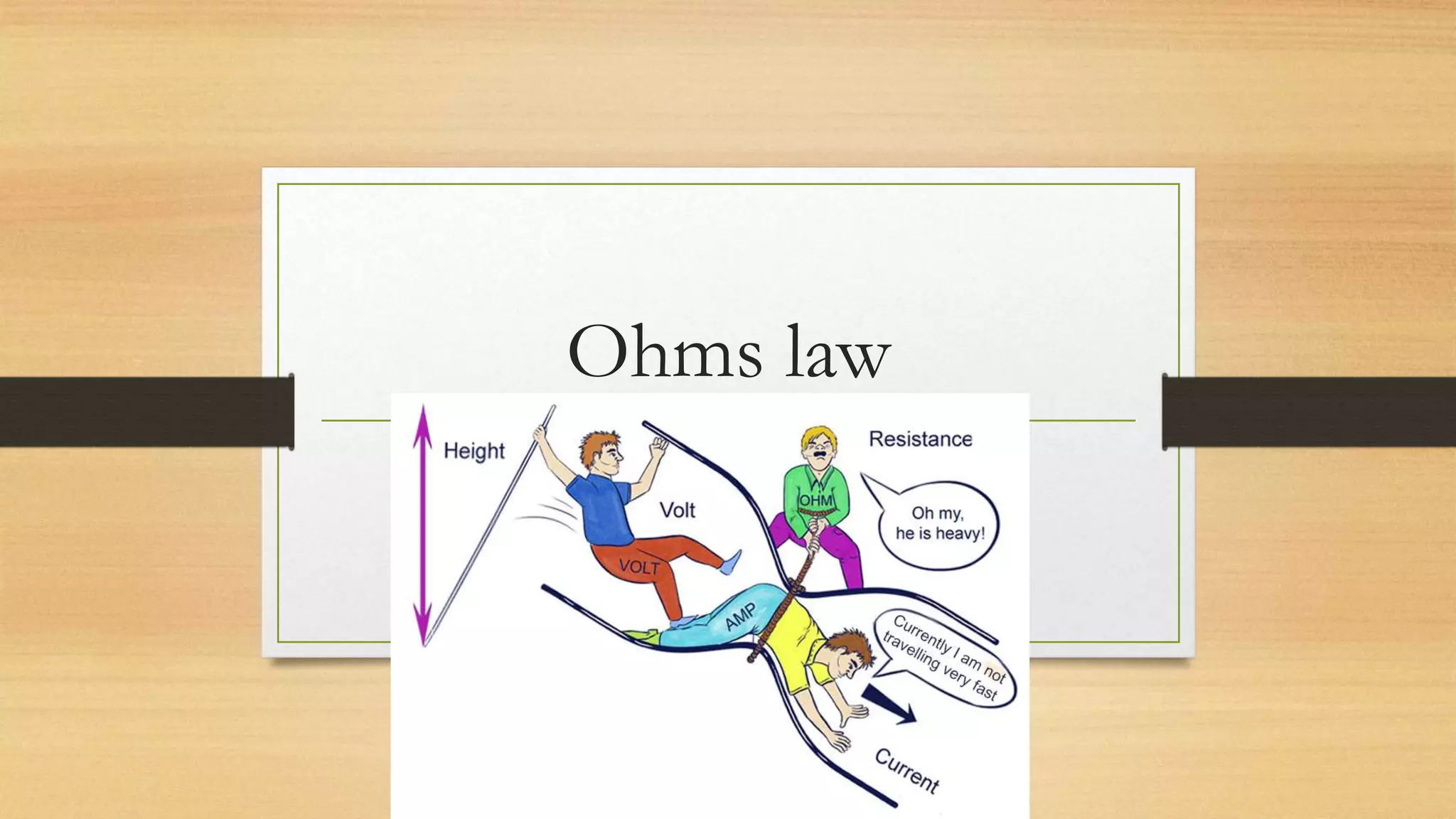
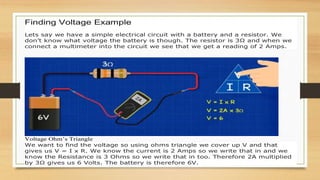
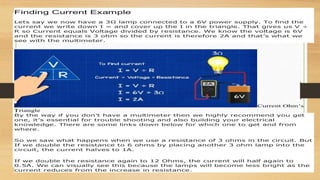
Ohm's law states that voltage equals current multiplied by resistance (V=IR), and it can be used to calculate any two of the three variables if the third is known. The letter I represents current because it is named after André-Marie Ampère, who undertook experiments on current. V typically represents voltage but may also be represented by E, which stands for electromotive force. Examples are provided for using Ohm's law to calculate voltage, current, and resistance.