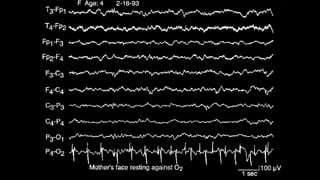
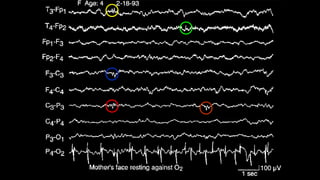
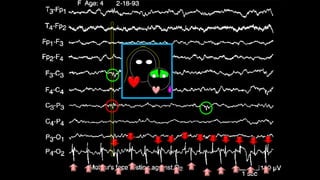
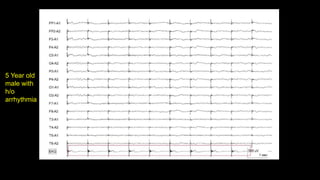
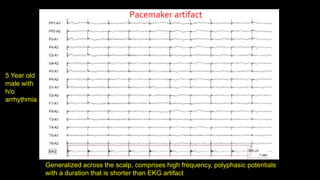
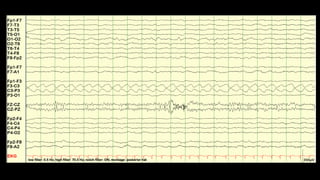
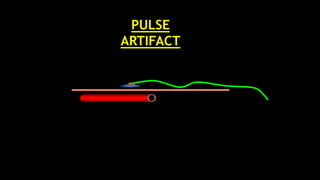
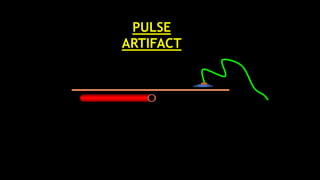
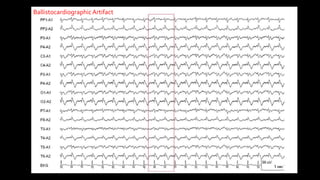
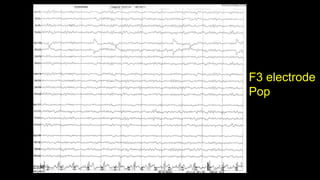
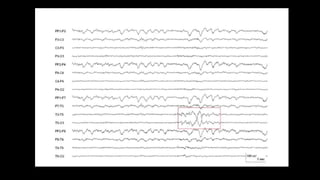
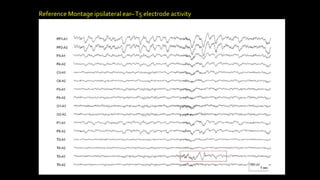
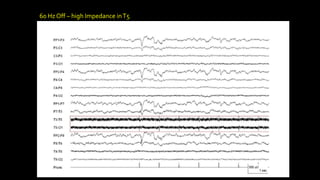
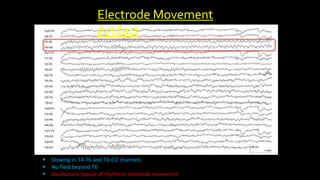
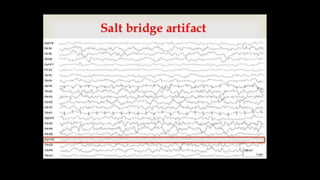
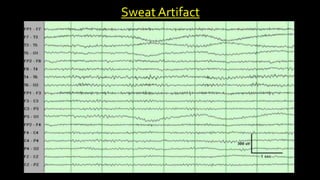
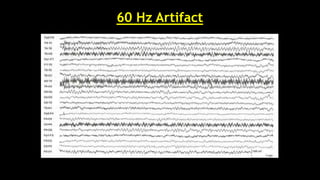
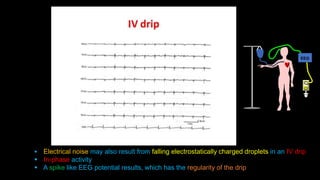
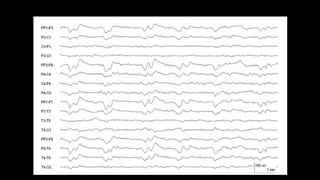
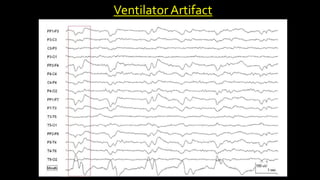
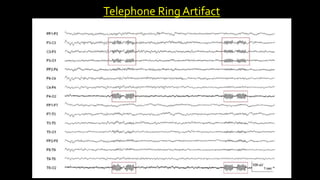
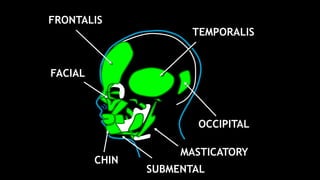
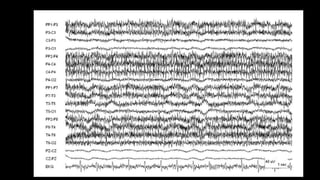
