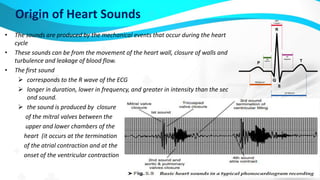
This document summarizes various medical instrumentation techniques including electromyography (EMG), electrooculography (EOG), electroretinography (ERG), and phonocardiography (PCG). It describes what each technique measures, how it is performed, and what the recorded signals can indicate about physiological function and abnormalities. EMG measures muscle electrical activity using needle electrodes, EOG records eye movement potentials, ERG captures the eye's response to light using corneal and skin electrodes, and PCG detects heart sounds through a microphone to analyze valves, rhythm, and blood flow. Modern machines provide full-color waveform displays and recording capabilities to aid clinical diagnosis and research.