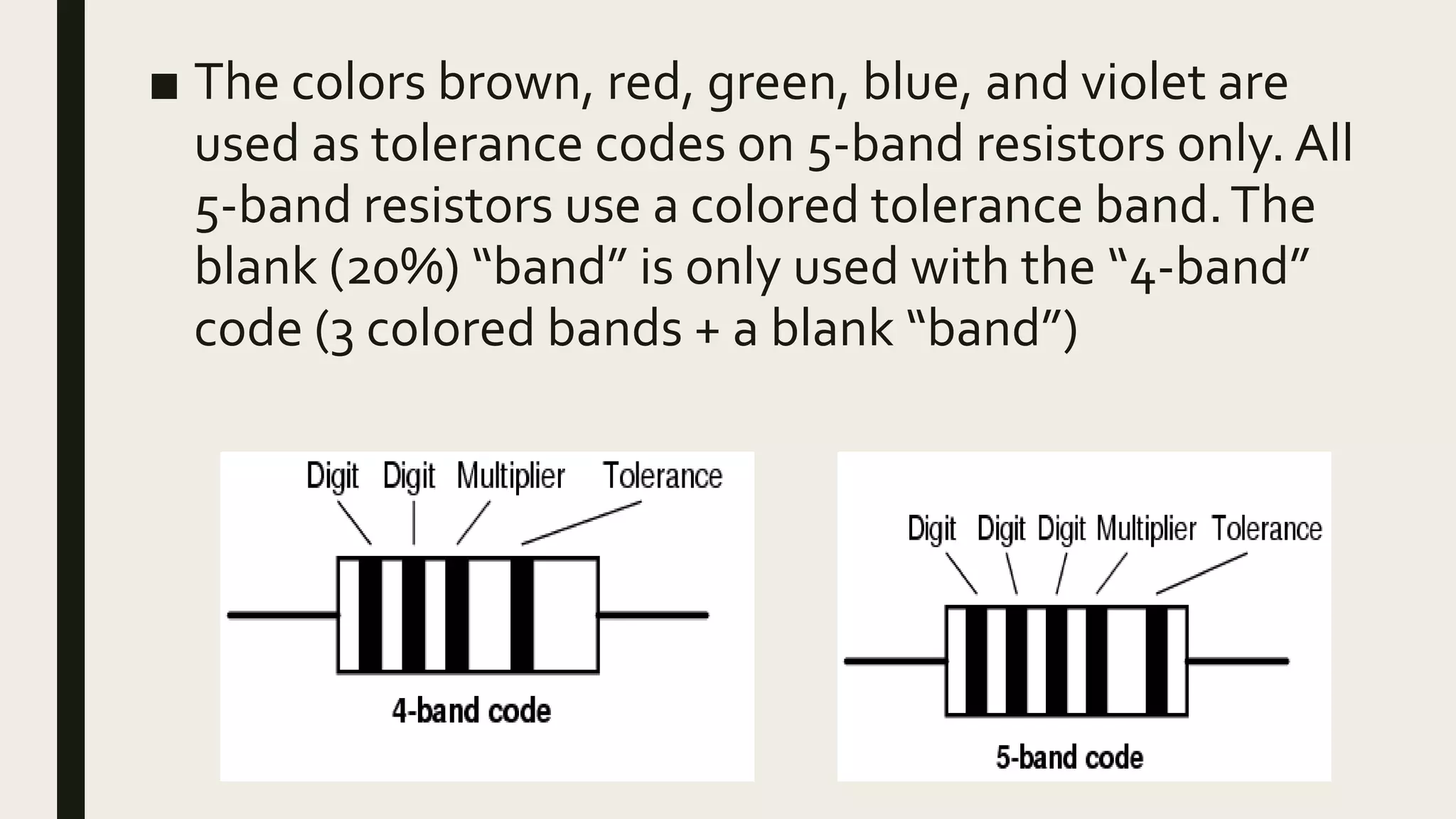
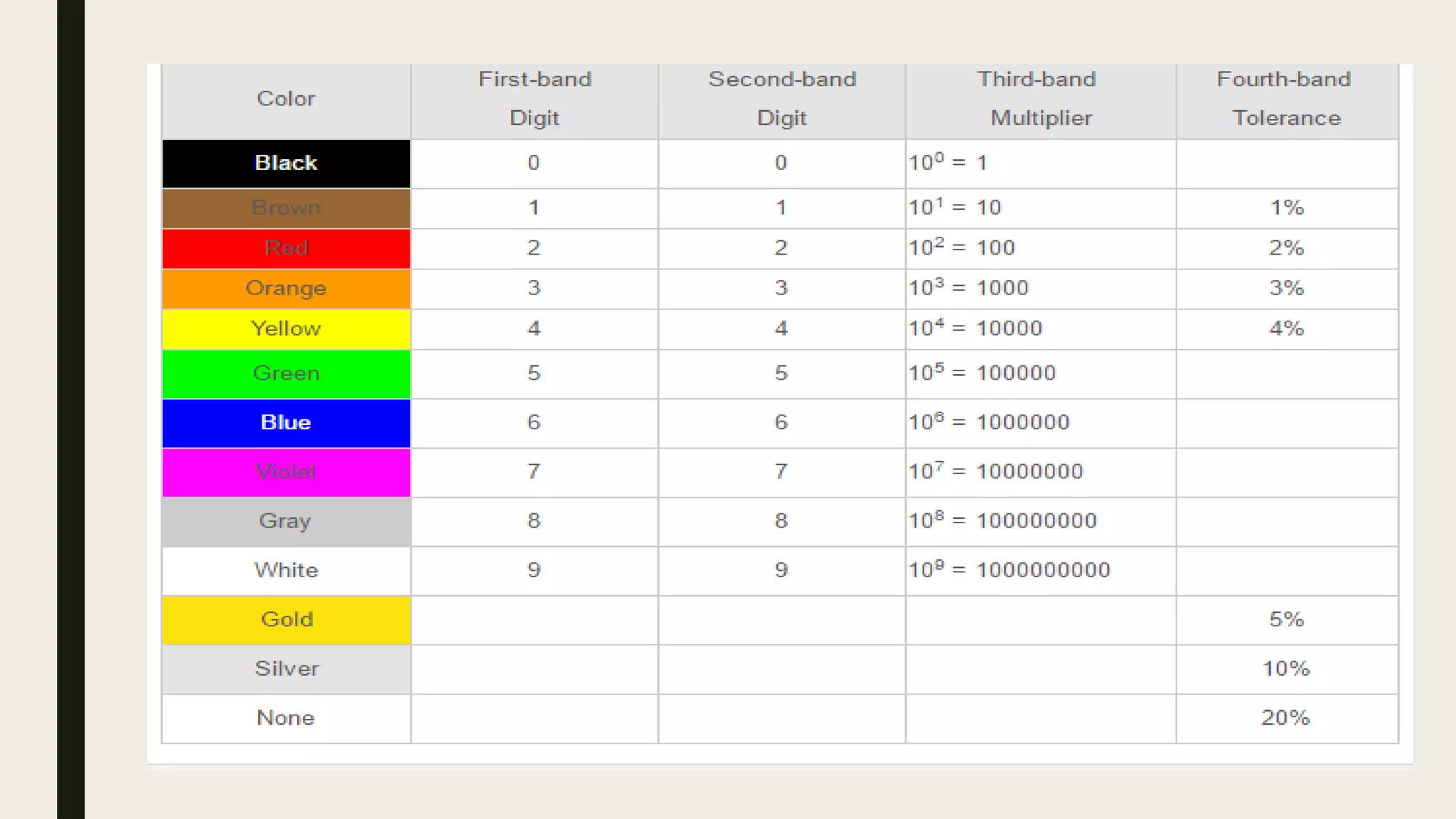