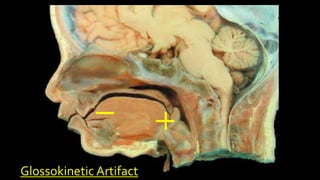
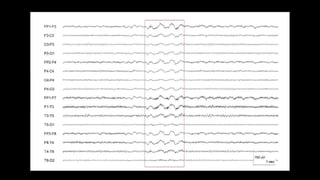
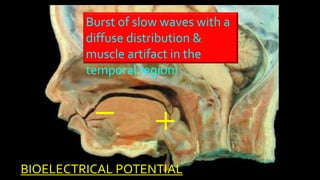
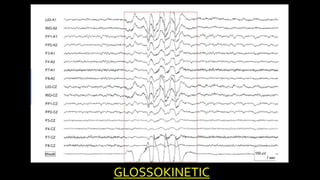
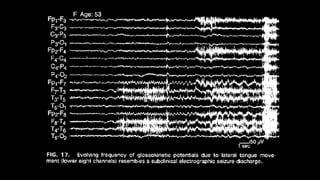
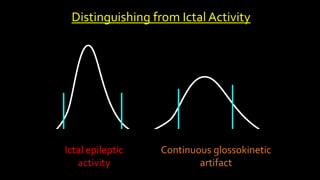
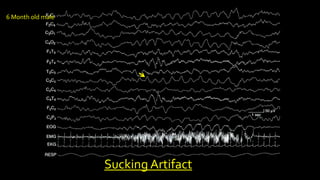
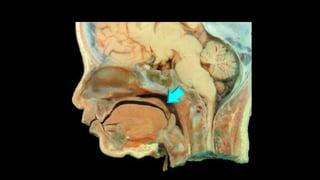
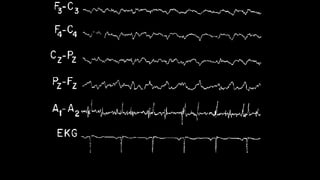
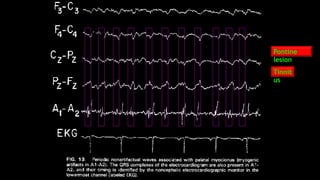
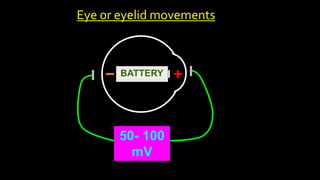
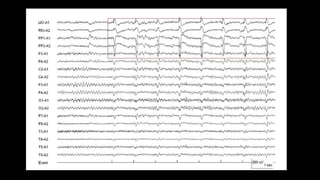
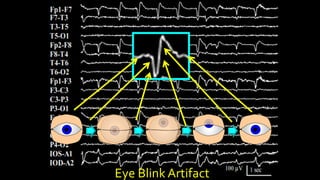
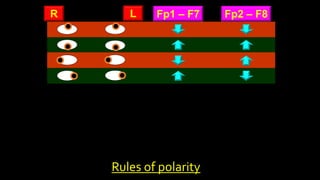
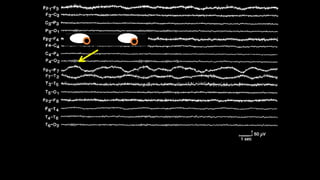
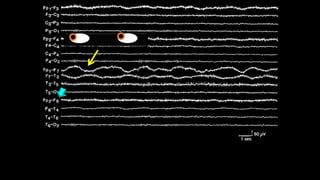
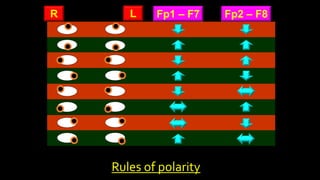
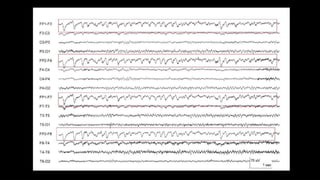
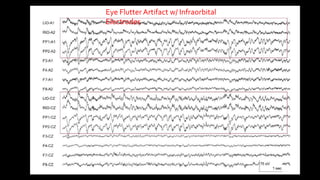
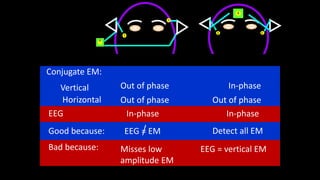
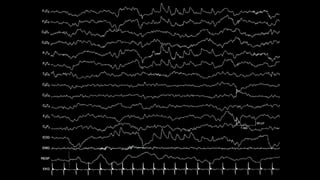
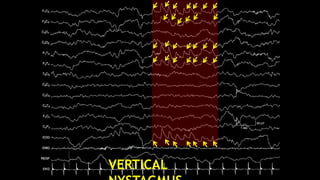
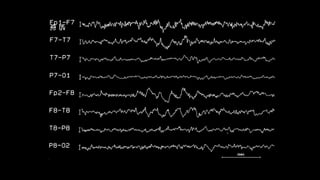
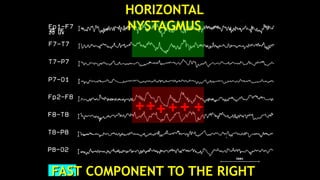
