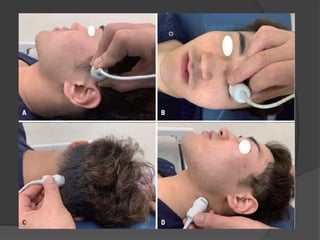
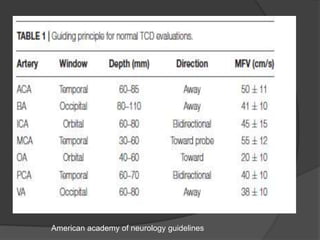
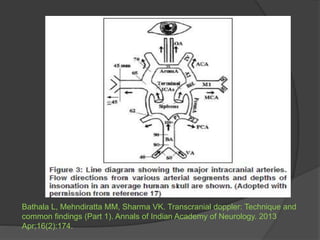
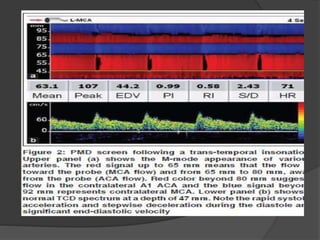
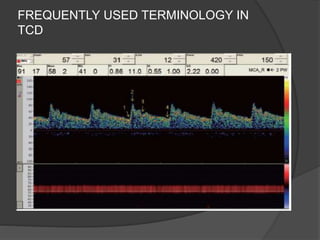
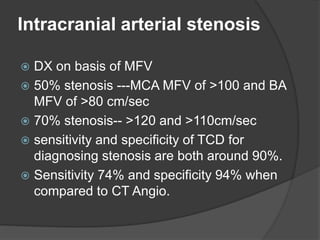
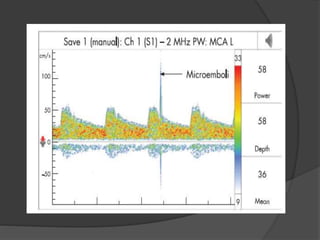
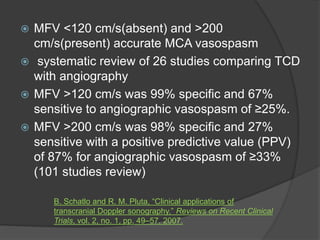
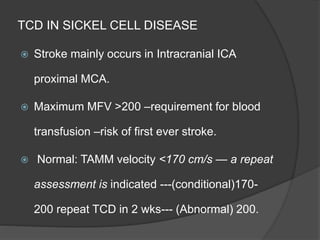
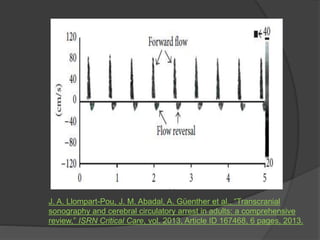
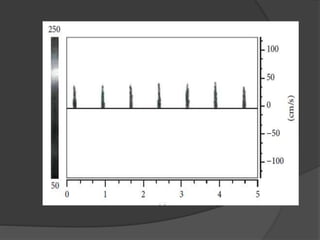
Transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasonography is a noninvasive technique used to evaluate cerebral blood flow velocities. It was originally introduced in 1982 to detect vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage. TCD is now used for a variety of purposes including detection of stenosis, occlusion, emboli, shunts, and vasospasm. It provides diagnostic information for conditions such as stroke, sickle cell disease, brain death, and arteriovenous malformations. TCD utilizes Doppler effect to measure blood flow velocities in basal cerebral arteries which provides data to assess hemodynamics and diagnose various cerebrovascular diseases.