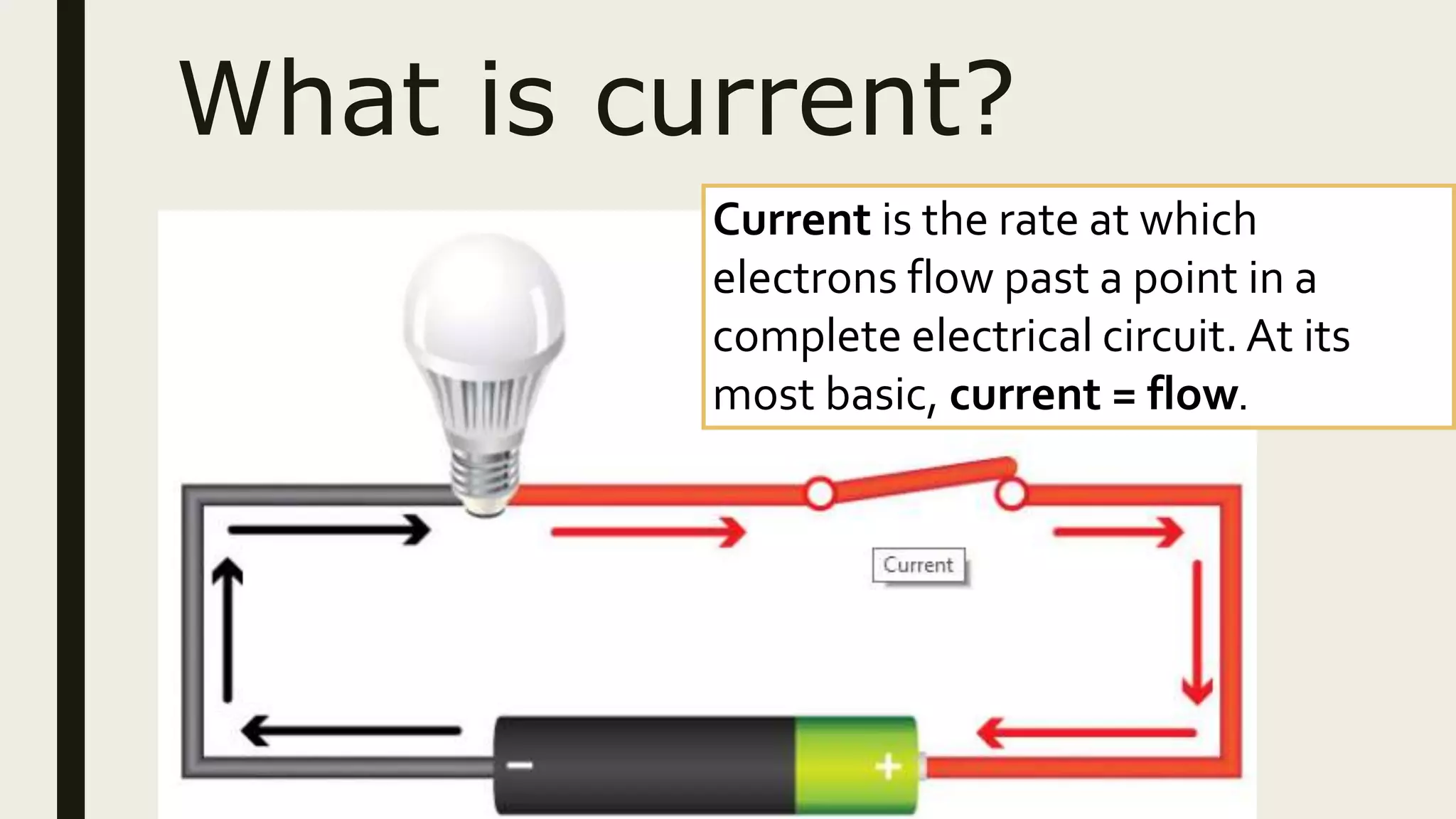
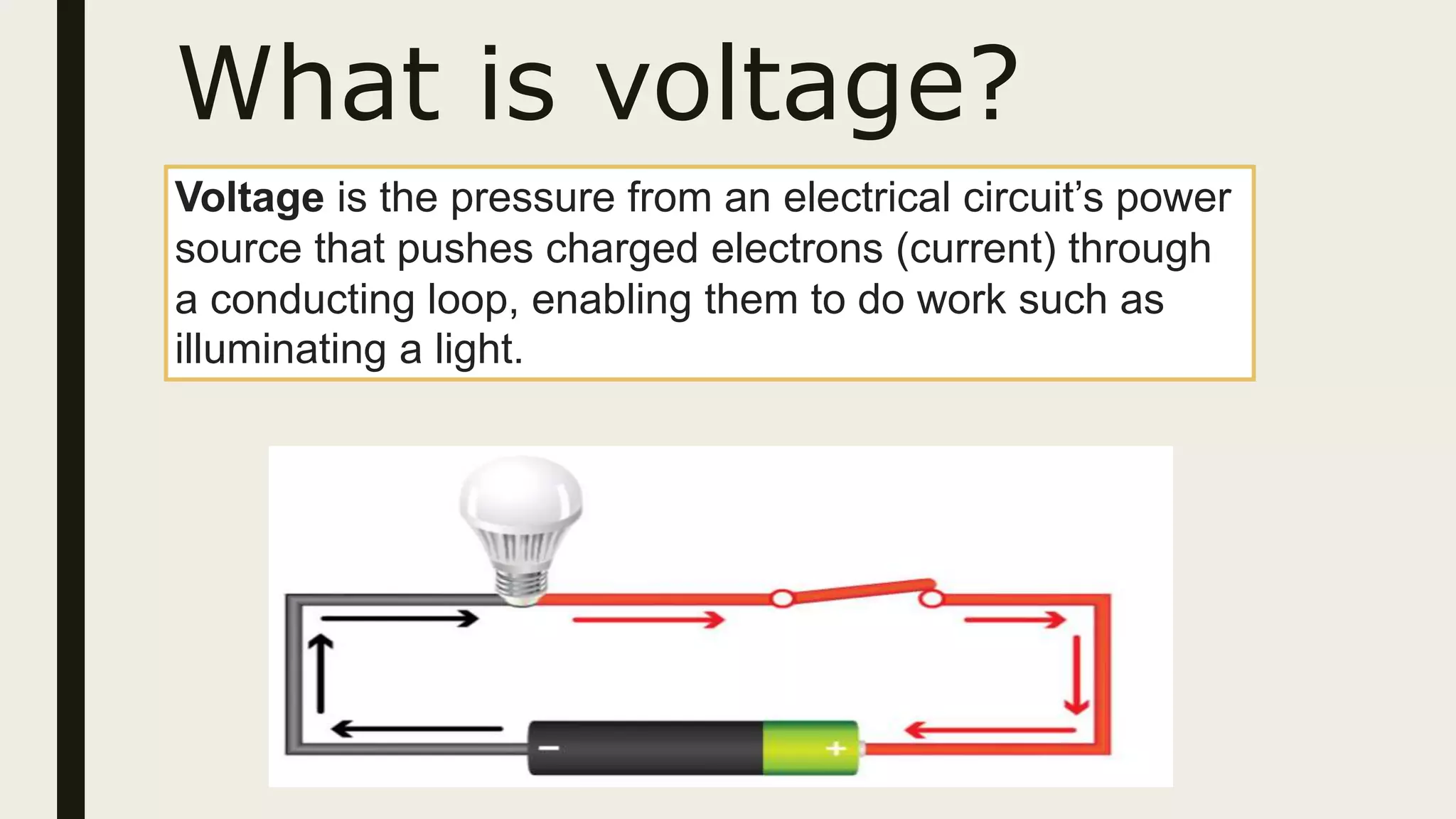
