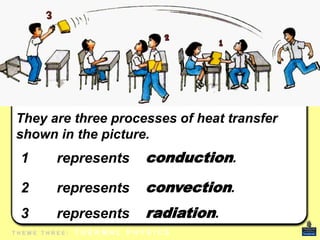
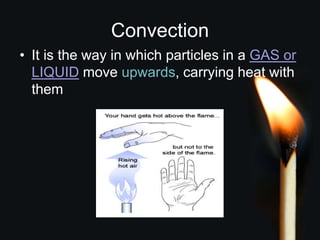
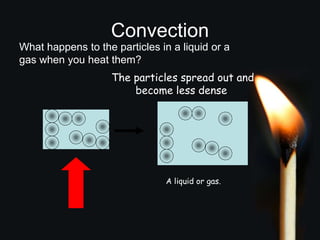
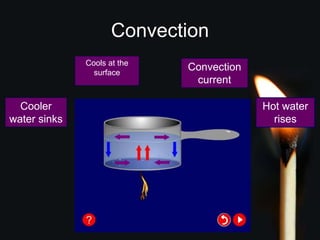
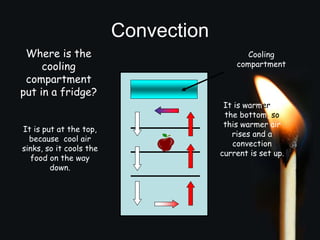
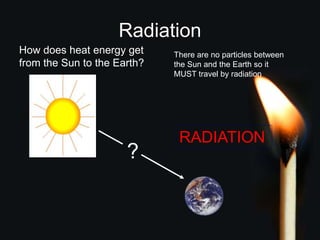
This document discusses heat transfer and thermal energy. It defines heat as a form of energy that causes particles to move and take up more space. Heat is transferred between objects by conduction, convection, or radiation. Conduction involves direct contact between particles, convection involves the movement of fluids like gases and liquids, and radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves without a medium. The document differentiates between heat and temperature, explaining that temperature measures how hot an object is while heat refers to the total thermal energy. It also covers how heating and cooling affect the expansion and contraction of materials.