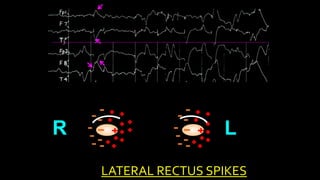
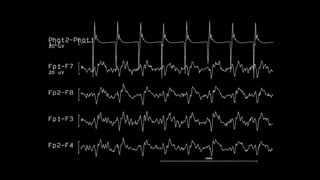
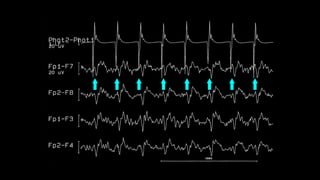
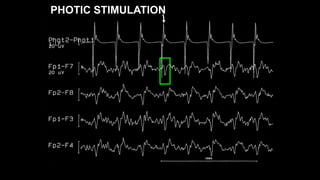
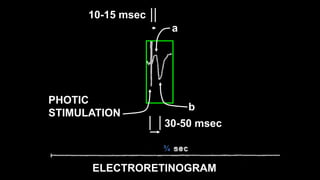
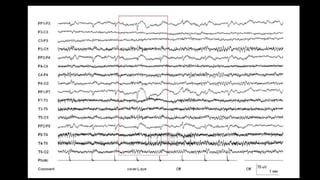
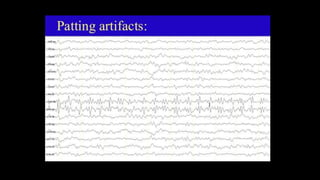
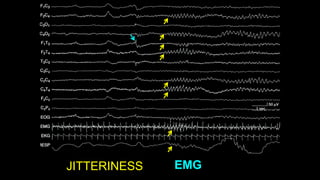
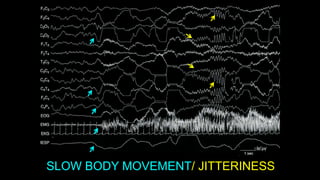
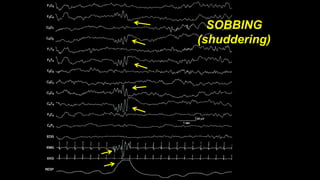
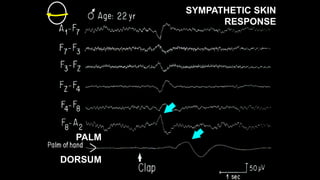
The document discusses various types of EEG artifacts and their origins, categorized as physiological and extraphysiological. It outlines key types of artifacts, such as cardiac, muscle, and ocular artifacts, including their identifying characteristics and potential resolutions for cleaner EEG recordings. The effects of external devices and bioelectrical potentials on EEG readings are also explored, emphasizing the importance of proper setup and monitoring during EEG procedures.