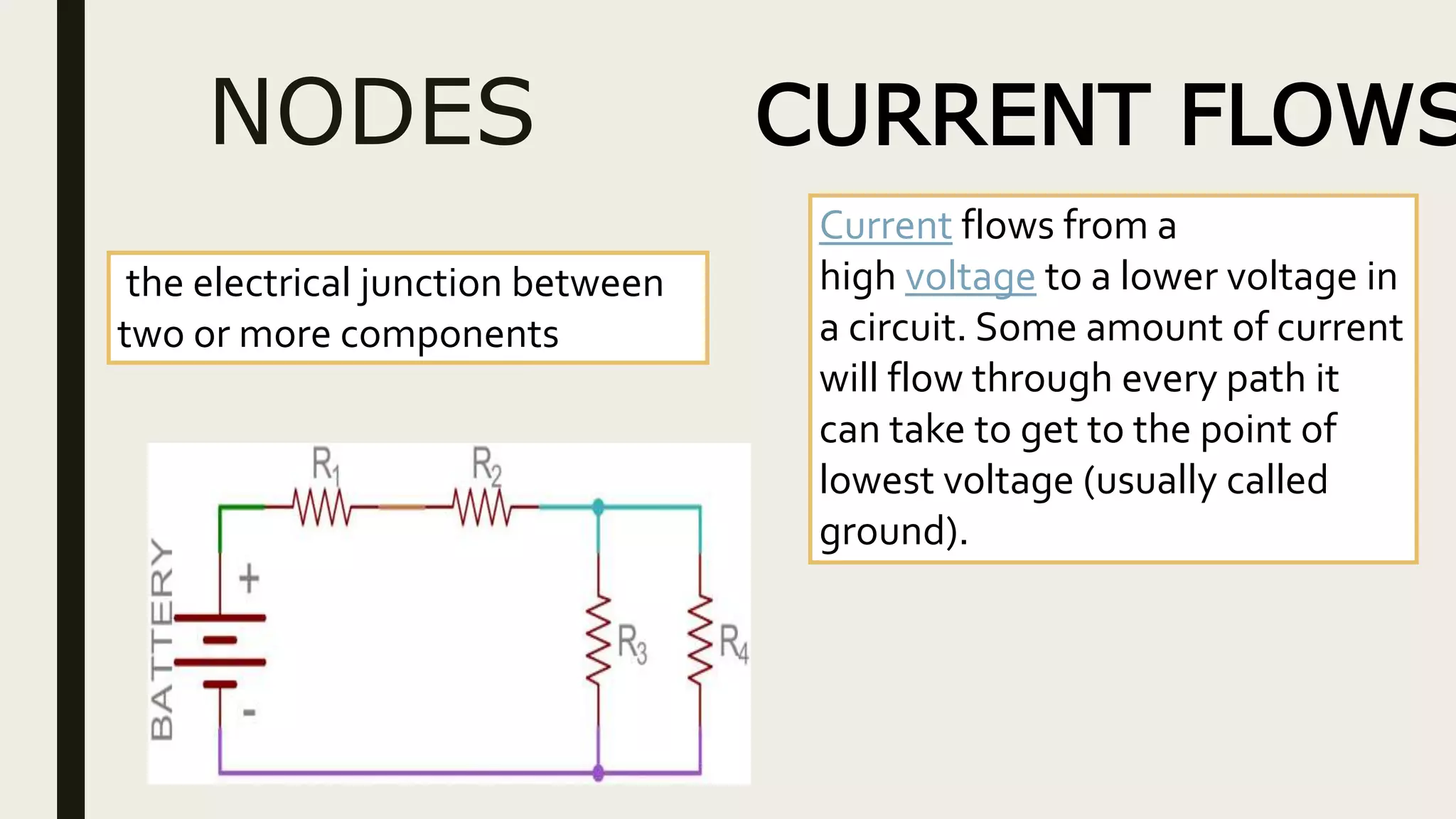
1. Current is the flow of electrons through a circuit, measured in amps. Voltage is the electrical pressure that pushes electrons through a circuit, measured in volts. Resistance opposes the flow of electrons and is measured in ohms.
