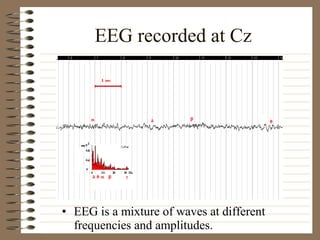
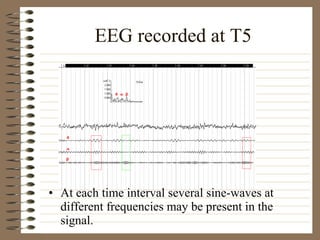
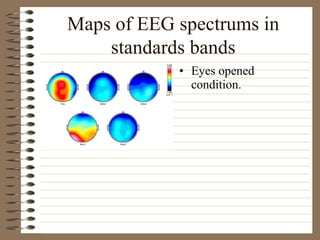
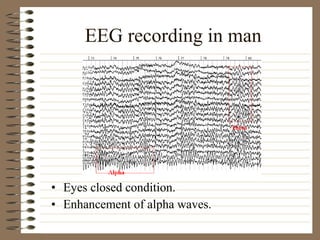
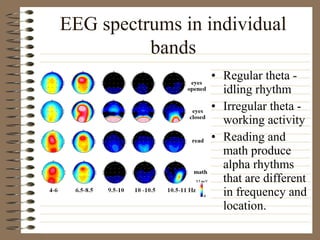
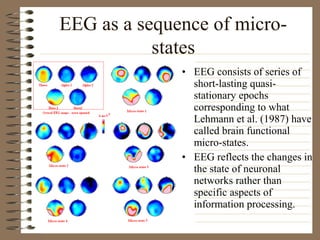
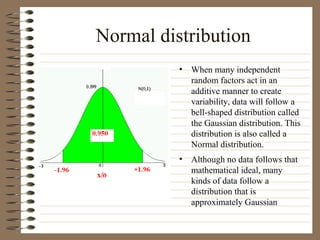
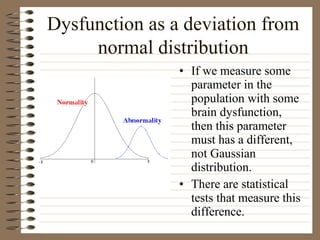
This document provides information about EEG recordings and analysis. It discusses topics like the Nyquist theorem, types of EEG recordings, artifacts in EEG like EMG and eye blinks, reviewing EEG characteristics, spectral maps of EEG under different conditions, microstates in EEG, normal and abnormal distributions in EEG data, and life span normative EEG databases.