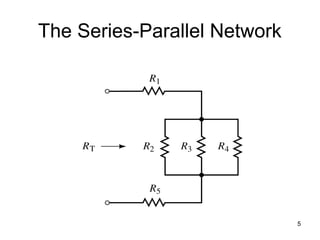
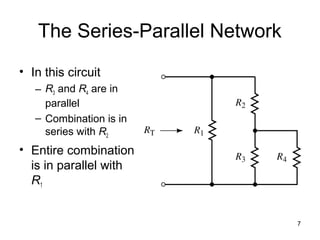
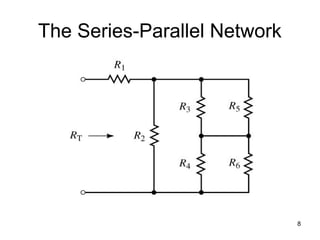
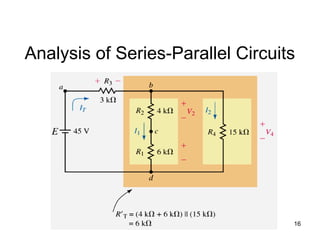
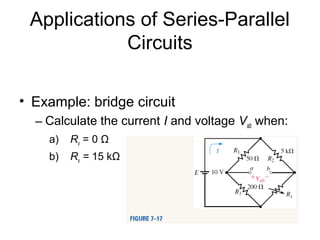
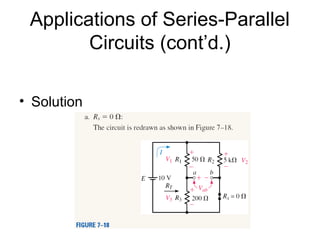
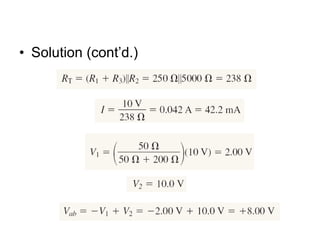
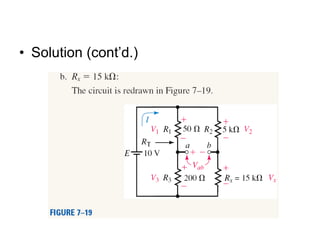
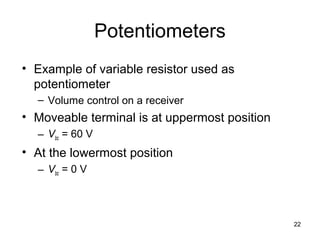
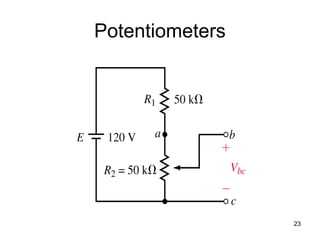
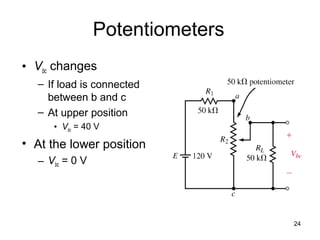
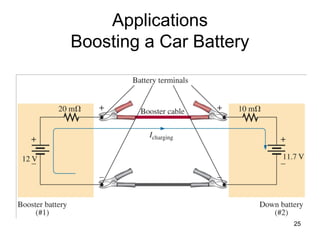
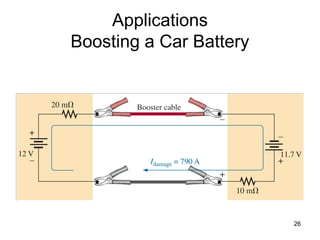
This document discusses series-parallel circuits and their analysis. It covers identifying components that are in series and parallel, and how to simplify circuits by recognizing series and parallel combinations. The key steps for analyzing series-parallel circuits are outlined, including redrawing the circuit, labeling nodes, determining the equivalent resistance, calculating currents and voltages. Examples are provided for calculating currents and voltages in a bridge circuit with different resistances, as well as the voltage produced by a potentiometer at different positions. Applications discussed include boosting a car battery.