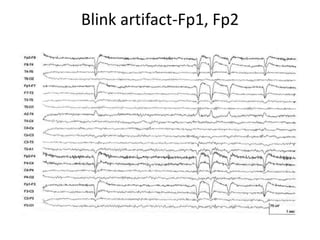
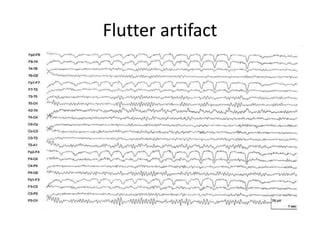
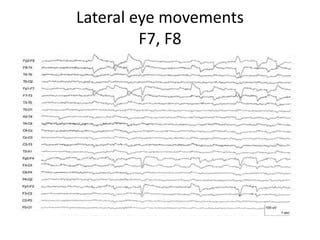
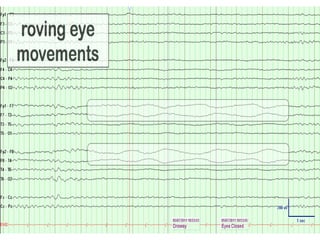
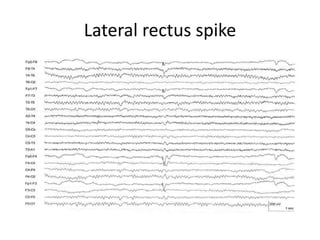
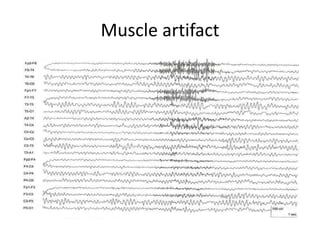
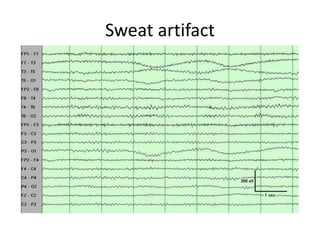
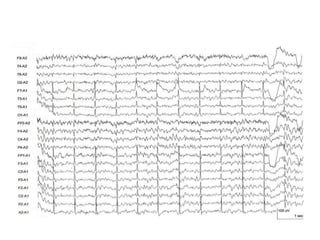
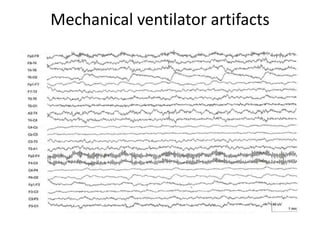
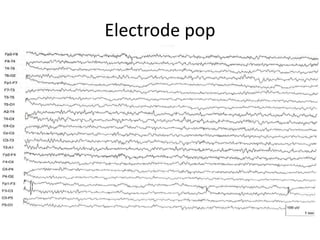
This document discusses different types of artifacts that can appear in EEG recordings. It divides artifacts into physiological artifacts, caused by body movements or electrical activity, and non-physiological artifacts, caused by external electrical interference or equipment issues. Specific artifacts covered include eye blinks and movements, muscle activity, sweat, ECG interference, ventilator and pulse artifacts, electrical interference, and electrode and lead movement issues. Proper identification of artifacts is important for interpreting EEG recordings.