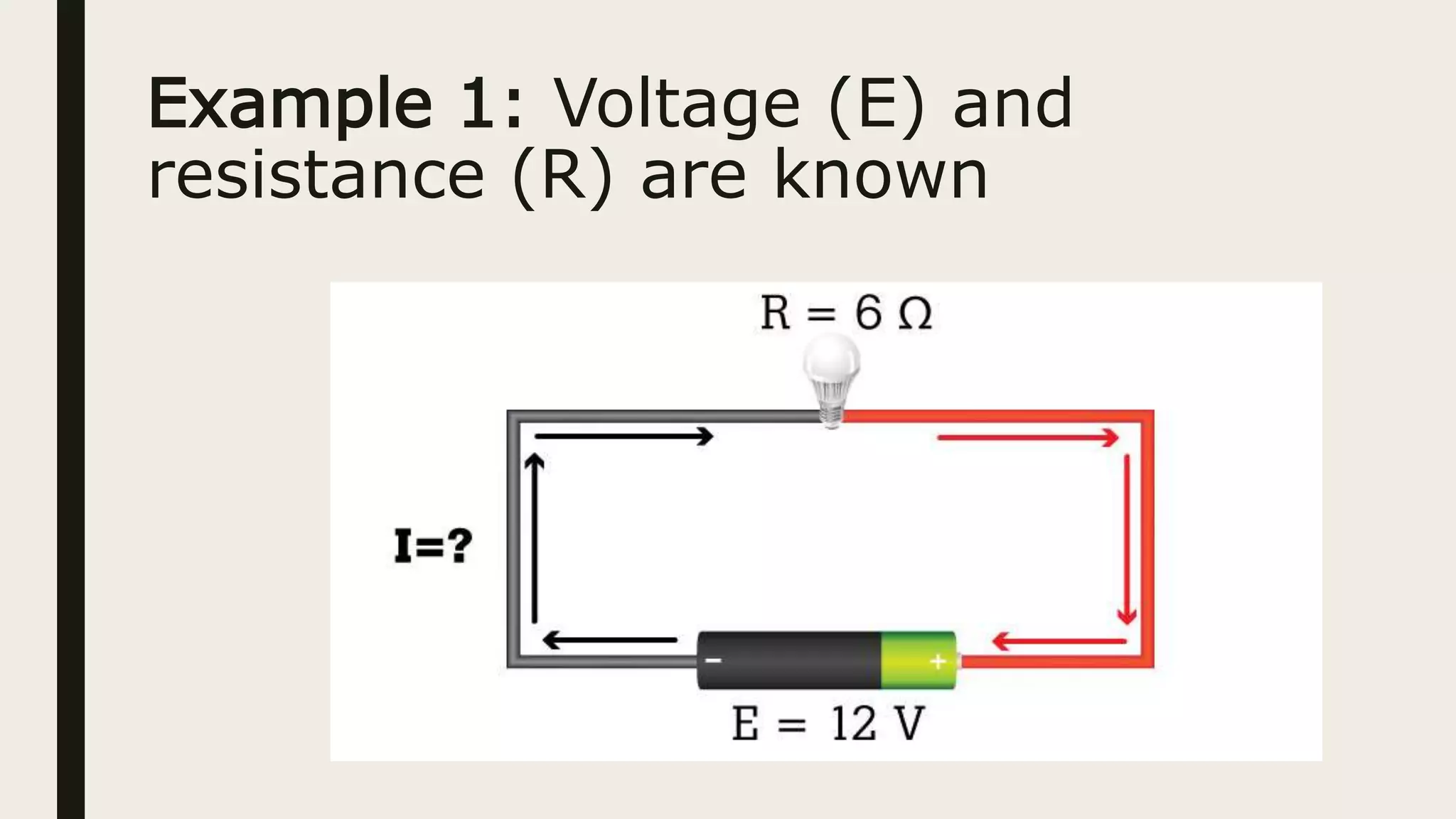
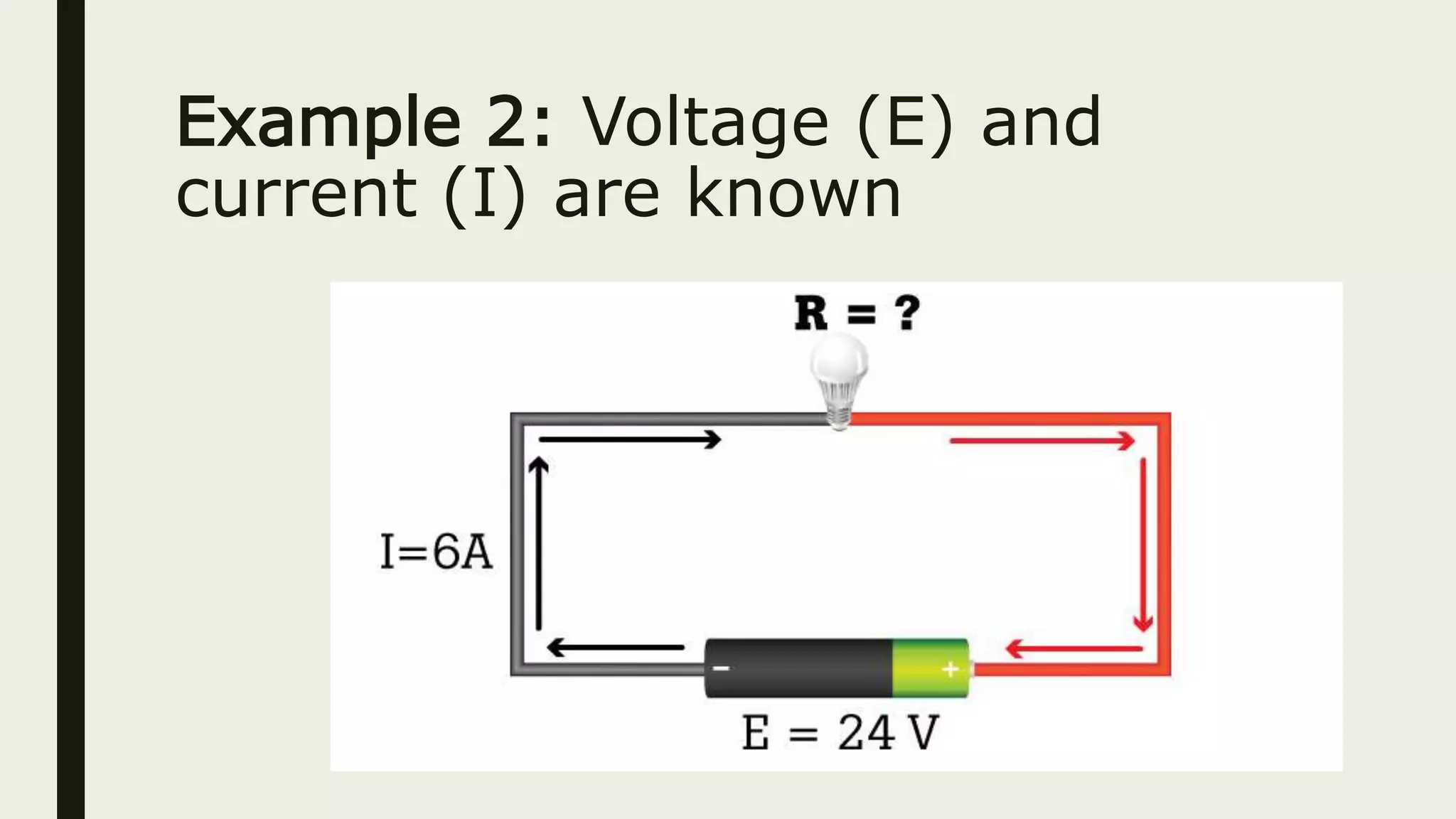
2. Ohm's Law describes the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in a circuit using the formula E=IR. It can be used to calculate any one variable if the other two are known.
