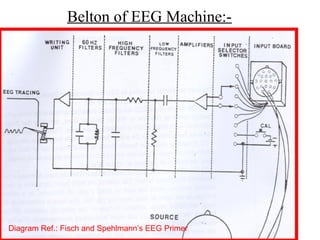
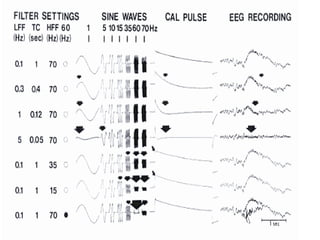
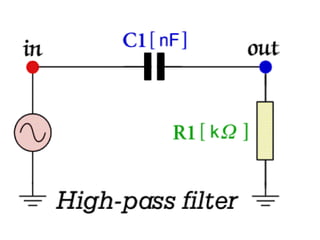
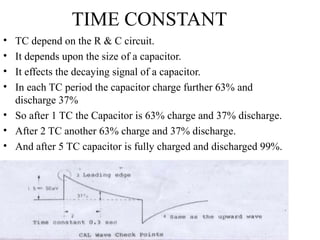
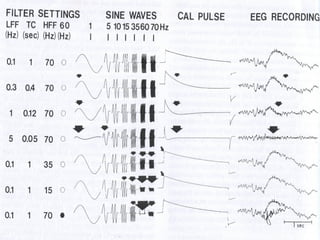
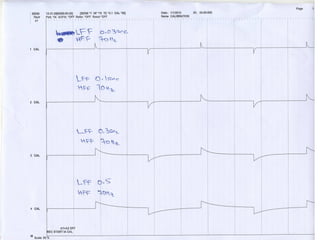
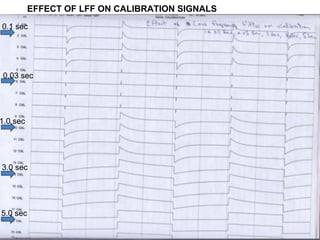
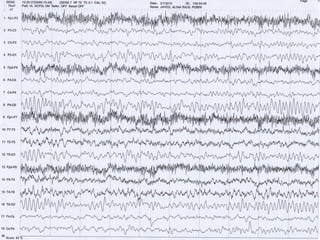
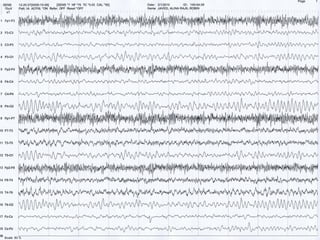
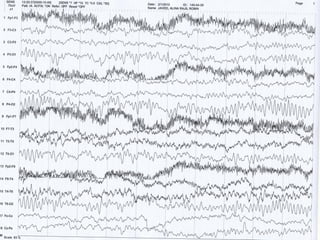
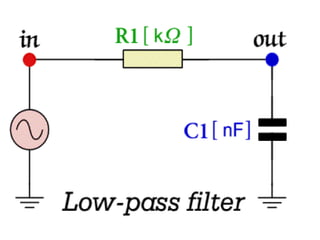
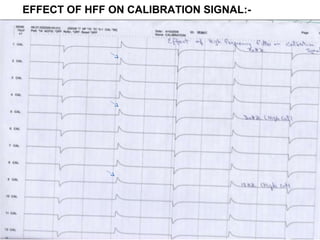
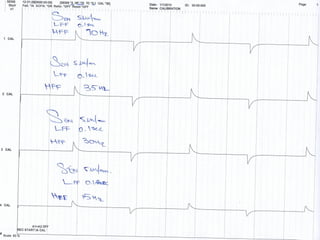
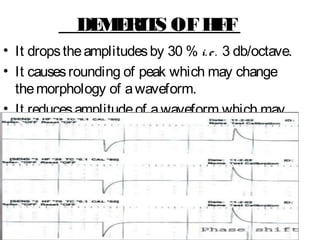
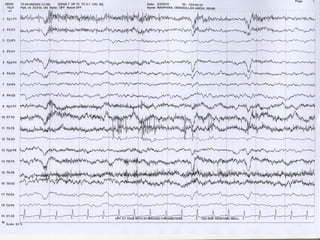
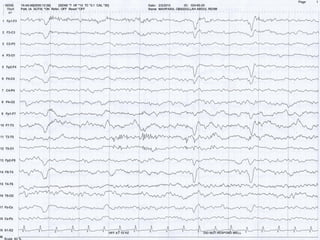
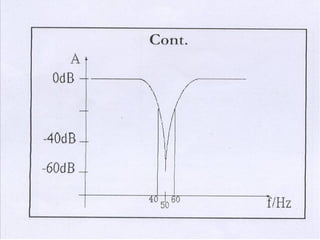
This document discusses electronic filters used in EEG machines, which perform signal processing to enhance desired frequency components while eliminating unwanted ones. It details the types of filters—low-frequency (high-pass), high-frequency (low-pass), and notch filters—along with their mechanisms, effects on EEG signals, and merits and demerits. Additionally, it highlights the significance of capacitance and resistance in filter design and their impact on signal quality in EEG recordings.