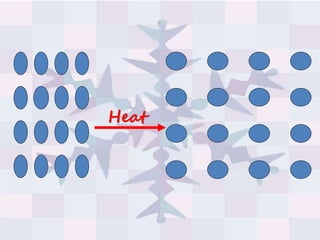
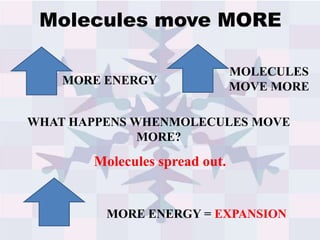
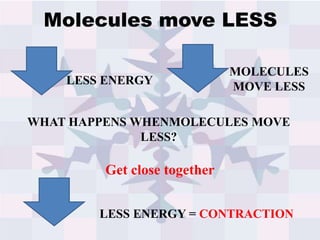
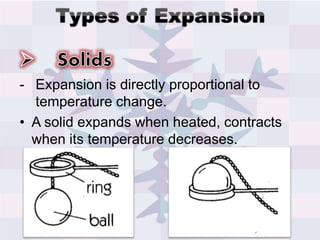
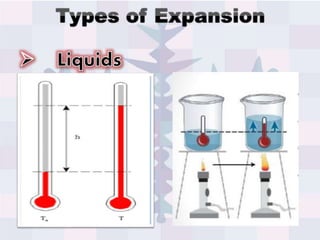
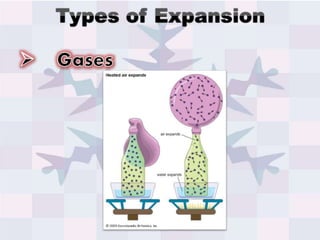
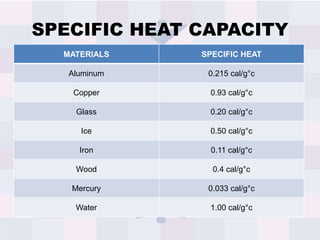
The document explains concepts related to heat and temperature, including the transfer of thermal energy and the relationship between temperature and particle motion. It discusses thermal expansion, phase changes, and specific heat capacity, emphasizing how different materials absorb heat at varying rates. Additionally, it provides a formula for calculating heat absorbed by materials based on mass, specific heat, and temperature change.