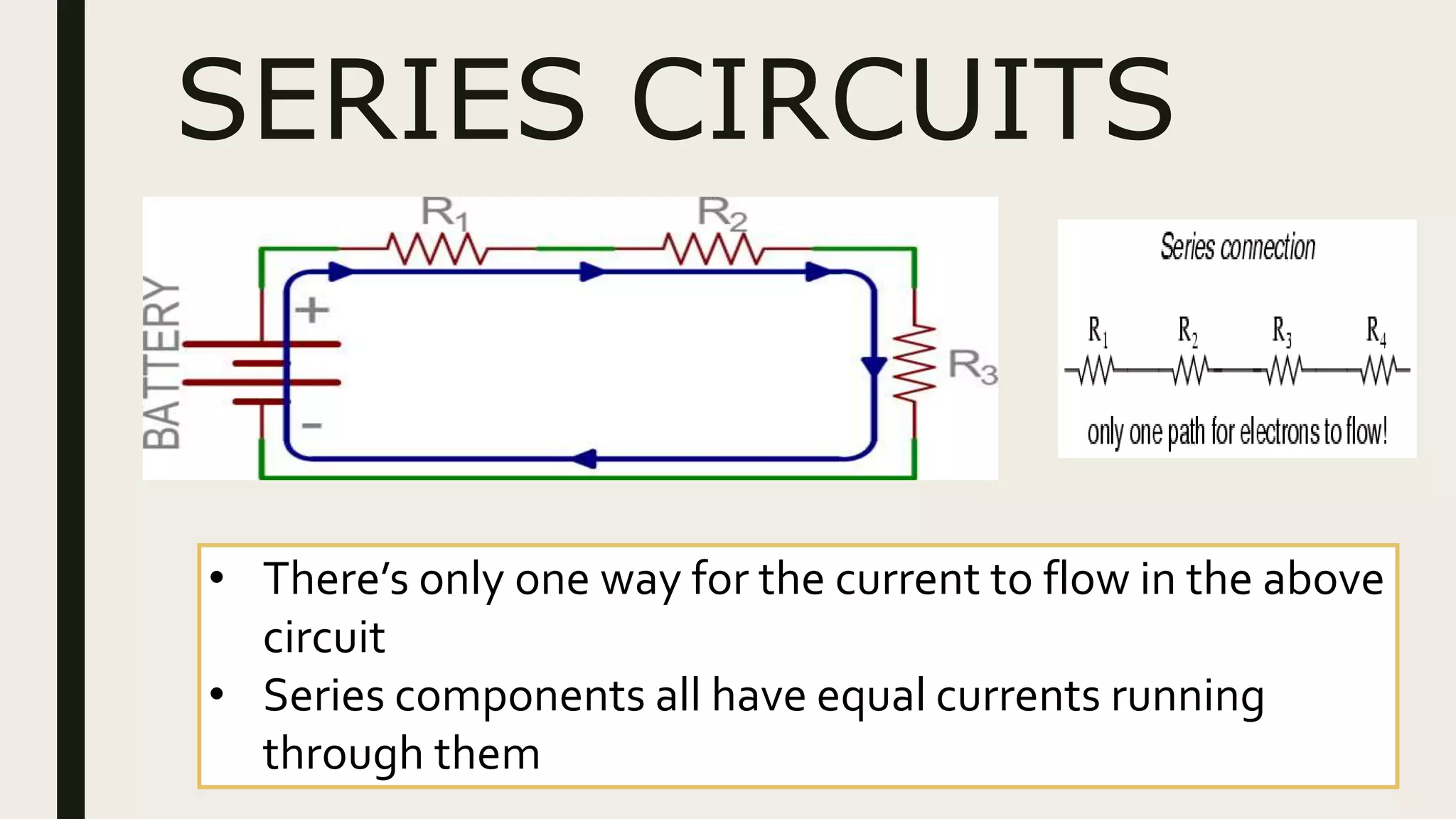
3. Circuits can be connected in series, parallel, or series-parallel configurations which determine how current and voltage are distributed.










![To find theVoltage, (V )
[V = I x R ]
V (volts) = I (amps) x R (Ω)
To find the Current, ( I )
[ I =V ÷ R ] I (amps) =V (volts) ÷ R (Ω)
To find the Resistance, ( R )
[ R =V ÷ I ] R (Ω) =V (volts) ÷ I (amps)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electricalcircuit-161011011659/75/Electrical-circuit-16-2048.jpg)